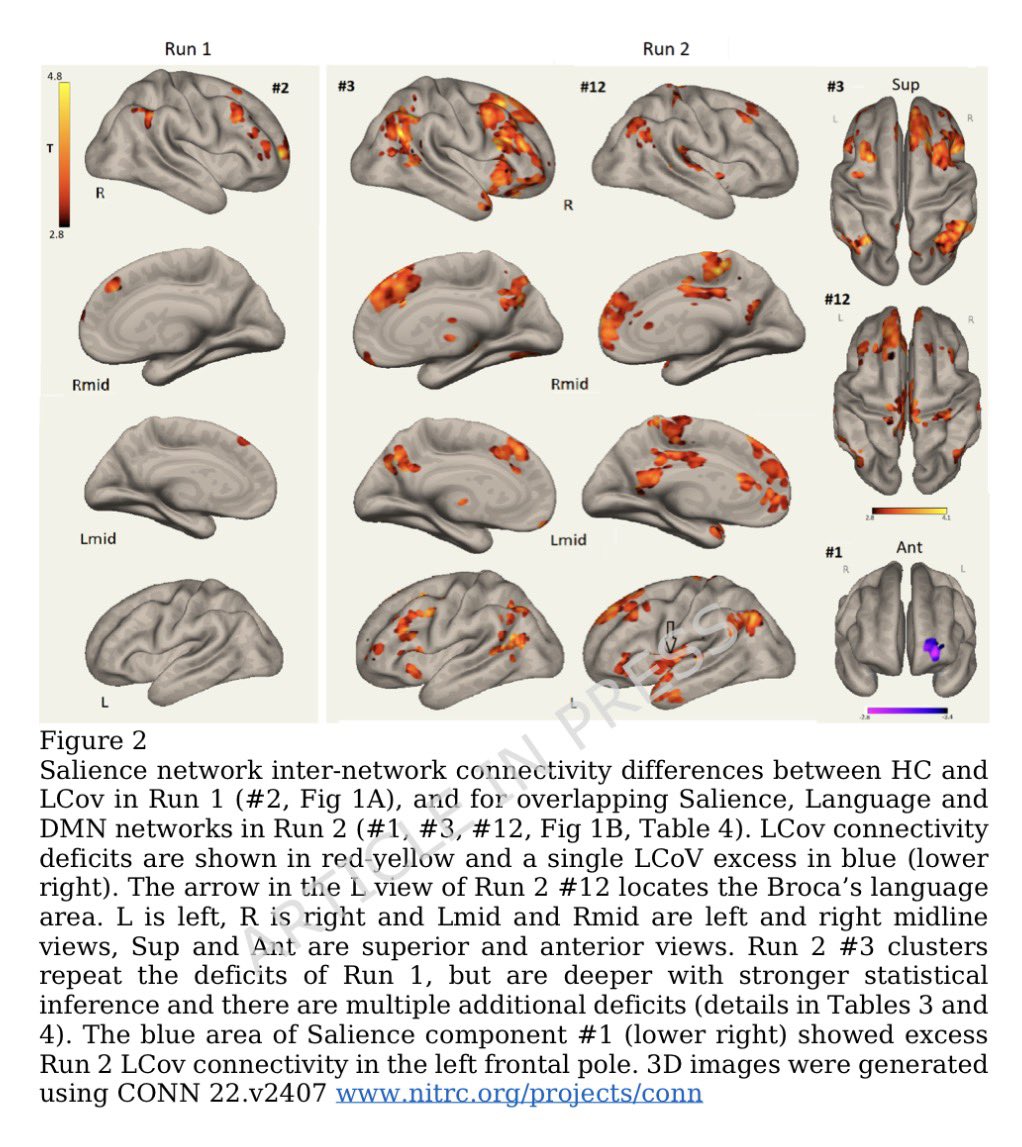
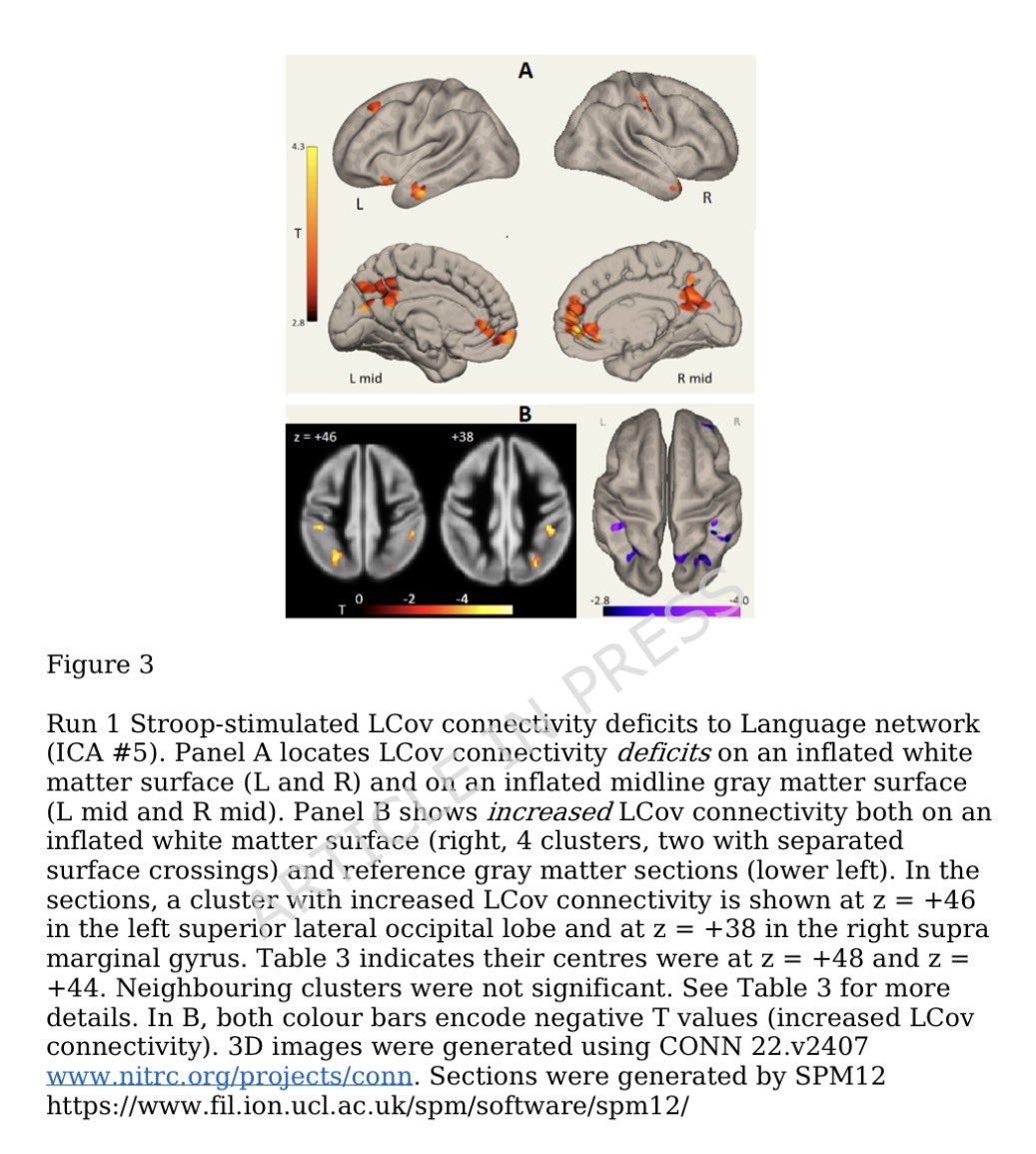
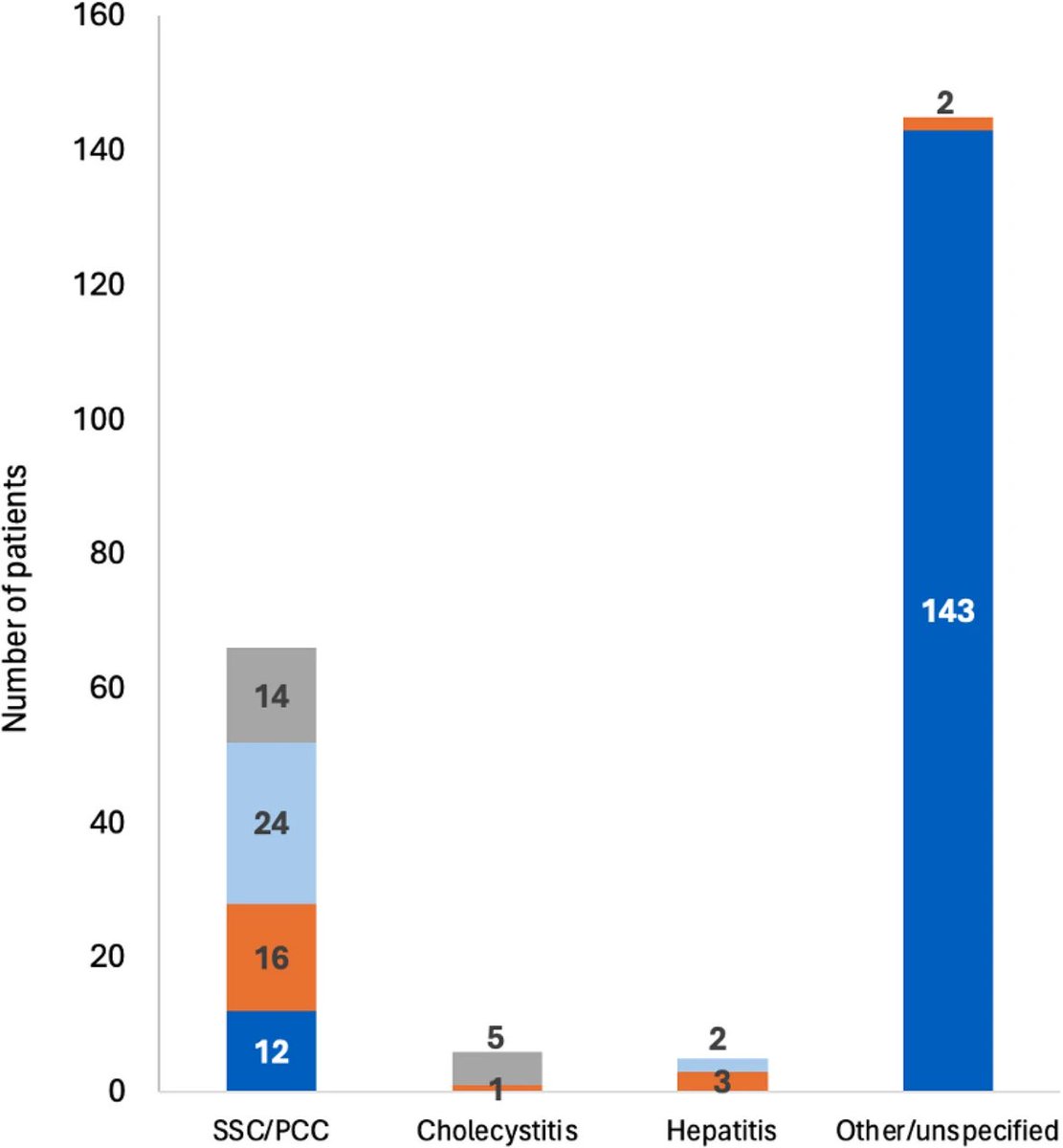
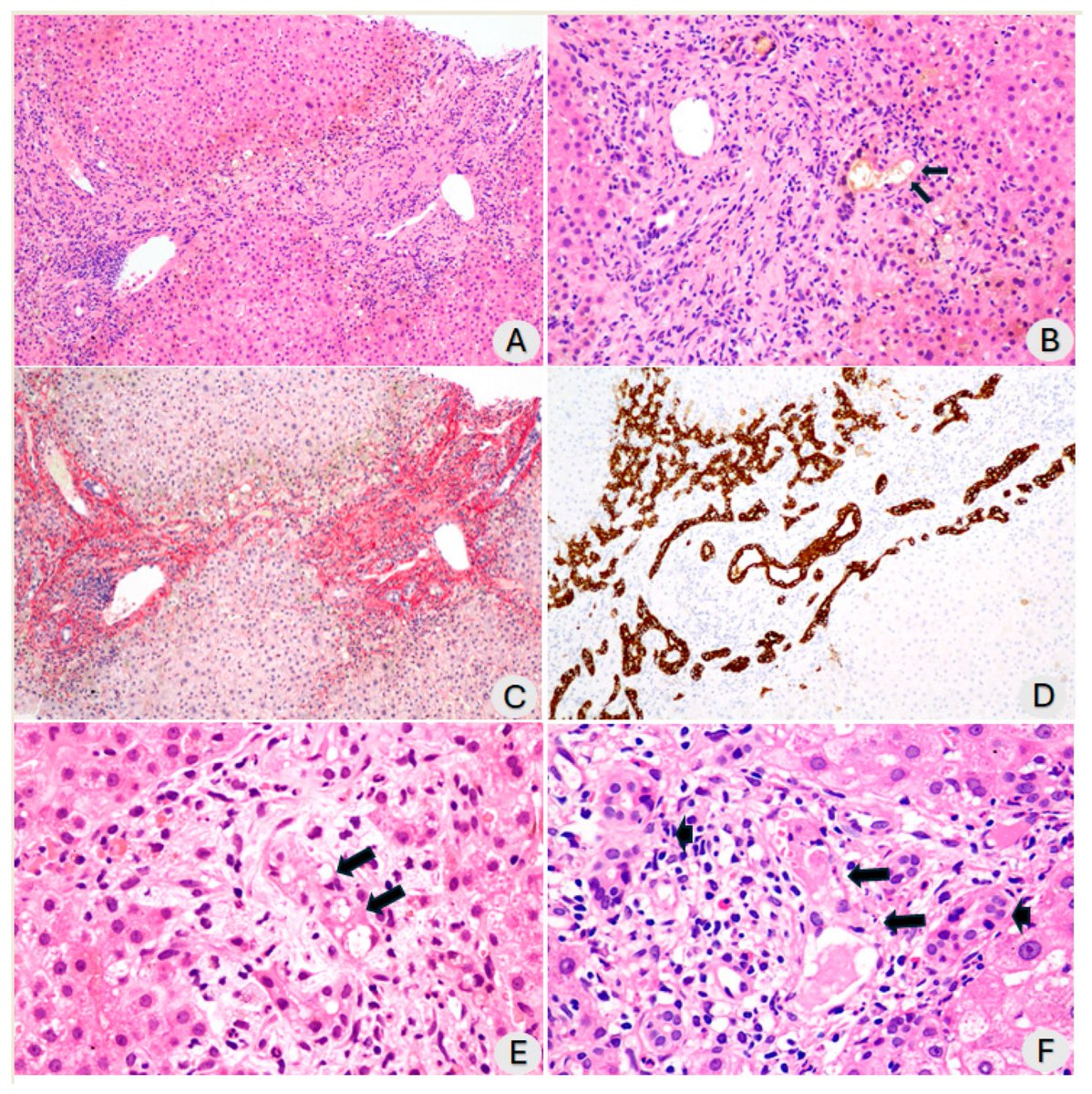
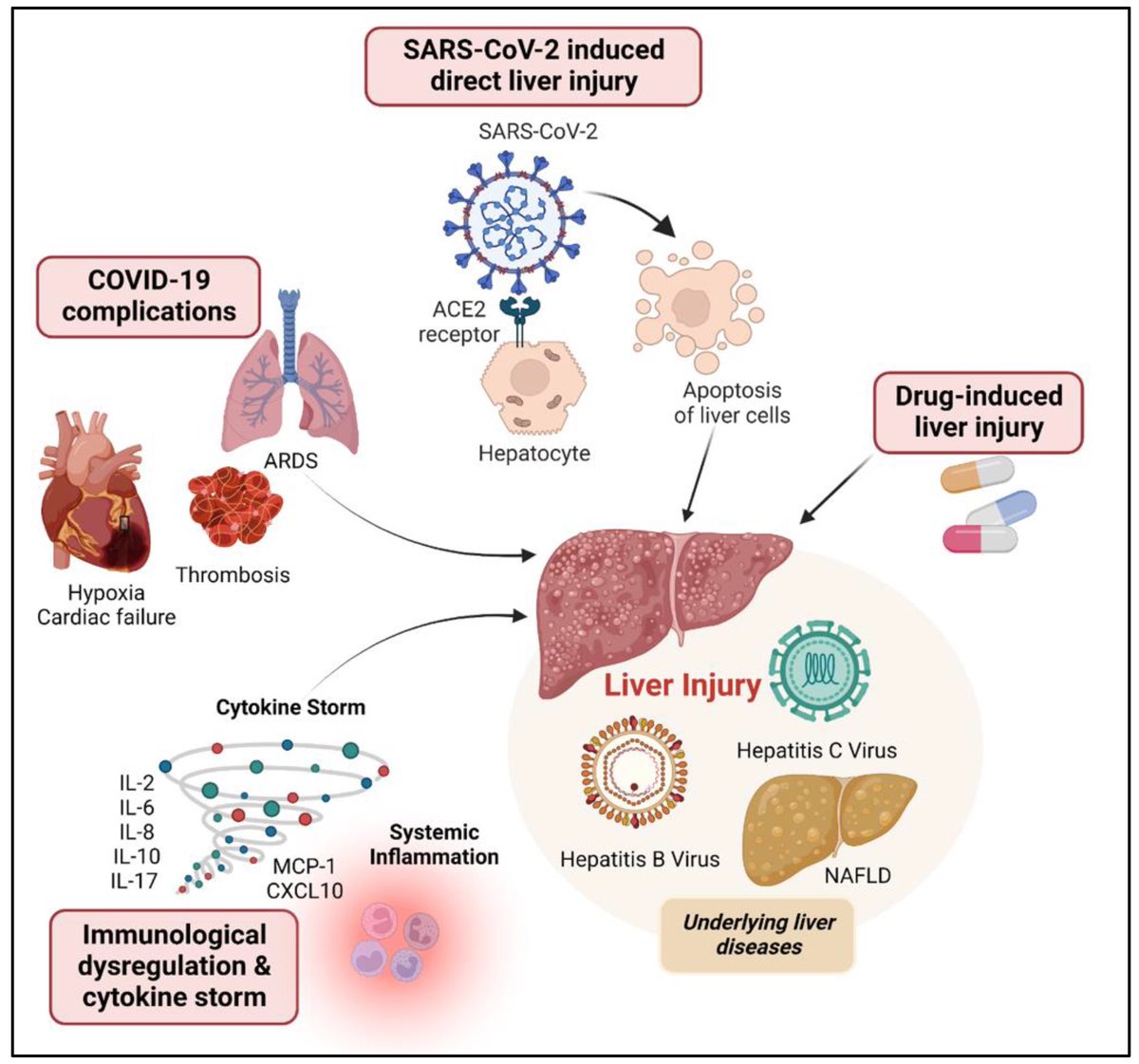
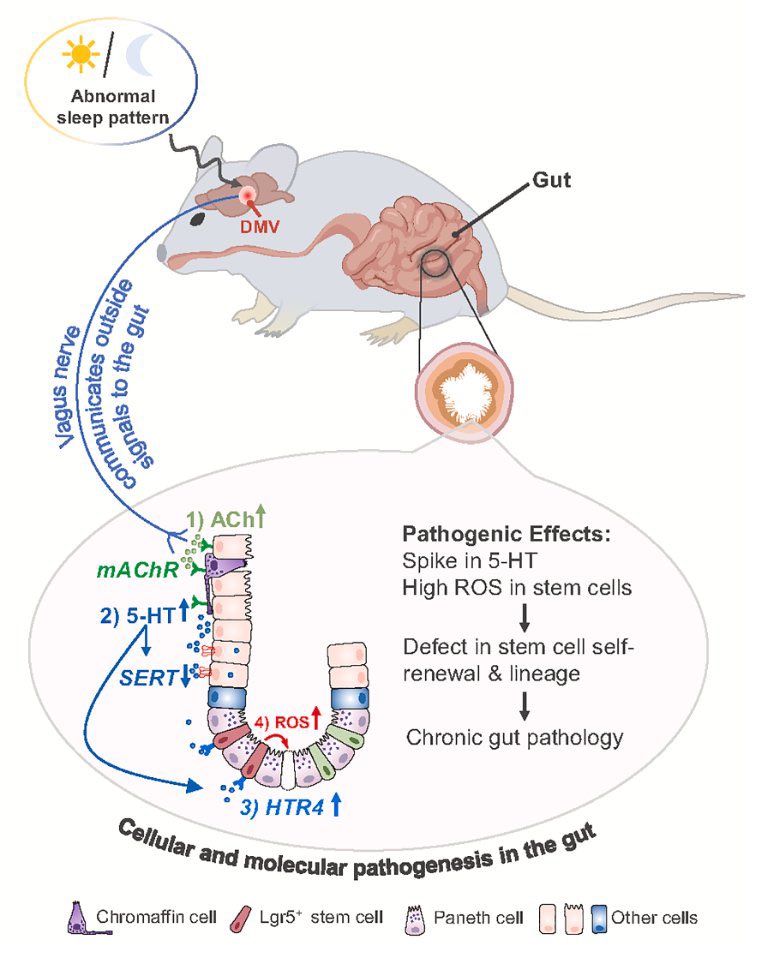
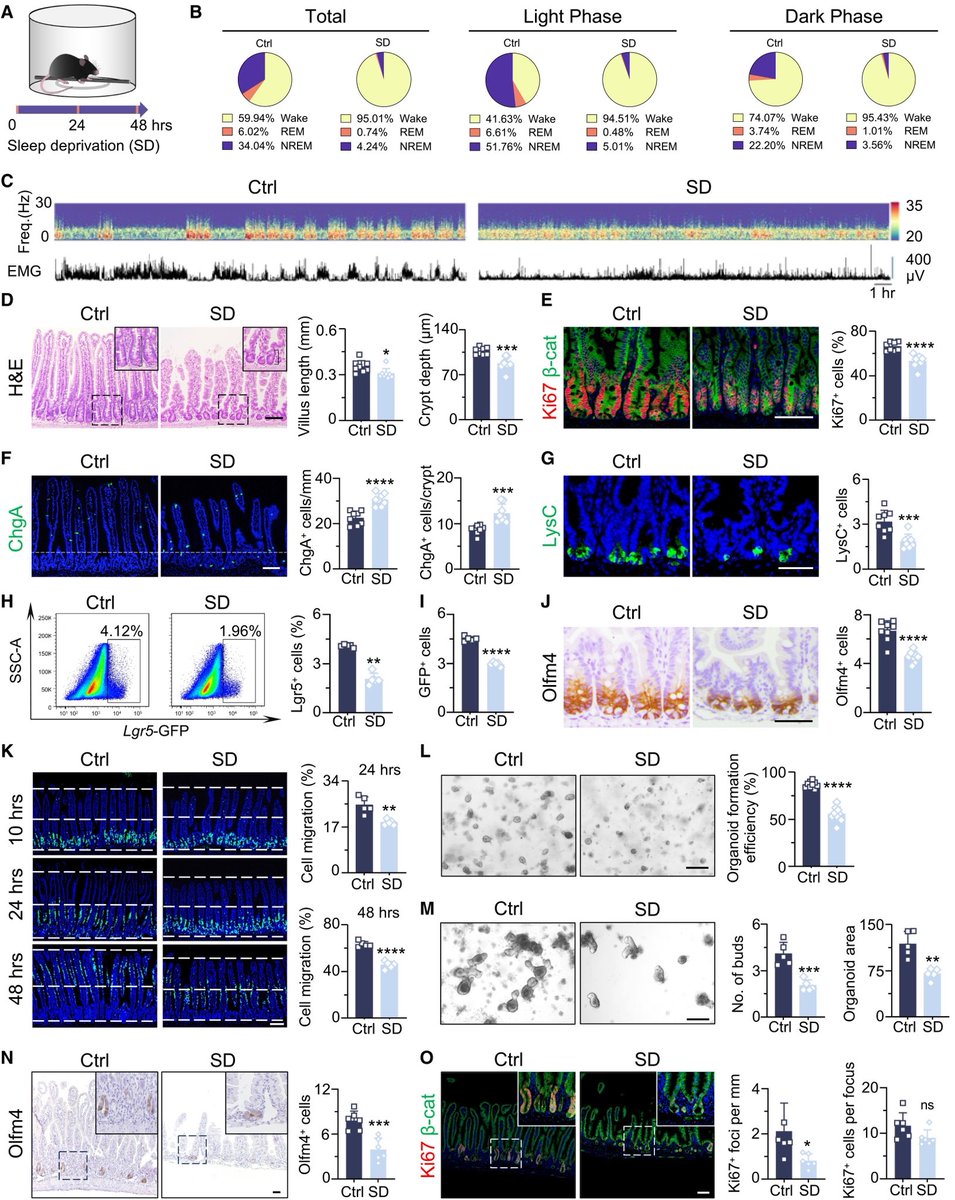
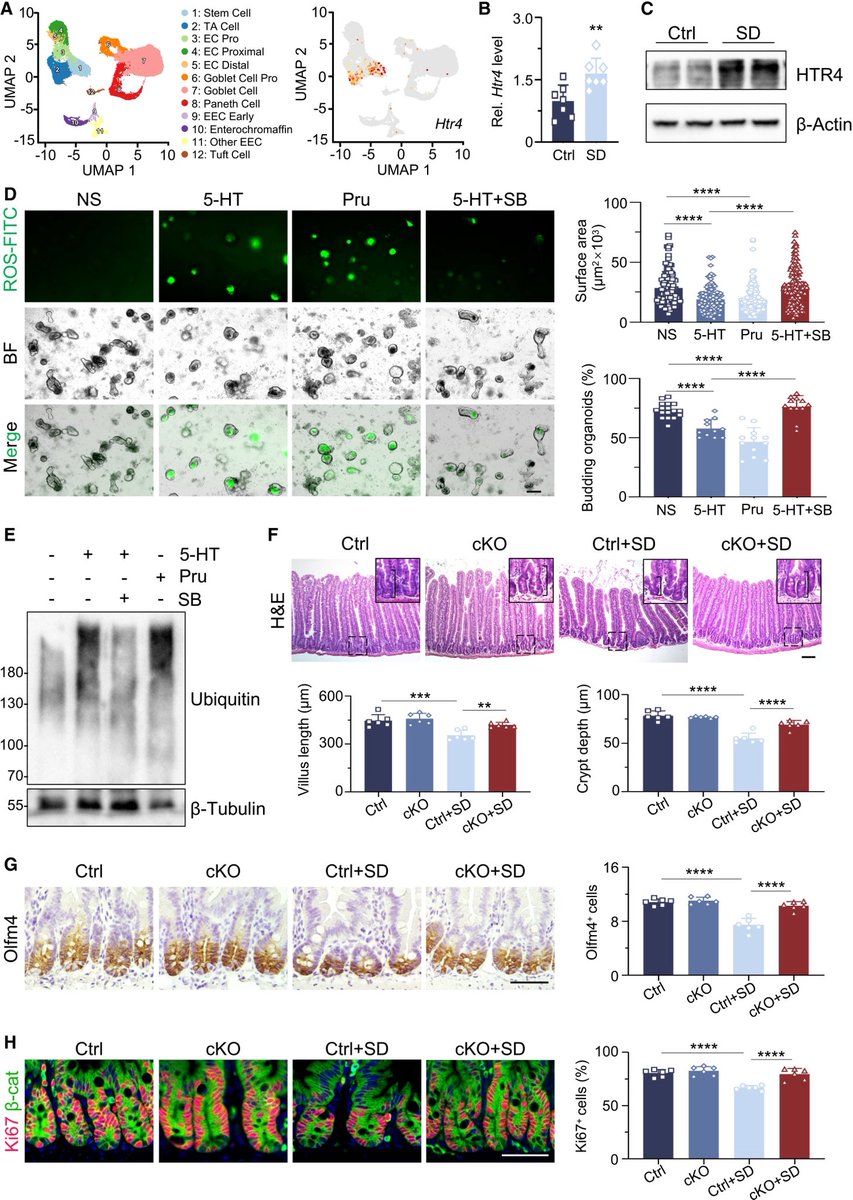
How SARS-CoV-2 replicates once it enters the cells, has made surprising discoveries that could be the foundation for future antiviral therapies. It also has important implications as replication of the SARS-CoV-2 has, so far, received less attention from researchers. 1/ 

The viral life cycle can be broken down into 2 main stages: the 1st where the virus enters the cell, & 2nd is replication where the virus uses the molecular machinery of the cell to replicate itself by building its parts, assembling them into new viruses that can then exit 2/ 

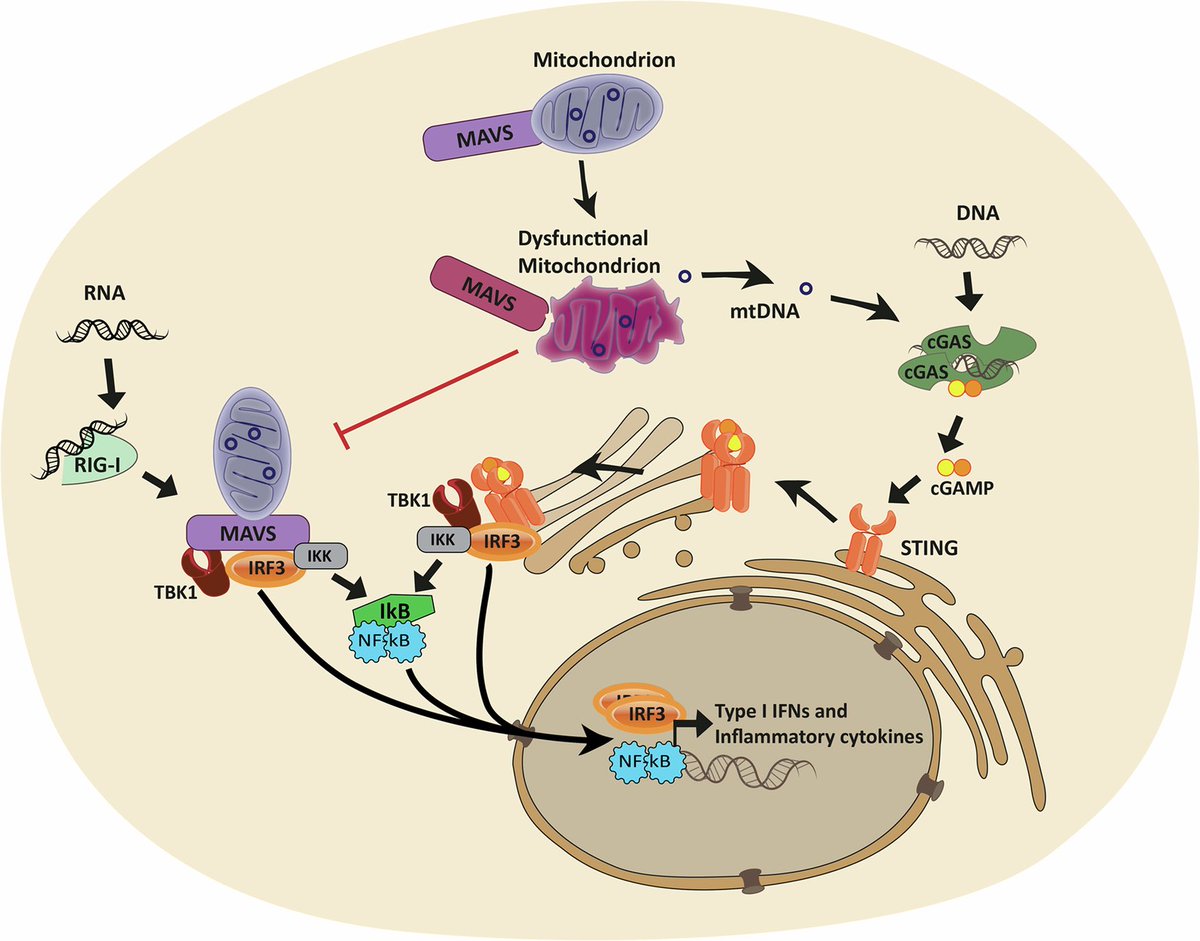
The new study focuses on how the Envelope protein of SARS-CoV-2 controls late stages of viral replication. Coronaviral Envelope (E) proteins are pentameric viroporins that play essential roles in assembly, release, and pathogenesis. 3/ 

The researchers marked the Envelope protein with fluorescent tags to track its movement within cells and used proteomics to identify key pathways that allow SARS-CoV-2 to take over the internal compartments of the infected cell—known as organelles—for its replication. 4/ 

They identified a surprising aspect of its replication in its use of a compartment called the lysosome during viral release. The Envelope protein localises itself to the Golgi complex and to lysosomes. 5/ 

Lysosomes are acidic, degradative organelles, but SARS-CoV-2 uses its Envelope protein as an ion-channel to neutralize their acidity and so enhance viral release. 6/ 

So the data outline trafficking pathways and routes taken by the E viroporin of SARS-CoV-2, linking viral sequences with cellular factors that govern movement between the ER, Golgi, and lysosomes. 7/ 

Such insights on replication could eventually be applied to create new antivirals that inhibit the channel activity of the Envelope protein. These could apply not only to SARS-CoV-2, but to the β-coronavirus family and any other virus that replicates with the same mechanisms. 8/
These findings show what an exquisite cell biologist the SARS-CoV-2 virus is, and shed new light onto how infection with SARS-CoV-2 can disrupt the function of essential intracellular compartments, known as organelles 9/9
science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh