𝗖𝗛𝗜𝗟𝗗𝗥𝗘𝗡 𝗔𝗧 𝗥𝗜𝗦𝗞 !!!
𝗦𝗔𝗥𝗦-𝗖𝗼𝗩-2 𝗜𝗺𝗺𝘂𝗻𝗲 𝗥𝗲𝘀𝗽𝗼𝗻𝘀𝗲𝘀: 𝗔𝗿𝗲 𝗖𝗵𝗶𝗹𝗱𝗿𝗲𝗻 𝗟𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝘁𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗲𝗱?
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…

𝗦𝗔𝗥𝗦-𝗖𝗼𝗩-2 𝗜𝗺𝗺𝘂𝗻𝗲 𝗥𝗲𝘀𝗽𝗼𝗻𝘀𝗲𝘀: 𝗔𝗿𝗲 𝗖𝗵𝗶𝗹𝗱𝗿𝗲𝗻 𝗟𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗣𝗿𝗼𝘁𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗲𝗱?
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…

2) The study compared humoral and cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in 28 children and 28 adults approximately 7 months after mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Both children and adults had comparable levels of antibodies targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and RBD
Both children and adults had comparable levels of antibodies targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and RBD

3) However, children had lower antibody levels against the nucleocapsid protein compared to adults.
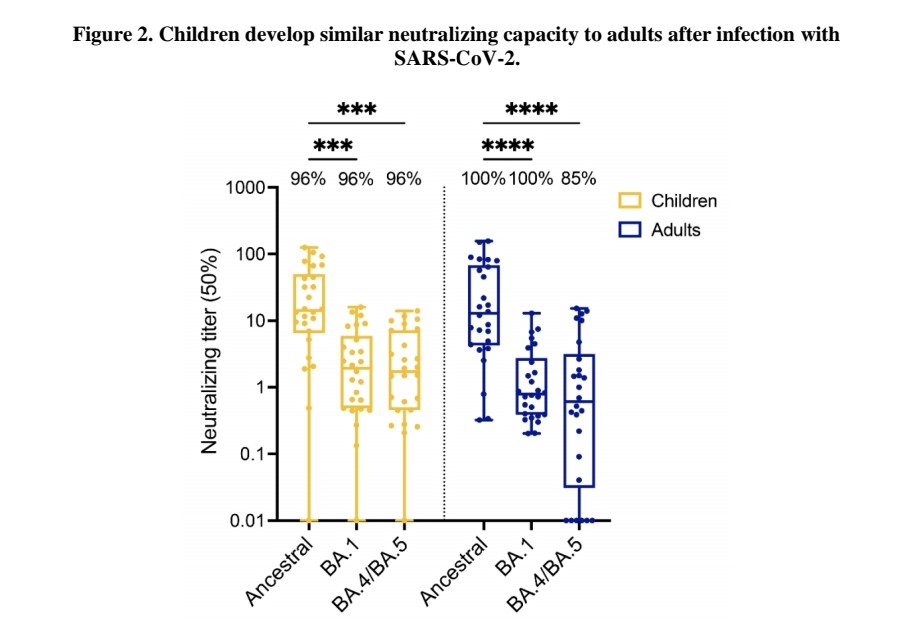
Neutralizing antibody titers against ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and Omicron variants were similar between children and adults.
Neutralizing antibody titers against ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and Omicron variants were similar between children and adults.

4) Cellular immune responses as measured by IFN-γ ELISpot were significantly lower in children compared to adults. The median response in children was approximately half that of adults.
In children, the magnitude of T-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 was similar to responses ...
In children, the magnitude of T-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 was similar to responses ...
5) ...against seasonal human coronaviruses that cause common colds. In contrast, adults showed a greatly enhanced response specifically to SARS-CoV-2.
T-cell responses in children showed stronger immunodominance towards the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein ...
T-cell responses in children showed stronger immunodominance towards the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein ...
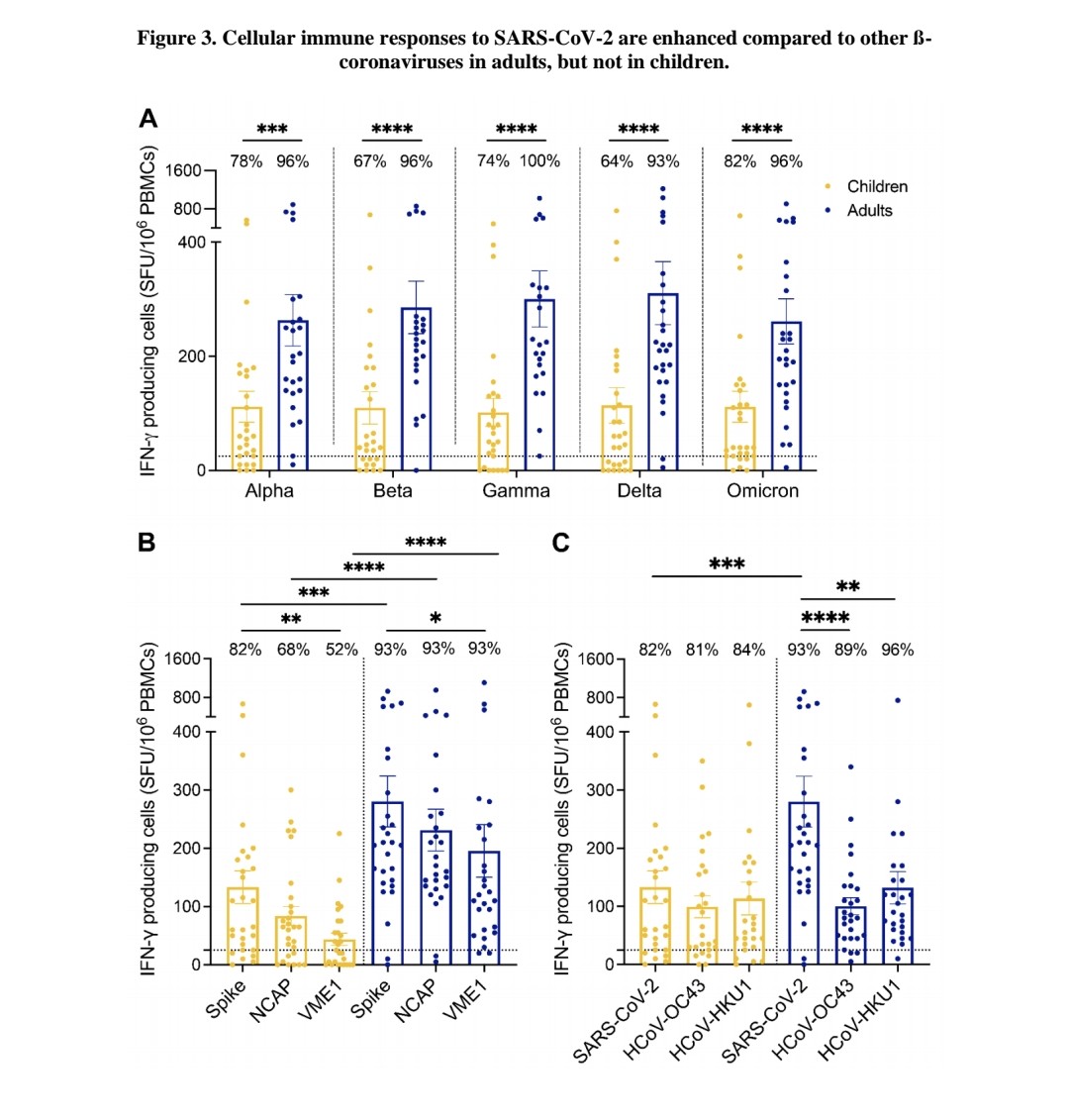
6) ...compared to other viral proteins, more so than in adults.
In summary, the study found that while humoral immunity was comparable, cellular immune memory was reduced in children relative to adults after SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Thanks for reading 🙏 and protect your kids.
In summary, the study found that while humoral immunity was comparable, cellular immune memory was reduced in children relative to adults after SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Thanks for reading 🙏 and protect your kids.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh



















