In today's #vatniksoup, I'll iterate on the Kremlin's main narratives and how they're currently being used to legitimize Russia's sham election, protest military aid to Ukraine, and confuse people with "whataboutism" ("What about the US/Gaza/Iraq/Israel/Ukraine?").
1/15
1/15

Of course none of this is new, it's just that the scale is much more massive than we've ever seen before. Russia's "Firehose of Falsehood" strategy attempts to flood us with a huge volume of emotional and biased content to confuse us and distract us from the topic at hand.
2/15
2/15

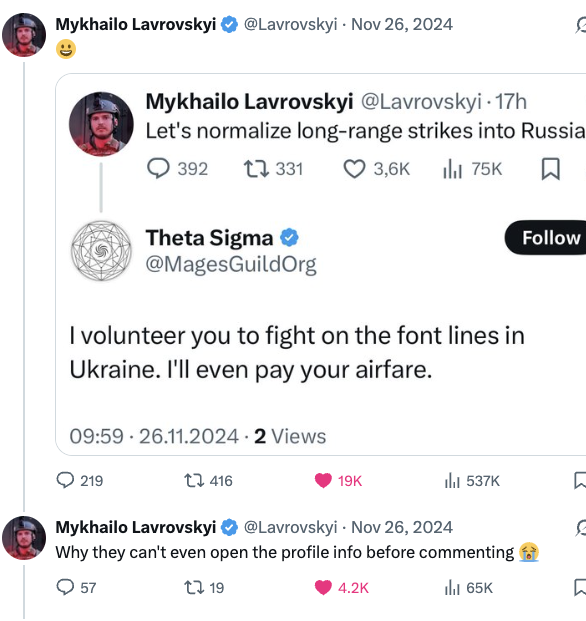
I'll use few of my recent posts about the Russian sham elections as an example. In the second photo, you see the massive amount of comments compared to likes/shares of the post - a ratio of 1:4 is actually very rare and suggests that the post was found by trolls and bots.
3/15


3/15


This type of posts are also great for discovering the Kremlin troll factory talking points - there aren't that many and they often like to spread the same lies they've done since 2014. Let's take a look at some of them and also see why they're wrong.
4/15


4/15


Let's start with the most classic strategy called "whataboutism". It's not a new tactic,as it was already used by the Soviet propagandists to divert any criticism towards their country. "What about US invasion of Iraq" & "What about Gaza" are typical examples of whataboutism.5/15






Then there's the deflection tactic of referring to the cancelled elections in Ukraine. It's actually written in the Ukrainian Constitution that elections are not being held during war time, because voting in the middle of an invasion is close to impossible.
6/15




6/15




Now, let's compare Ukrainian presidents to Russian and Belarusian presidents since 2000 - Russia has had 2 (technically 1), and Belarus has had one. It's very easy to see which regimes have limited free speech and taken control over their societies.
7/15
7/15

Whenever you bring up the war crimes done by the Russians in Ukraine, Kremlin trolls can't stop talking about the "genocide in Donbas". According to the story, Ukraine "shelled Donbas for 8 years", killing civilians and children in the process.
8/15




8/15




This of course never happened, and even Prigozhin's employees admitted that the people interviewed were actually crisis actors. The unrest was funded by the Kremlin and mercenaries/FSB agents like Igor Girkin. Full debunk here:
9/15

9/15
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1611980244252258304

Then there's an example that's a bit more obscure, but it's more popular among the Russian-speaking population - the 2014 Odesa clashes.
This false narrative claims that "Ukrainian neo-Nazis" burned Russian-speaking Ukrainians alive.
Debunk here:
10/15


This false narrative claims that "Ukrainian neo-Nazis" burned Russian-speaking Ukrainians alive.
Debunk here:
10/15
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1704058527864569958


Another classic is the "Ukrainian neo-Nazis" BS. Ukrainian far-right parties had 2,2% support in the 2019 elections. It's actually Russia that has a massive neo-Nazi problem, and their armies are actually infested with them:
11/15



11/15
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1597153011838513152
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1683803128053788672



Another narrative related to this is the "Azov uses civilians as human shields". Throughout the war, Russia has conducted war crimes against civilians, by for example shooting fleeing vehicles and ambulances. They have also targeted hospitals and rescue workers.
12/15




12/15




Then there's the "peaceniks", or accounts that are constantly calling for Ukraine to negotiate for peace, even though Putin himself said recently that "It would be ridiculous for us to start negotiating with Ukraine".
Debunk:
13/15


Debunk:
13/15
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1719701732240789616
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1757334171586891953


Expect to see a lot of similar posts in the near future, as they'll be used to attack any pro-Ukrainian stances on X. Also, there will be many more related to the US military aid to Ukraine and to support Donald Trump for the presidency.
14/15




14/15




It's worth noting, that before NAFO came along, all this was happening uncontested. Actually, these narratives still have very little resistance on social media sites like TikTok and Facebook. So, thanks NAFO!
15/15

15/15
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1685232995651751937

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh