Amidst the growing number of confirmed civilian casualties from the recent terrorist attack in Moscow, Putin and state-affiliated media and bloggers continue to link it to Ukraine. Given the gravity of these implications, we need to examine key details and assertions. 🧵Thread: 

2/ Firstly, on March 7th, the US Embassy in Russia issued a public warning regarding extremist plans to target large gatherings in Moscow, including concerts. Subsequently, after the attacks, the US confirmed sharing this info with RU security forces. US officials suspect ISIS-K 

3/ From the outset of the attack, there were efforts to link it to Ukraine. This included the circulation of the van photos with Belarusian license plates, blurred to insinuate Ukrainian origin, as well as claims in RU media suggesting Slavic attackers with fake beards were seen 

4/ Prominent Russian propagandist Margarita Simonyan, closely tied to the Kremlin, pushes the narrative of Ukrainian ties. This echoes Putin's speech about 'Ukrainians leaving the open window at the border for terrorists', confirming that the narrative originates in Kremlin 

5/ The group was allegedly detained in the same white car in Bryansk Oblast. The journey typically exceeds 4 hours. Given the number of traffic cameras for identification on the way, it's astonishing they made it that far. It's either severe incompetence or deliberate malice 

6/ The attack occurred mere minutes away from a major base of the militarized police (Rosgvardia) in Moscow, yet armed units arrived significantly later, allowing the perpetrators to flee in the same vehicle they arrived in. It's either deliberate negligence or gross incompetence 

7/ Despite claims, there is no concrete evidence linking these attacks to Ukraine. Regardless of the actual perpetrators, it's likely that Russian authorities will exploit the attack to propagate a "Ukrainian trace" narrative, prioritizing political agendas over facts
8/ Any statements made by detained suspects lose credibility due to FSB pressure applied towards them. For instance, one of the detainees, Shamsutdin Fariddun, already admitted receiving payment to carry out the attack from an anonymous person who contacted him through Telegram 
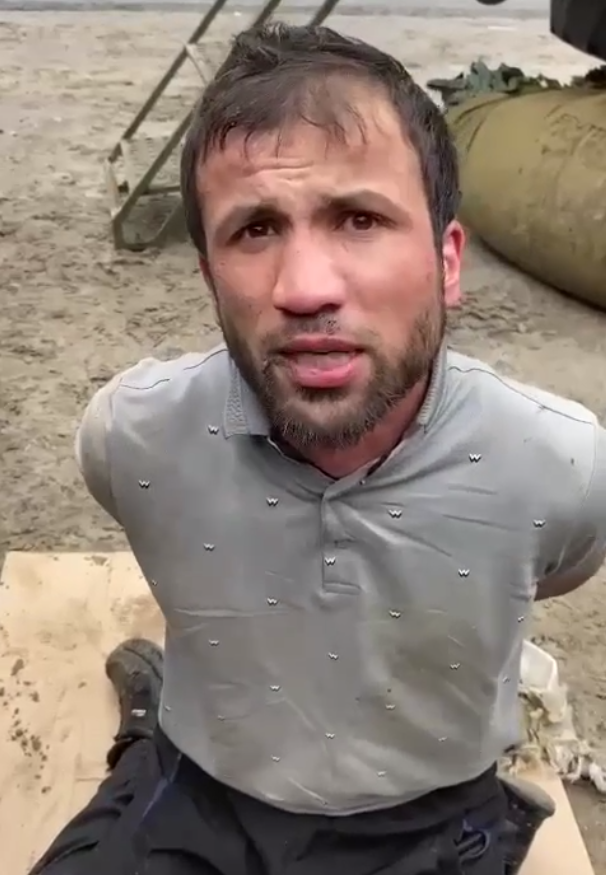

9/ In one of the videos, a detained person is shown having his ear cut off by Russian servicemen. Undoubtedly, under such pressure, they will confess to anything, whether it be ties to Ukraine, the CIA, or even admitting involvement in the assassination of Kennedy. 

10/ If the described failures are indeed due to gross incompetence, it reveals significant vulnerabilities in Russia's ability to counter such threats, posing a risk of future attacks. If it was intentionally overlooked, it will likely continue as well.
11/ Additionally, Russia's history of supporting terrorism in various regions, including Ukraine, Syria, CAR, and Mali, as well as assassinations in countries like the UK and Germany, underscores the ongoing threat posed by Russian state-sponsored terrorism 

12/ This tragedy also underscores the Russian state's inconsistent approach to terrorism, maintaining relationships with organizations like Hamas, Taliban, and Houthis despite their history of terrorist activities. Such ambiguity always leads to unintended consequences.
13/ In conclusion, while the loss of civilian lives in such attacks is tragic, the Russian government's priorities seem to lie elsewhere, sacrificing the lives and safety of its citizens for broader geopolitical goals under Putin's regime.
Please like and share this thread (the initial message), as many messages discussing the Ukrainian topic or war aren't receiving much attention on X. Therefore, I'm asking you to help with the algorithm by liking and sharing the top message of the thread. Thank you.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh