views
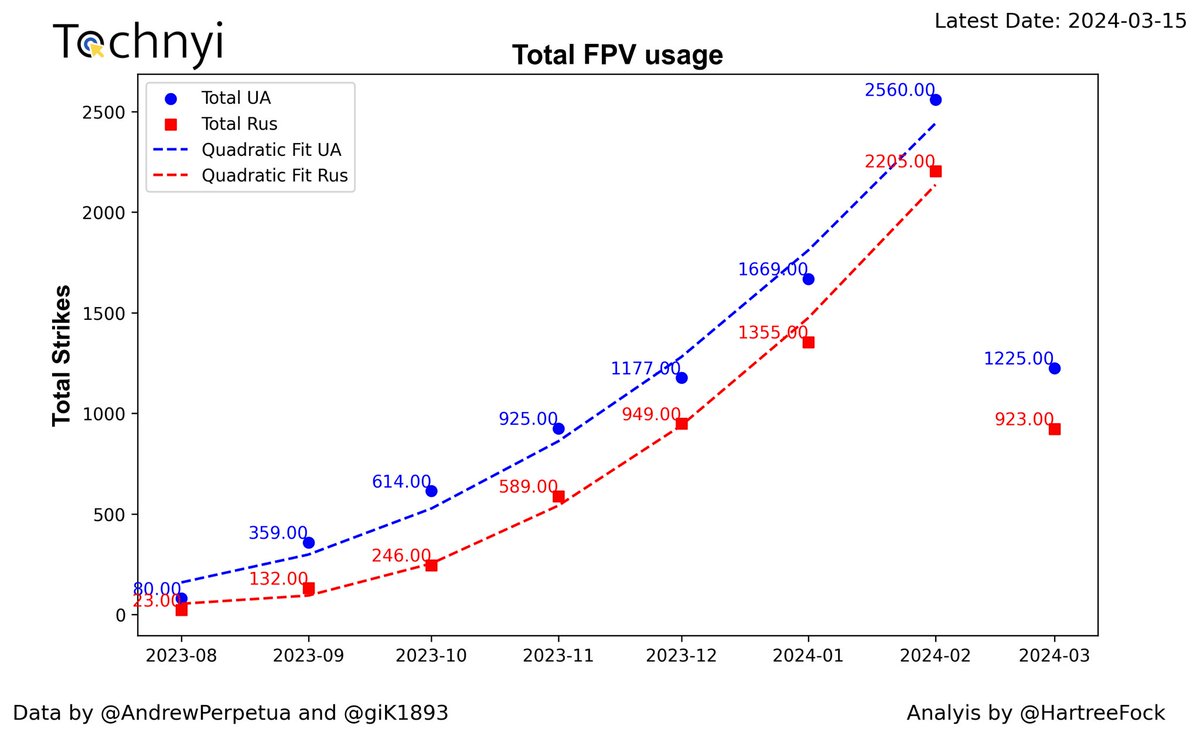
1/7 We can start with the graphs that depict the strikes on infantry and vehicles. The data is based on information gathered by @AndrewPerpetua and @giK1893 . As I write this thread, the current situation is very different from what I had expected. The current level of use of FPV drones from the Russian side has plummeted in all stats. Ukraine performed nearly the same number of strikes on infantry and vehicles in March, a week ahead of the month's end. This growth is swift, considering the initial numbers and the apparent difficulties observed in December. There is still a week of data to collect, and we will see in the weeks to come if Russia has a backlog of information to release, or if there are simply fewer drones in operation. We will deal with this specific topic at the end.



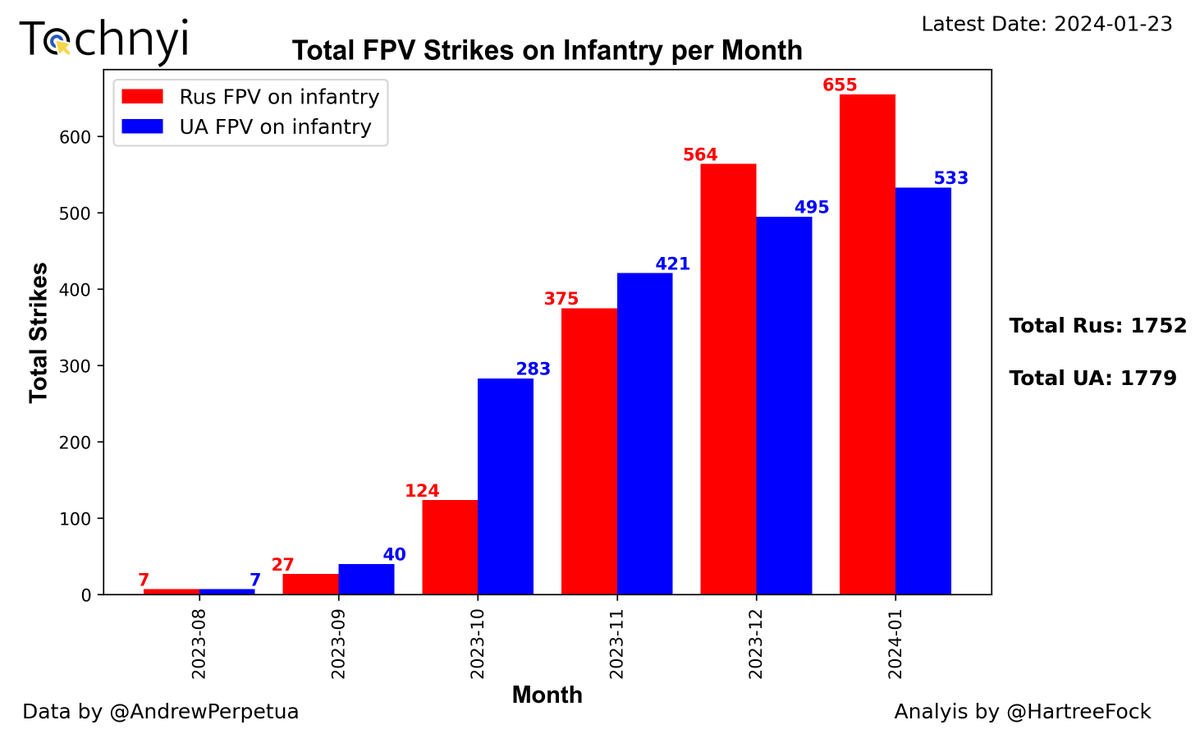
2/7 The latest data shows that Ukrainian forces have achieved remarkable results when it comes to striking enemy positions, managing to score more hits in less than a month. On the other hand, Russian forces seem to be struggling to keep up. Trenches remain the most hazardous place to be, as they account for a staggering 70.2% of all the strikes conducted so far.



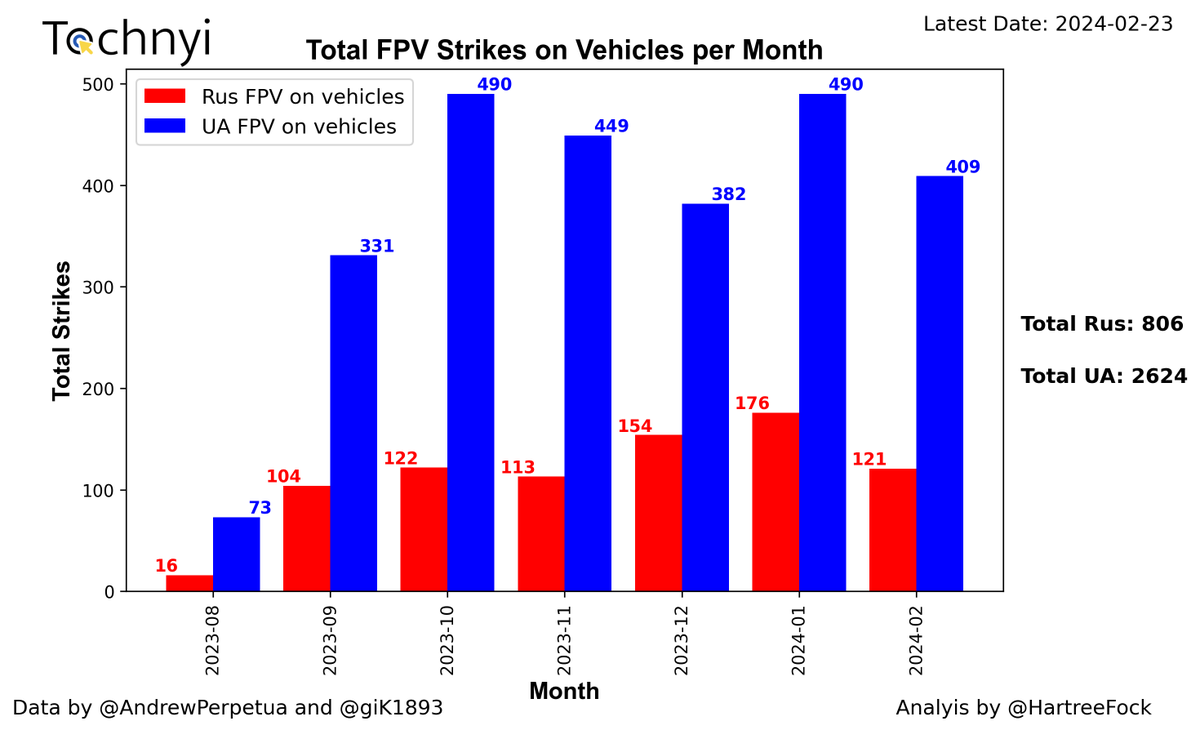
3/7 It Is important to look at the graph below to understand the significance of the data collected. The bar chart displays a month-by-month comparison between Ukrainian and Russian FPV strikes. After a decline in December, which suggested a potential advantage for the Russian forces, a steady growth in Ukrainian strikes is visible. In March, there were 423 more Ukrainian strikes than Russian strikes. This indicates that the Ukrainians are committed to using drones, particularly FPV, to deter the Russian military.

4/7 Looking at the progression with a week to go, it is very well in line with the expected values, however, it is also possible to see a slight change in the rate of growth but at the moment this is only a speculation, and few more weeks are needed to fully have a representative dataset, so far Ukraine is growing faster than Russia. This is well depicted by the plot of the total strikes from both sides, where Ukrainian forces dominate with 10289 strikes against 6869.



5/7 It has been observed that Russians are falling behind when it comes to night vision technology. This issue is unlikely to be solely related to the reliability and availability of drones. Instead, it is more likely to be a problem with their incapability to adapt to changes. This may be due to the structure of the Russian Army, which is unable to adapt quickly. This topic was discussed with Dima from @wilendhornets and the discussion was hosted live by @tochnyi, .
https://x.com/tochnyi/status/1770851111827652666?s=20

6/7 I'd like to address a comment that has been frequently seen in the comment section, which concerns information obtained through verbal communication with soldiers. Recently @ATipplingPhilo reported to us about news from Casiv Jar claiming that there was a superiority in FPV drone usage from the Russian side. However, if we look at the data from March 2024, we can see that there is a very large hot zone in Donetsk. If we examine this hot zone more closely, we find that the peak zone is located on the outskirts of Casiv Jar.

7/7 An similar example to the one carried out can be conducted with the FPV strikes executed by the Ukrainian forces. The blue stars in the map indicate the locations where FPV drone strikes were performed. Upon analysing the map, one can observe that there are various concentration areas where the strikes using FPV drones are being carried out. The area of Stepove, Orlivka, and Lastochkyne, in particular, has a high density of FPV drone strikes, especially on the streets and treelines. Other locations along the front line have also been used as examples.
This highlights the relevance of data geolocation and the importance of taking information with a grain of salt, especially when it comes from sources with limited situation awareness on the frontline. Is always paramount to have a general overview of the frontline to understand where one of the two sides is using a specific resource more intensely.
This highlights the relevance of data geolocation and the importance of taking information with a grain of salt, especially when it comes from sources with limited situation awareness on the frontline. Is always paramount to have a general overview of the frontline to understand where one of the two sides is using a specific resource more intensely.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh