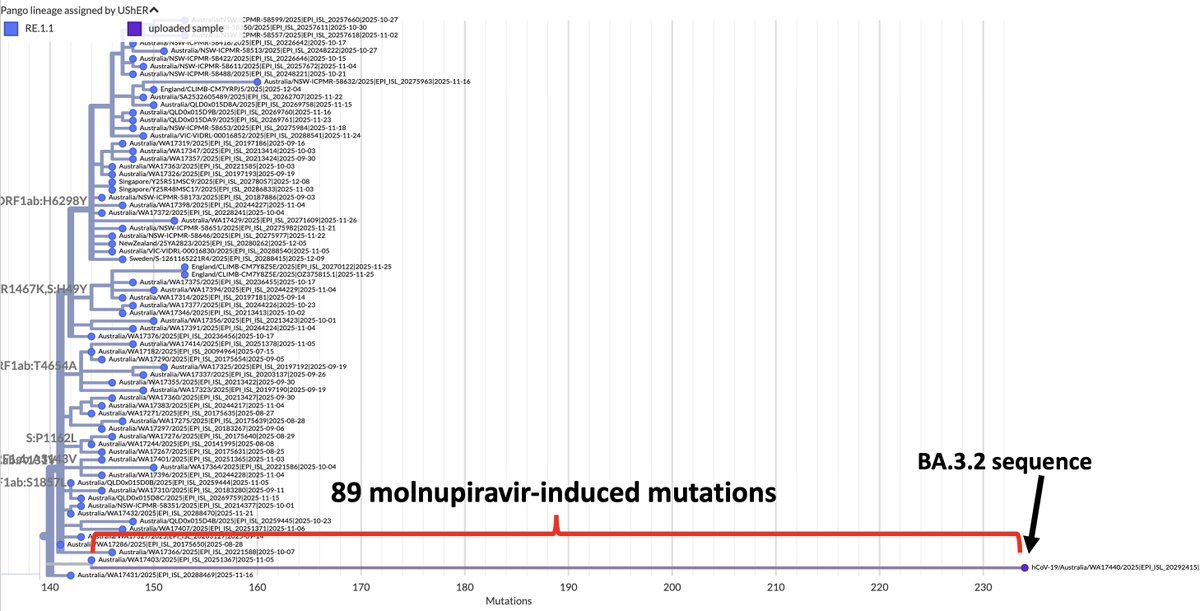
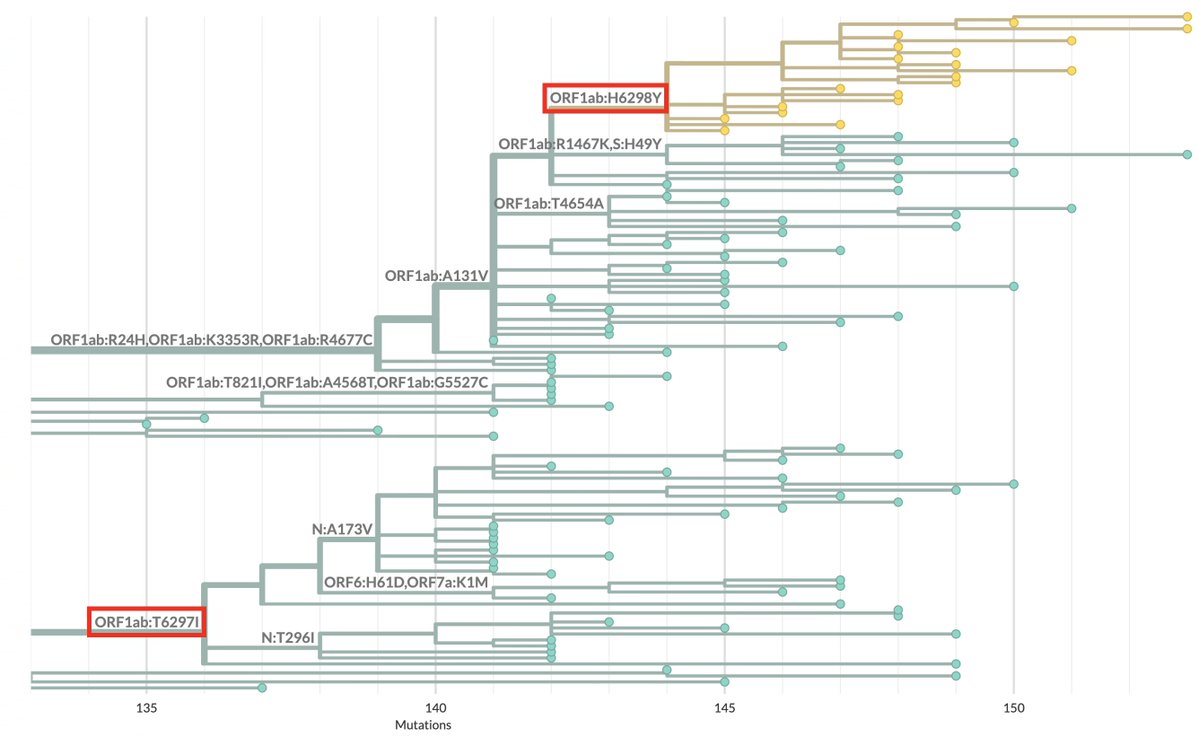
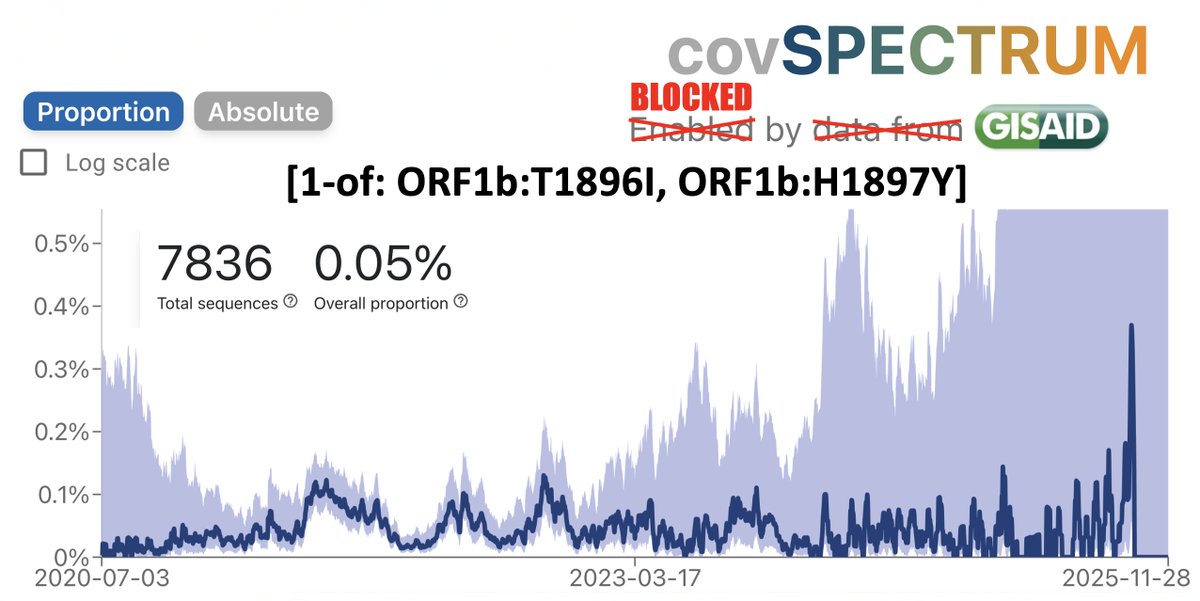
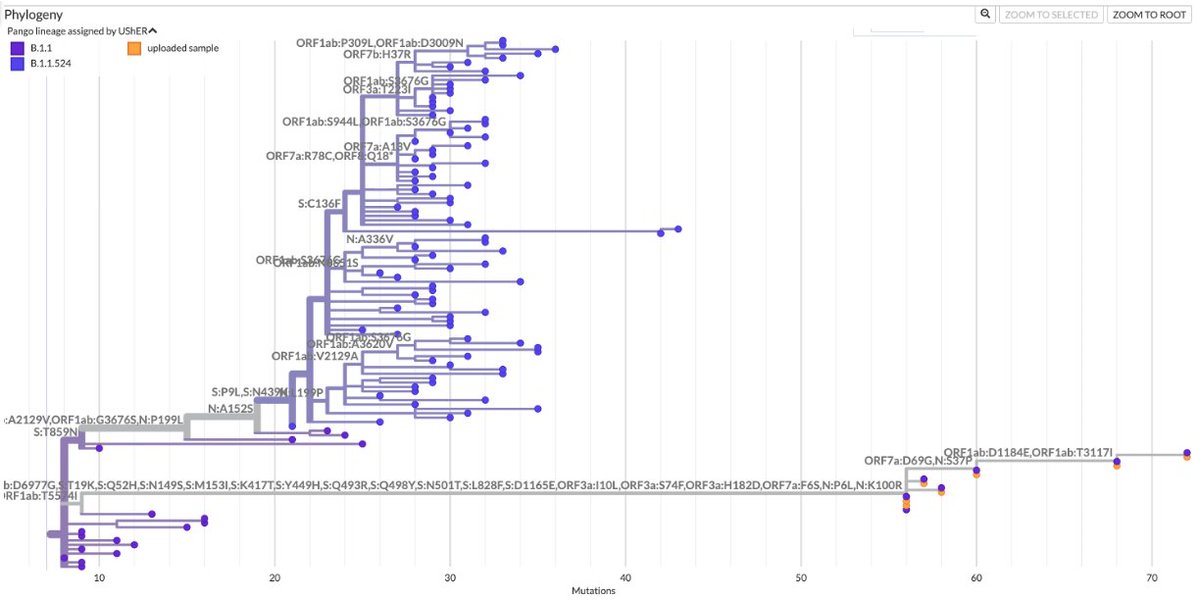
A dozen more sequences of this JN.1 + K444R + Y453F just dropped. All from Brazil, all collected in 2024. 12/13 are from the Brazilian state of Bahia, but those 12 sequences come from 11 different cities. This has the potential to be a big deal.
https://twitter.com/LongDesertTrain/status/1752102061171241416
BA.2.86 had extremely high ACE2 affinity, but as you can see in @yunlong_cao's tweet below, JN.1's S:L455S, while a crucial antibody-evasion mutation, squandered pretty much all the extra ACE2 affinity of BA.2.86 (higher = weaker ACE2 binding). 2/4
https://twitter.com/yunlong_cao/status/1714694260740813290
By itself, lower ACE2 binding probably isn't a huge detriment, but it left JN.1 with little room to evolve further RBD mutations, which nearly always reduce ACE2. This is probably why JN.1's RBD has remained virtually unchanged since its emergence. 3/4
https://twitter.com/PeacockFlu/status/1548068169838780418
Y453F has granted huge increases in ACE2 binding in previous variants, so it likely will do the same for JN.1. This could give JN.1 the mutational flexibility it has so far lacked, opening the door to further spike mutations. Stay tuned. 4/4 github.com/cov-lineages/p…
@yousitonmyspot I think the bigger story is the possibility of further RBD mutations due to the incr. ACE2 binding from Y453F. That probably gives JN.1 much more room to maneuver.
OTOH, Y453F has caused instability in some previous lineages, so it may impose a cost as well. Too soon to say.
OTOH, Y453F has caused instability in some previous lineages, so it may impose a cost as well. Too soon to say.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh