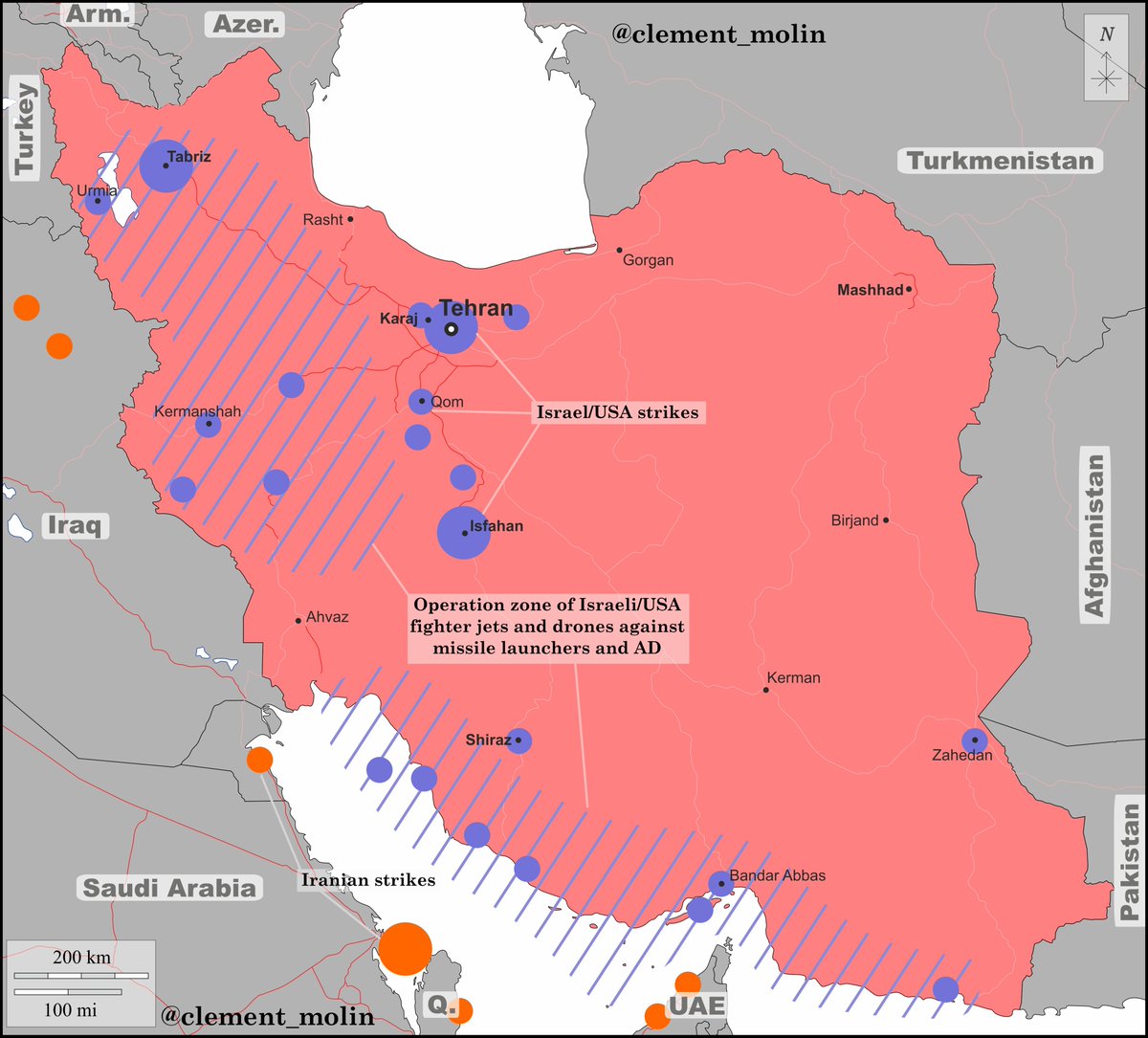
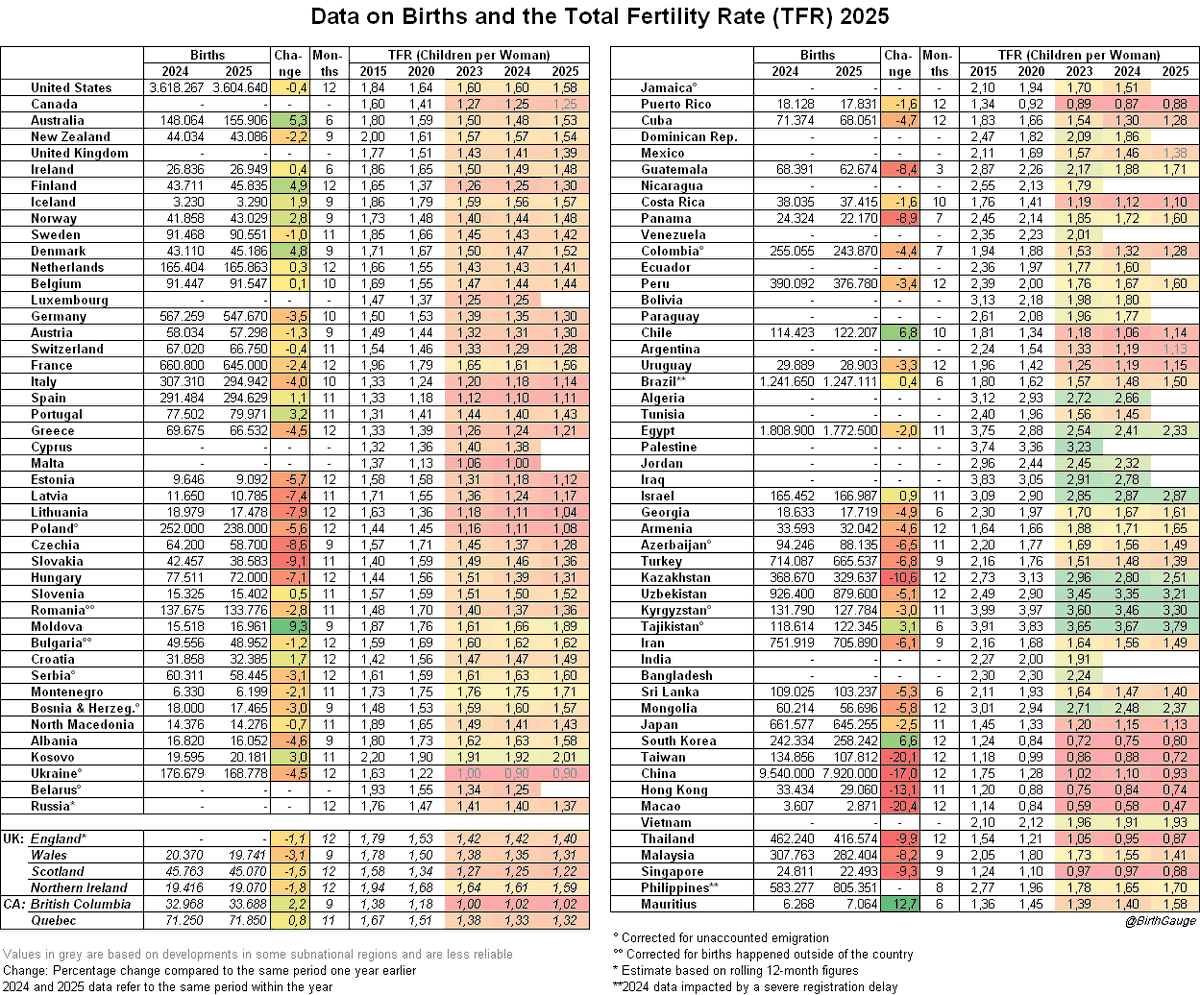
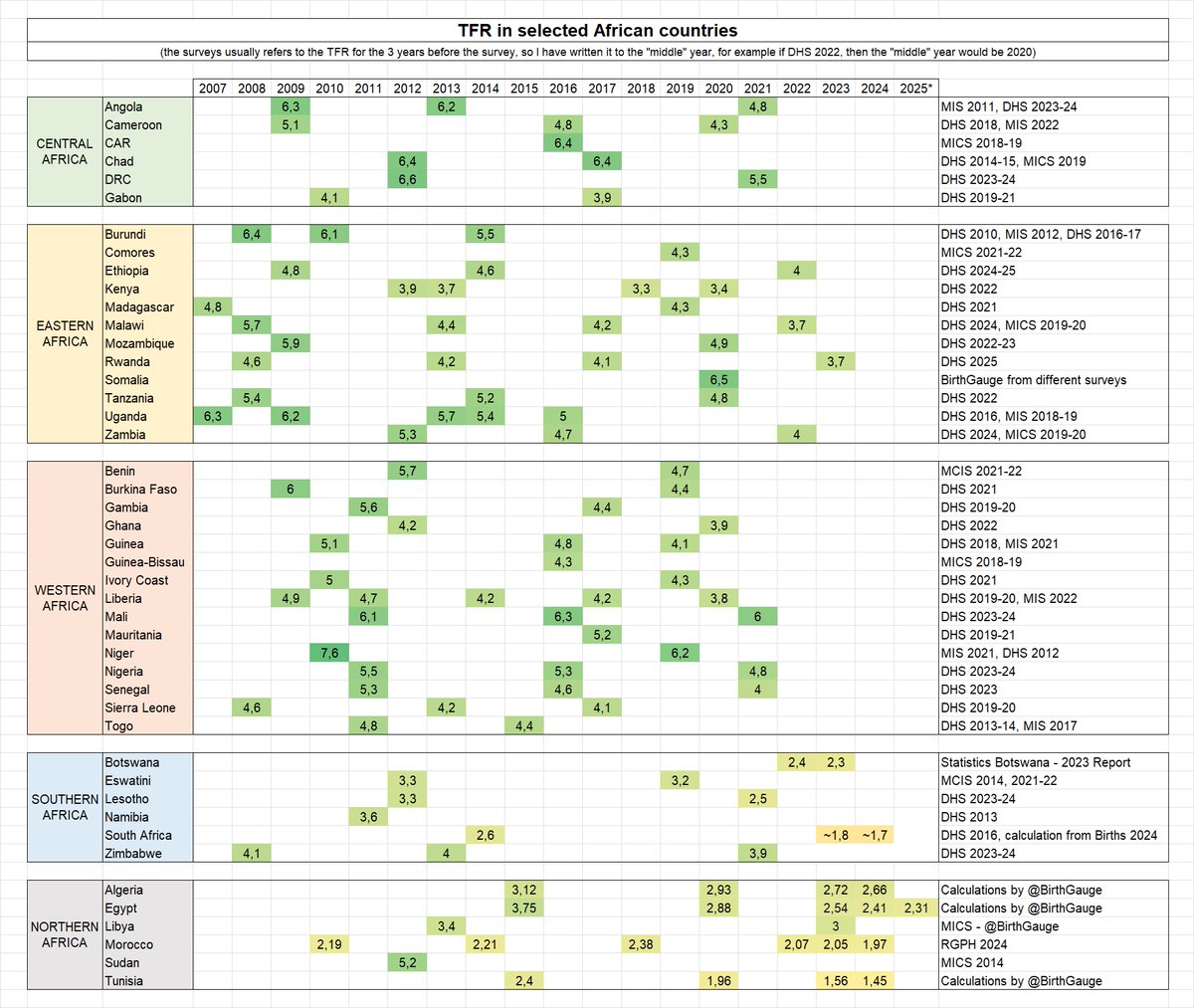
« The Donbass Line🇺🇦 »
Since 2014, 2022 and more recently winter 2023, Ukraine has been building a huge defensive system. The multilayered “Donbass Line” composed of many trench network is quite similar to Russian Surovikin system.
🧵THREAD on Ukrainian in depth defenses⬇️
1/25
Since 2014, 2022 and more recently winter 2023, Ukraine has been building a huge defensive system. The multilayered “Donbass Line” composed of many trench network is quite similar to Russian Surovikin system.
🧵THREAD on Ukrainian in depth defenses⬇️
1/25

When we talk of defensive trench network, the huge Surovikin line is the first thing we think about: trenches, bunkers, mines, dragon teeths…
This particular system, sometimes compared to the Maginot line was one of the assets that stopped Ukrainian summer counteroffensive.
2/
This particular system, sometimes compared to the Maginot line was one of the assets that stopped Ukrainian summer counteroffensive.
2/

Since it is already mapped by many, it is not useful to talk about it.
However, I’ve also mapped pre-2022 Russian defenses. It is interesting to see that these particular trenches system can still be used in case of a Ukrainian breakthrough.
3/
However, I’ve also mapped pre-2022 Russian defenses. It is interesting to see that these particular trenches system can still be used in case of a Ukrainian breakthrough.
3/

Let’s talk about Ukrainian defensive lines I called “Donbass line”.
Donbass line is quite different and more complex than Russian Surovikin system: it is composed of highly defended fortified system, separated by fields.
Zoom in⬇️
4/
Donbass line is quite different and more complex than Russian Surovikin system: it is composed of highly defended fortified system, separated by fields.
Zoom in⬇️
4/

If we take the example of Ukrainsk-Muraka line (facing south near Kourakhove), we can see on this Sentinel-2 imagery that each system is separated by a kilometer at least.
Each fort can defend itself from every direction: you have to take all of them to advance.
5/
Each fort can defend itself from every direction: you have to take all of them to advance.
5/

Contrary to Russian line, Ukrainian one is composed of many forts that are defending each other.
The 2014-15 Popasna-Luhanske line is a good example: to breakthrough, you have to assure that no other fort has fire control on you. (This particular line was however abandoned)
6/
The 2014-15 Popasna-Luhanske line is a good example: to breakthrough, you have to assure that no other fort has fire control on you. (This particular line was however abandoned)
6/

The line 0:
This was the 2014-2022 line, it was composed of 2 systems near Marioupol (overrun in a few days because of the lack of personal), 2 lines near Popasna (Ukr retreated to the city) and one line between Marinka and Horlivka, with some part still standing.
7/



This was the 2014-2022 line, it was composed of 2 systems near Marioupol (overrun in a few days because of the lack of personal), 2 lines near Popasna (Ukr retreated to the city) and one line between Marinka and Horlivka, with some part still standing.
7/



The really first line built from February to June 2022, preparing the retreat of Sievierodonetsk was built from southern Bakhmout to Siversk, passing through Soledar
This defensive system had 2 lines, both were overrun in Bakhmout and Soledar but are still standing in Siversk.
8/
This defensive system had 2 lines, both were overrun in Bakhmout and Soledar but are still standing in Siversk.
8/

At the same time, Ukrainians built lines 1, 2 and 3 in northern Donbass. Today, they are still building these lines.
Line one: Siverski-Donets river/Tchasiv Yar/Toretsk.
9/
Line one: Siverski-Donets river/Tchasiv Yar/Toretsk.
9/

Line two and three are the defenses of Kramatorsk and Sloviansk: 2 lines are protecting Sloviansk from the North, an anti tank ditcj and 1 line protecting the twin cities from the west.
+ 2 lines protecting Kostiantinivka/Droujkivka.
10/
+ 2 lines protecting Kostiantinivka/Droujkivka.
10/

Now, as some may ask themselves, the defenses after Avdiivka are already prepared but non-sufficient: main line is 17km from the city.
This line is however behind a river and lakes, making it a natural barrier.
11/
This line is however behind a river and lakes, making it a natural barrier.
11/

The final objective of the Russian offensive may be to reach Pokrovsk, the last big city and industrial center of Ukrainian Donbass (with Kramatorsk).
The Ukrainian Armed Forces have built a two layered trench system all around the city.
13/
The Ukrainian Armed Forces have built a two layered trench system all around the city.
13/

Support lines:
Donbass is a thing, but there are 3 other fronts: Kherson, South (Zaporijia) and Louhansk/Kharkiv.
Apart from Mykolaiv defense network and old Russian Kherson defenses, I haven’t found any Ukrainian line in the oblast.
14/
Donbass is a thing, but there are 3 other fronts: Kherson, South (Zaporijia) and Louhansk/Kharkiv.
Apart from Mykolaiv defense network and old Russian Kherson defenses, I haven’t found any Ukrainian line in the oblast.
14/

In Zaporijia oblast, there are at least 2 main defensive lines, plus a line defending the city itself. In Louhansk frontline, we have the Lyman-Borova line quite impressive. There is also a line near Izioum.
15/
15/

Currently, I’m investigating Ukrainian defenses on Russian border: the Koupiansk-Vovtchansk line, the Kharkiv defenses and border defenses in Sumy and Tchernihiv oblast.
For now I havn’t find many things, suggesting it is just the beginning.
16/
For now I havn’t find many things, suggesting it is just the beginning.
16/

How does those systems look like? This image is a high resolution one (from google earth pro): you can see part of the western Sloviansk defense.
A Ukrainian trench is never linear, and it is not always linked to avoid loosing a whole line if one part has fallen.
17/
A Ukrainian trench is never linear, and it is not always linked to avoid loosing a whole line if one part has fallen.
17/

Ukrainians made fun of Russian anti-tank ditches and dragon teeths, but they are now using it. You can also see this new basement to protect soldiers from artillery and FPV shells.
18/




18/




To geolocalise these trench network, I used 4 elements:
-Google earth updates (from June to august 2022)
-Sentinel-2 imageries, most of them until may-july 2022 (since it is the best time to see trenches)
-Geolocated Videos showing trenches (Kreminna forest)
-Esri Imageries
19/




-Google earth updates (from June to august 2022)
-Sentinel-2 imageries, most of them until may-july 2022 (since it is the best time to see trenches)
-Geolocated Videos showing trenches (Kreminna forest)
-Esri Imageries
19/




Since some may ask, this work is not helping Russia. Why?
-We mapped Russian positions and defenses before
-Russia has satellites, and IA that can detect these lines
-For most of it, it is now nearly 6-month-old
-The map is indicative and non-exhaustive
20/
-We mapped Russian positions and defenses before
-Russia has satellites, and IA that can detect these lines
-For most of it, it is now nearly 6-month-old
-The map is indicative and non-exhaustive
20/
I’ve been mapping Ukrainian and Russian defensive lines since nearly 2 years, this is the first part of my final project, it will be updated and improved many times in a row.
Here is the link to have it on your computer. Please credit me when using it!
21/google.com/maps/d/edit?mi…
Here is the link to have it on your computer. Please credit me when using it!
21/google.com/maps/d/edit?mi…
Keep in mind that when I’m using Sentinel-2, I can’t be precise, and there may be errors since it is sometime really difficult to know if there is a trench or not.
I will improve the map with updates of Maxar imageries in Google Earth.
22/
I will improve the map with updates of Maxar imageries in Google Earth.
22/
Here you can find the link for my interpretation of the lines. Since it is not a continuous defensive system, it is only an interpretation of hundreds of trenches. As tweet #21, you can download both trenches and defensive lines.
23/google.com/maps/d/edit?mi…
23/google.com/maps/d/edit?mi…
Since some people have already asked me, if you want to buy me a coffee for my volunteer work (tens of hours of work in my free time), you can here:
Thank you
24/buymeacoffee.com/clement.molin
Thank you
24/buymeacoffee.com/clement.molin
This is the end of the thread
If you like it, you can repost the first tweet. Make sure to follow both my account @clement_molin and my think tank @atummundi
I will do a French version soon.
25/25
If you like it, you can repost the first tweet. Make sure to follow both my account @clement_molin and my think tank @atummundi
I will do a French version soon.
25/25

@escortert @Pouletvolant3 @frog_of_war @wolski_jaros @guillaume_ancel @Michel_Goya @ObsDelphi @CartesDuMonde @AudrandS @Black_BirdGroup @emilkastehelmi @GeoConfirmed @UAControlMap @Stevius21 @Danspiun @Tatarigami_UA @NOELreports @IntelCrab @egea_blog (some that may be interested)
@escortert @Pouletvolant3 @frog_of_war @wolski_jaros @guillaume_ancel @Michel_Goya @ObsDelphi @CartesDuMonde @AudrandS @Black_BirdGroup @emilkastehelmi @GeoConfirmed @UAControlMap @Stevius21 @Danspiun @Tatarigami_UA @NOELreports @IntelCrab @egea_blog @jdomerchet @DefMon3 @Tendar @Thinker_View @ChrisO_wiki @AndrewPerpetua @COUPSURE
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh