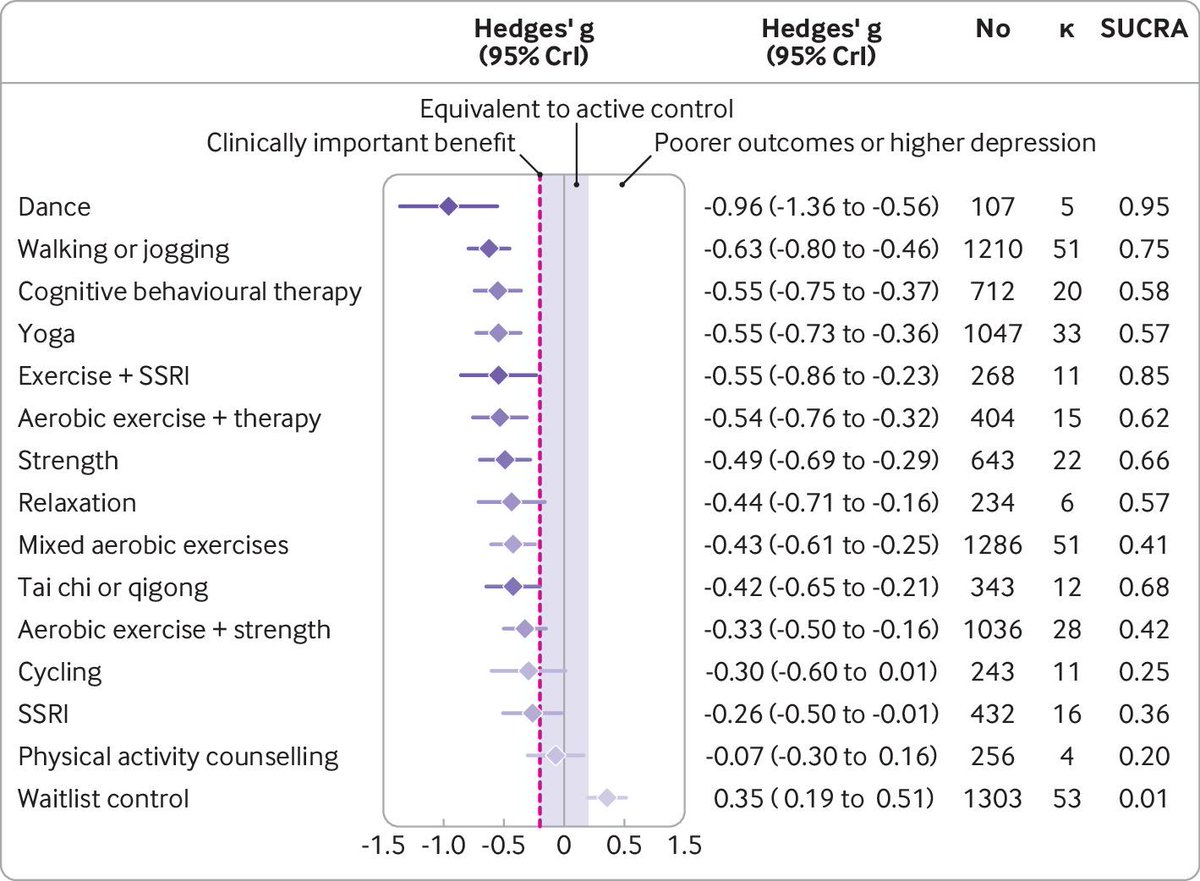
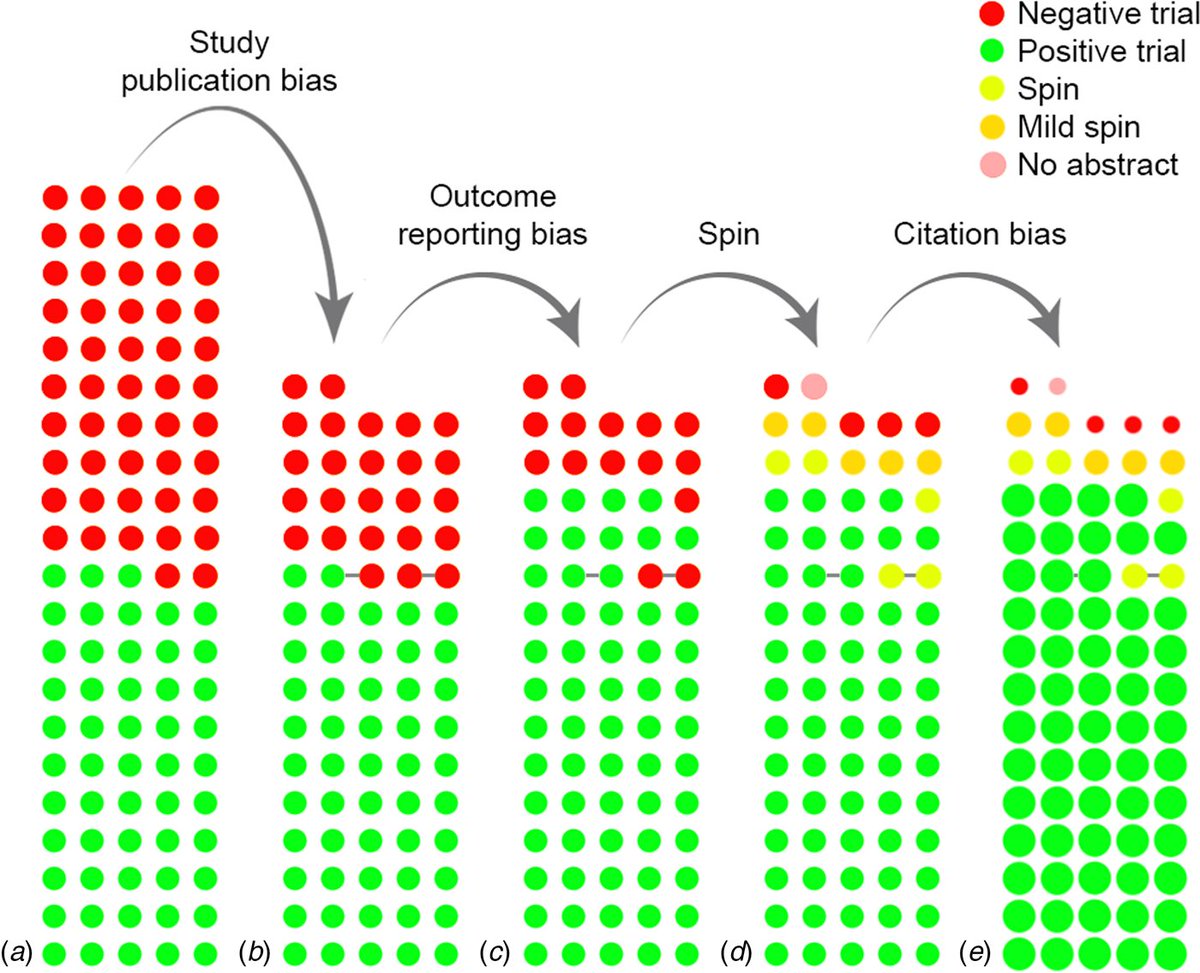
These findings are from a descriptive study published in Psychological Medicine which mapped the repetition among the 1419 symptoms described in 202 diagnoses of adult psychopathology in section II of the DSM-5. 2/10 cambridge.org/core/journals/…


The first stage of coding aimed to distil the constituent symptoms of the diagnoses in chapters 1–19 of section II of the DSM-5. The resulting list of symptoms was then coded for content overlap using both qualitative content coding and natural language processing. 3/10
In total, 202 diagnoses were represented, including 135 primary disorders and 76 specifiers or other specified disorders with additional symptoms. While repetition appeared to be pervasive, the majority (63.2%) of the 628 distinct symptoms were unique to a single diagnosis. 4/10 

Overall, of the 202 diagnoses represented, 140 (69.3%) had at least one symptom that repeated in another diagnosis – 118 (58.4%) in a diagnosis in another chapter. 5/10 

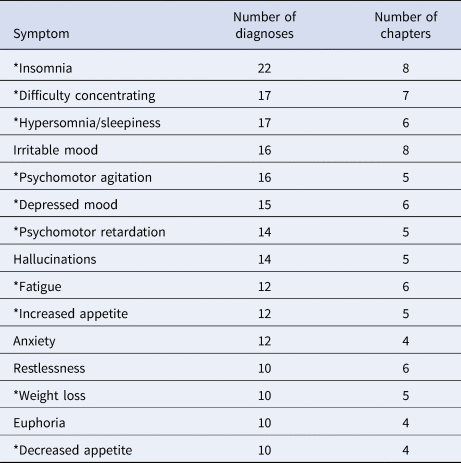
A noteworthy finding was that the symptoms in the DSM-5 that repeat most frequently, and that repeat across most chapters, are dominated by symptoms of major depressive disorder (MDD). 6/10 

Specifically, 10 of the top 15 most non-specific symptoms in the DSM-5 appeared in the diagnostic criteria for MDD. 7/10 
Perhaps MDD symptoms are psychological responses to stress, similar to how fever – a symptom that also cuts across numerous diagnostic categories – reflects an inflammatory response to cell damage or stress. 8/10
The pervasiveness of MDD symptoms throughout the DSM-5 likely hampers diagnostic accuracy through misattribution of symptoms in other diagnoses to MDD, and inflation of the rates of comorbidity due to symptom overlap with other diagnoses. 9/10
Ultimately, more empirical work on fine-grained clinical phenomena promises to improve on the reliability and validity of the DSM-5 constructs that frame much research and practice. 10/10
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh