𝘒𝘦𝘺 𝘚𝘵𝘶𝘥𝘺 : 𝙎𝘼𝙍𝙎-𝘾𝙤𝙑-2 𝙩𝙧𝙖𝙣𝙨𝙢𝙞𝙨𝙨𝙞𝙤𝙣 𝙗𝙚𝙩𝙬𝙚𝙚𝙣 𝙪𝙣𝙫𝙖𝙘𝙘𝙞𝙣𝙖𝙩𝙚𝙙 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙫𝙖𝙘𝙘𝙞𝙣𝙖𝙩𝙚𝙙 𝙥𝙤𝙥𝙪𝙡𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣𝙨 𝙤𝙫𝙚𝙧 𝙩𝙞𝙢𝙚
H/t @coopSpeak
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38574059/

H/t @coopSpeak
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38574059/
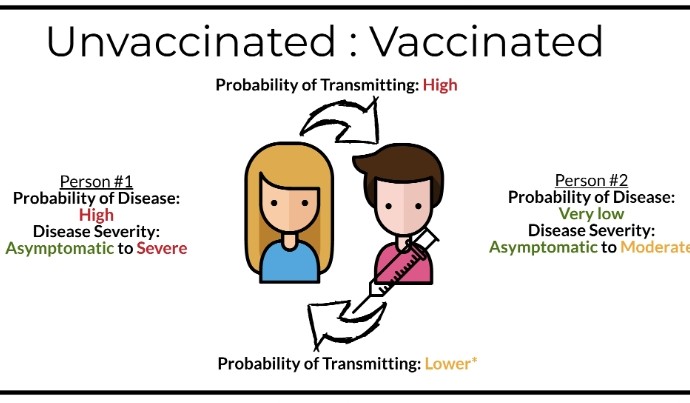
2) The authors developed a mathematical model to examine the dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 transmission between vaccinated and unvaccinated populations over time.
They previously found that vaccination reduces infection risk for both vaccinated individuals and the overall population..
They previously found that vaccination reduces infection risk for both vaccinated individuals and the overall population..

3) ...even with imperfect vaccines. Risk to vaccinated individuals disproportionately comes from contact with unvaccinated individuals.
They updated their model to incorporate new understandings of waning vaccine immunity, boosters, and Omicron immune evasion.
They updated their model to incorporate new understandings of waning vaccine immunity, boosters, and Omicron immune evasion.

4) Even with vaccine efficacy as low as 20% and waning immunity, vaccinated individuals had lower infection incidence over 10 years compared to unvaccinated.
Cumulative infection risk was 3-4 times higher for unvaccinated individuals. Unvaccinated individuals contributed ...
Cumulative infection risk was 3-4 times higher for unvaccinated individuals. Unvaccinated individuals contributed ...

5) ...to vaccinated individuals' risk at twice the expected rate based on contacts.
Overall, the updated model supported their original conclusion - vaccination decreases infection risk for both individuals and populations, with disproportionate risk to vaccinated individuals...
Overall, the updated model supported their original conclusion - vaccination decreases infection risk for both individuals and populations, with disproportionate risk to vaccinated individuals...

6) ...coming from unvaccinated contacts.
In summary, the authors found that their previous conclusions about the protective effects of vaccination held even after accounting for evolving understandings of Omicron immunity and waning protection over time.
Thanks for reading 🙏
In summary, the authors found that their previous conclusions about the protective effects of vaccination held even after accounting for evolving understandings of Omicron immunity and waning protection over time.
Thanks for reading 🙏
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh


















