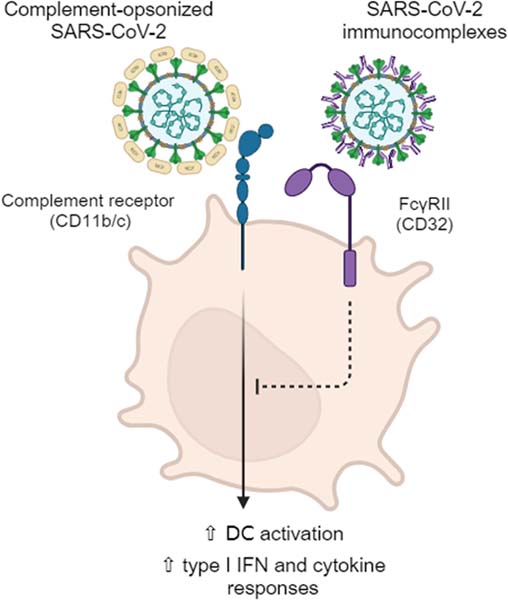
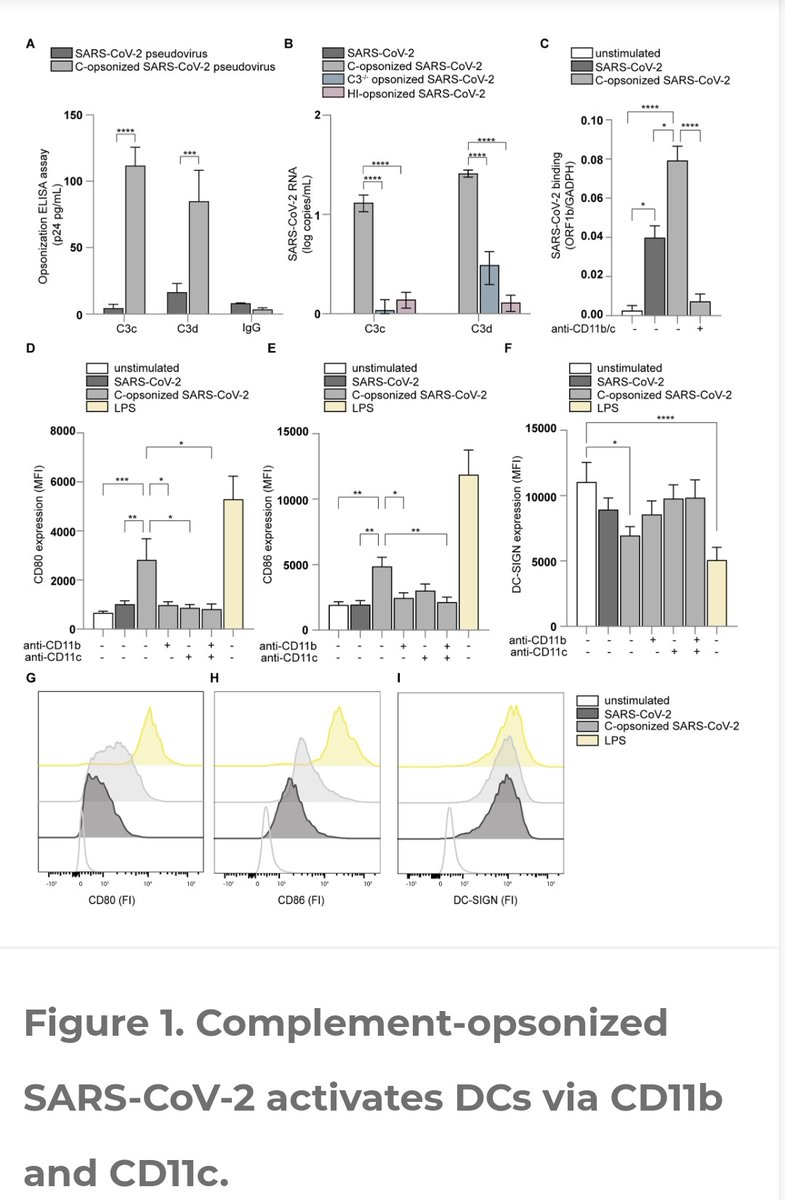
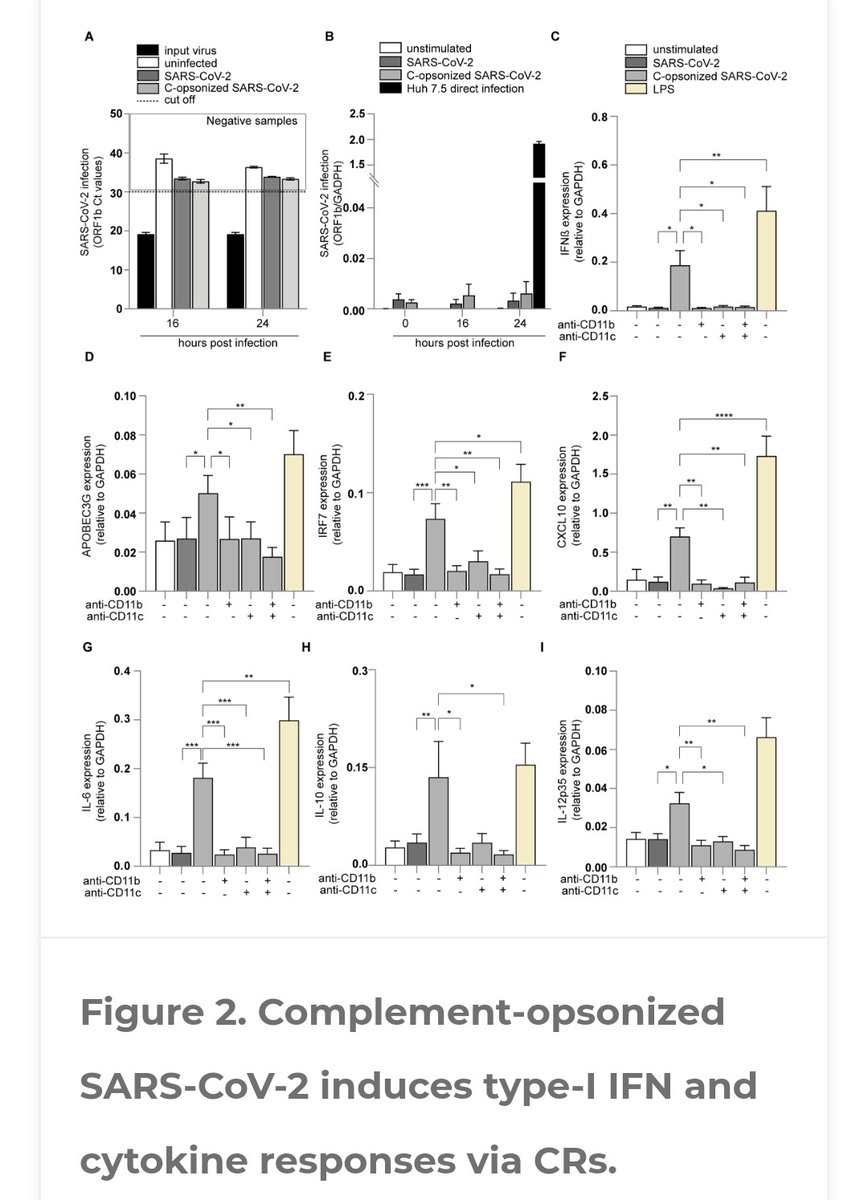
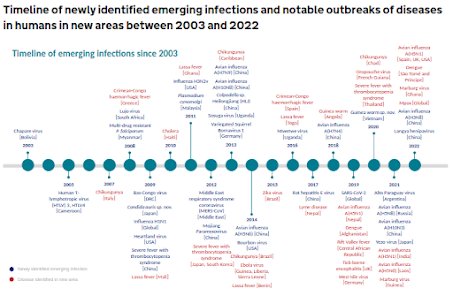
WHEN the KILLER of the VIRUS is SICK !
(Cytotoxic CD8+ T cell attacking infected cell)
(Cytotoxic CD8+ T cell attacking infected cell)
2) CD8 T cells, or cytotoxic T cells or killer T cells, are a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response against viral infections. Effector CD8 T cells also produce cytokines, which can activate other immune cells, enhancing the immune response against infection.
3) These CD8+ T cells play a major role in virus clearance. Several studies have shown that they are depleted or exhausted or dysregulated causing permanent inflammation, a major cause of long COVID.
When the killer is sick, the virus persists and with it the damage ...
When the killer is sick, the virus persists and with it the damage ...
4) ... to the immune system and the human body.
For those who want to go further, we and friends recently posted several threads.
Thanks for reading 🙏
For those who want to go further, we and friends recently posted several threads.
Thanks for reading 🙏
https://twitter.com/vipintukur/status/1761568885642596801?t=rpq52JQnZs2iP6F8sEa8UQ&s=19
5) CD8 and long COVID
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1760403439220039915?t=RswMb6vmhbKU0QHDTJ9WhQ&s=19
6) CD8 cells leukopenia
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1646719768831971330?t=pjLazO574aEcT__miDUlww&s=19
7) Exhausted CD8 Tcells
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1630420108647493632?t=pjLazO574aEcT__miDUlww&s=19
8) CD8 T cells and cognitive dysfunction
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1743106810964238672?t=pjLazO574aEcT__miDUlww&s=19
9) A pan-variant vaccine to conserve CD8 T cells 😊
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1754892684940996712?t=pjLazO574aEcT__miDUlww&s=19
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh