𝗖𝗢𝗩𝗜𝗗-19 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗰𝗼𝗴𝗻𝗶𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲 𝗶𝗺𝗽𝗮𝗶𝗿𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁: 𝗙𝗿𝗼𝗺 𝗲𝘃𝗶𝗱𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲 𝘁𝗼 𝗦𝗔𝗥𝗦-𝗖𝗼𝗩-2 𝗺𝗲𝗰𝗵𝗮𝗻𝗶𝘀𝗺
onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/br…

onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/br…
2) COVID-19 can cause cognitive impairment (CI) affecting domains like memory, attention, and executive function. Around 30-80% of patients experience some form of CI.
SARS-CoV-2 is thought to cause CI through both direct neural invasion and neuroinflammatory mechanisms.
SARS-CoV-2 is thought to cause CI through both direct neural invasion and neuroinflammatory mechanisms.

3) Clinical evidence shows impaired performance on cognitive tests like MMSE and MoCA in COVID-19 patients. Neuroimaging shows changes in white matter integrity and hypometabolism in brain regions.
4) Proposed mechanisms for CI include direct viral toxicity, hypoxia, hypercoagulability, immune responses involving microglia/astrocyte activation and peripheral immune cell infiltration, BBB dysfunction, and cytokine dysregulation 
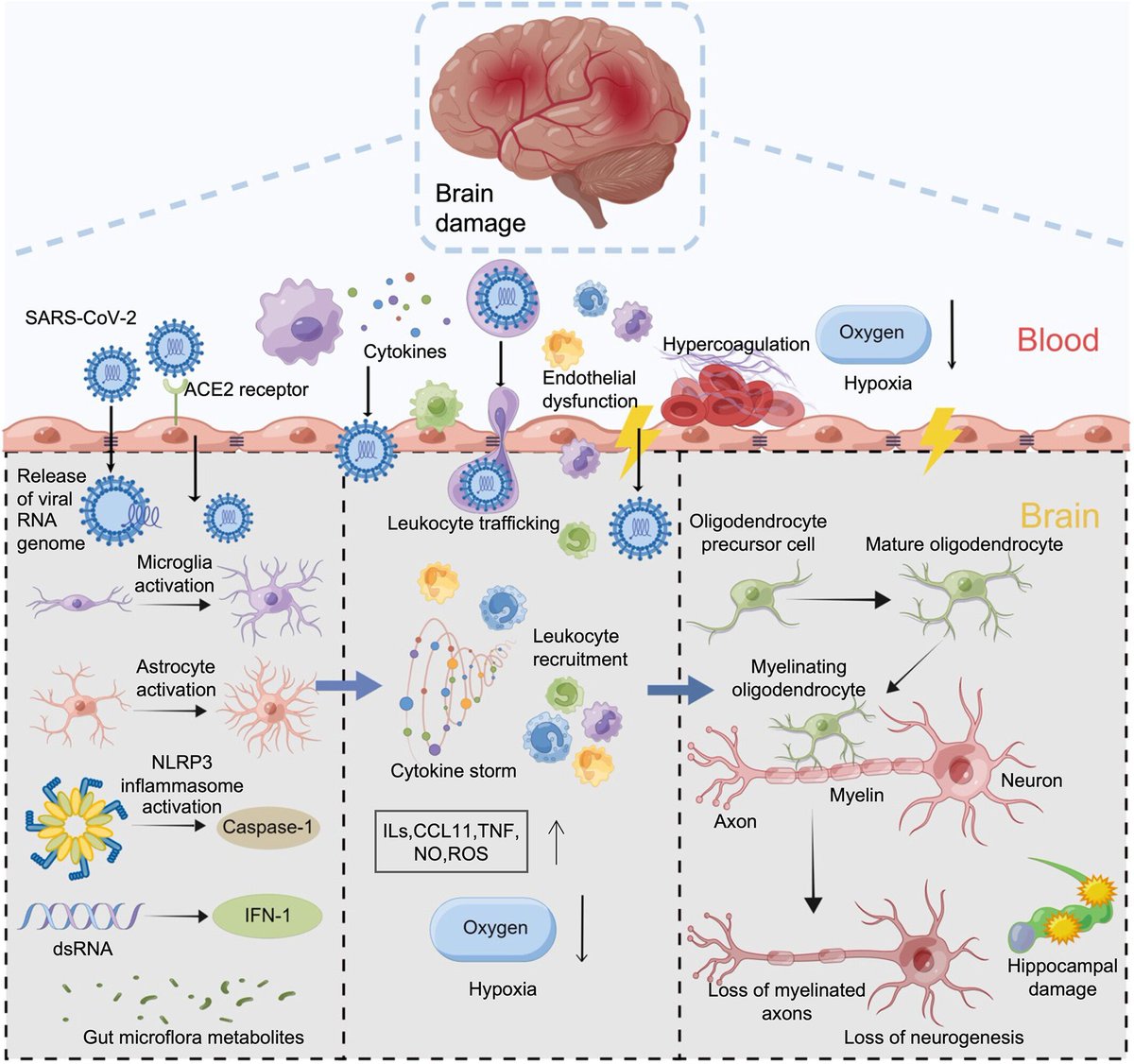
5) Neuroinflammation, mediated by microglia, astrocytes, and proinflammatory cytokines, is a major factor believed to underlie CI. SARS-CoV-2 infection can induce neuroinflammatory responses.
Other contributing factors may include metabolic alterations in infected astrocytes ...
Other contributing factors may include metabolic alterations in infected astrocytes ...
6) impacting neurons, changes to neurotransmitters like serotonin, and interactions with the gut microbiota and bradykinin system.
Future research priorities are elucidating regulatory mechanisms for microglia/astrocytes, investigating immune cell roles, and exploring BBB
Future research priorities are elucidating regulatory mechanisms for microglia/astrocytes, investigating immune cell roles, and exploring BBB
7) ...microbiota and cytokine involvement in CI pathogenesis.
Potential therapeutic strategies aim to reduce neuroinflammation through cytokine antagonists, BBB stabilization, microbiota modulation, and targeting underlying mechanisms like bradykinin.
Thanks for reading 🙏
Potential therapeutic strategies aim to reduce neuroinflammation through cytokine antagonists, BBB stabilization, microbiota modulation, and targeting underlying mechanisms like bradykinin.
Thanks for reading 🙏
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh