𝗜𝗻 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗝𝗨𝗡𝗚𝗟𝗘 𝗼𝗳 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗜𝗠𝗠𝗨𝗡𝗘 𝗦𝗬𝗦𝗧𝗘𝗠 :
𝗡𝘼𝙗𝙨, 𝙄𝙜𝘼, 𝙄𝙜𝙂, 𝙄𝙜𝙈, 𝘼𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙎, 𝘼𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙍𝘽𝘿, 𝘽 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡, 𝘾𝘿4+, 𝘾𝘿8+ 𝙏 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡, ...
(1𝘴𝘵 𝘱𝘢𝘳𝘵 ...)
(𝘤𝘳𝘦𝘥𝘪𝘵 : 𝘗𝘩𝘪𝘭𝘪𝘱𝘱 𝘋𝘦𝘵𝘮𝘦𝘳)
𝗡𝘼𝙗𝙨, 𝙄𝙜𝘼, 𝙄𝙜𝙂, 𝙄𝙜𝙈, 𝘼𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙎, 𝘼𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙍𝘽𝘿, 𝘽 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡, 𝘾𝘿4+, 𝘾𝘿8+ 𝙏 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡, ...
(1𝘴𝘵 𝘱𝘢𝘳𝘵 ...)
(𝘤𝘳𝘦𝘥𝘪𝘵 : 𝘗𝘩𝘪𝘭𝘪𝘱𝘱 𝘋𝘦𝘵𝘮𝘦𝘳)

2) When SARS-COV-2 enters the body, many components of the immune system, recognize it as foreign and mount a response to eliminate it. 

3) For laymen, it is not always easy to "navigate" among all the abbreviations used. In this thread, we will try to offer a quick overview of some of the key elements of the immune system and their differences. 

4) 𝘿𝙞𝙛𝙛𝙚𝙧𝙚𝙣𝙘𝙚𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙩𝙞𝙗𝙤𝙙𝙞𝙚𝙨/𝙞𝙢𝙢𝙪𝙣𝙤𝙜𝙡𝙤𝙗𝙪𝙡𝙞𝙣𝙨, 𝙣𝘼𝙗𝙨 /𝙄𝙜𝘼, 𝙄𝙜𝙂, 𝙄𝙜𝙈
Antibodies are proteins that are part of the immune system's response to antigens. These Y-shaped molecules are produced by specialized white blood cells called B cell
Antibodies are proteins that are part of the immune system's response to antigens. These Y-shaped molecules are produced by specialized white blood cells called B cell

5) NAbs stands for neutralizing antibodies. NAbs are particularly important because they can block the ability of the pathogen to infect host cells or cause harm. They do this by preventing the pathogen from binding to its target receptors on host cells, 

6) Immunoglobulins refer to a broader group of proteins that include antibodies, as well as other related proteins, such as cytokines and chemokines. They are classified into different classes and subclasses based on their structure and function, such as IgA, IgG, IgM ... 

7) 𝘿𝙞𝙛𝙛𝙚𝙧𝙚𝙣𝙘𝙚 𝙖𝙣𝙩𝙞𝙗𝙤𝙙𝙞𝙚𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙎, 𝙖𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙉, 𝙖𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙍𝘽𝘿
These terms refer to different types of antibodies that target specific components, spike protein (S), nucleocapsid protein (N), and receptor-binding domain (RBD).
These terms refer to different types of antibodies that target specific components, spike protein (S), nucleocapsid protein (N), and receptor-binding domain (RBD).

8) To put it simply 😂, we can therefore have, anti-S NAbs or anti-N NAbs but also anti-S IgG or anti-RBD IgM.
2𝘯𝘥 𝘱𝘢𝘳𝘵 𝘷𝘦𝘳𝘺 𝘴𝘰𝘰𝘯 ... 🤗
2𝘯𝘥 𝘱𝘢𝘳𝘵 𝘷𝘦𝘳𝘺 𝘴𝘰𝘰𝘯 ... 🤗

𝗜𝗻 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗝𝗨𝗡𝗚𝗟𝗘 𝗼𝗳 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗜𝗠𝗠𝗨𝗡𝗘 𝗦𝗬𝗦𝗧𝗘𝗠 :
𝗡𝘼𝙗𝙨, 𝙄𝙜𝘼, 𝙄𝙜𝙂, 𝙄𝙜𝙈, 𝘼𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙎, 𝘼𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙍𝘽𝘿, 𝘽 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡, 𝘾𝘿4+, 𝘾𝘿8+ 𝙏 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡, ...
(2𝘯𝘥 𝘱𝘢𝘳𝘵)
(𝘤𝘳𝘦𝘥𝘪𝘵 : 𝘗𝘩𝘪𝘭𝘪𝘱𝘱 𝘋𝘦𝘵𝘮𝘦𝘳)
𝗡𝘼𝙗𝙨, 𝙄𝙜𝘼, 𝙄𝙜𝙂, 𝙄𝙜𝙈, 𝘼𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙎, 𝘼𝙣𝙩𝙞-𝙍𝘽𝘿, 𝘽 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡, 𝘾𝘿4+, 𝘾𝘿8+ 𝙏 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡, ...
(2𝘯𝘥 𝘱𝘢𝘳𝘵)
(𝘤𝘳𝘦𝘥𝘪𝘵 : 𝘗𝘩𝘪𝘭𝘪𝘱𝘱 𝘋𝘦𝘵𝘮𝘦𝘳)
10) 𝘿𝙞𝙛𝙛𝙚𝙧𝙚𝙣𝙘𝙚 𝘽 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙏 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡
B cells are primarily involved in producing antibodies to recognize and neutralize antigens, while T cells have diverse functions, including coordinating immune responses, killing infected cells, and regulating immune reactions.
B cells are primarily involved in producing antibodies to recognize and neutralize antigens, while T cells have diverse functions, including coordinating immune responses, killing infected cells, and regulating immune reactions.

11) There are several types of T cells. Helper T cells play a crucial role in coordinating the immune response by activating other immune cells, such as B cells and cytotoxic T cells. Cytotoxic T cells directly attack and kill cells that have been infected with viruses.
12) Regulatory T cells help to regulate and suppress immune responses to prevent excessive inflammation and autoimmune reactions.
Among these T cells, two of them, play a key role against SARS-COV-2, CD4 and CD8 T cell
Among these T cells, two of them, play a key role against SARS-COV-2, CD4 and CD8 T cell

13) 𝘿𝙞𝙛𝙛𝙚𝙧𝙚𝙣𝙘𝙚 𝘾𝘿4 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝘾𝘿8 𝙏 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡
CD4 T cells, also known as helper T cells have a central role in coordinating immune responses. CD4 T cells recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells. Once activated..
CD4 T cells, also known as helper T cells have a central role in coordinating immune responses. CD4 T cells recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells. Once activated..

14) ...CD4 T cells release chemical signals called cytokines that help to activate other immune cells, such as B cells and cytotoxic T cells.
CD8 T cells, also known as cytotoxic T cells are primarily responsible for recognizing and killing infected cells or other abnormal cells.
CD8 T cells, also known as cytotoxic T cells are primarily responsible for recognizing and killing infected cells or other abnormal cells.

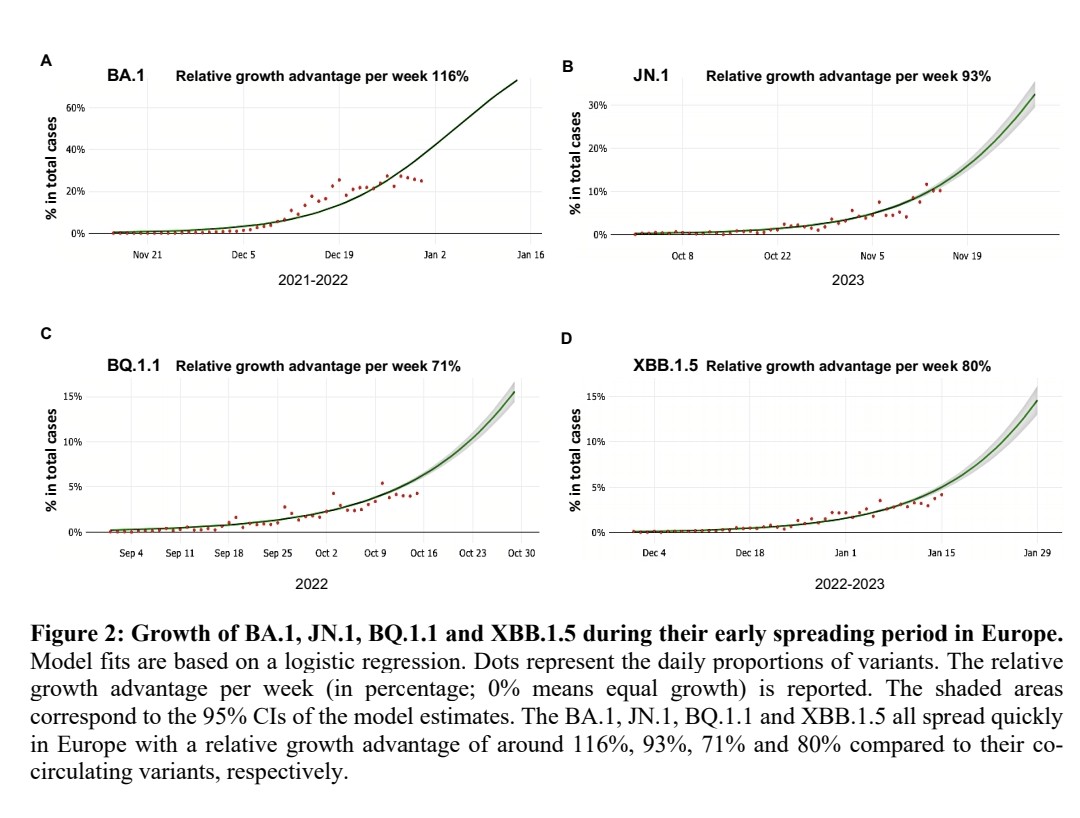
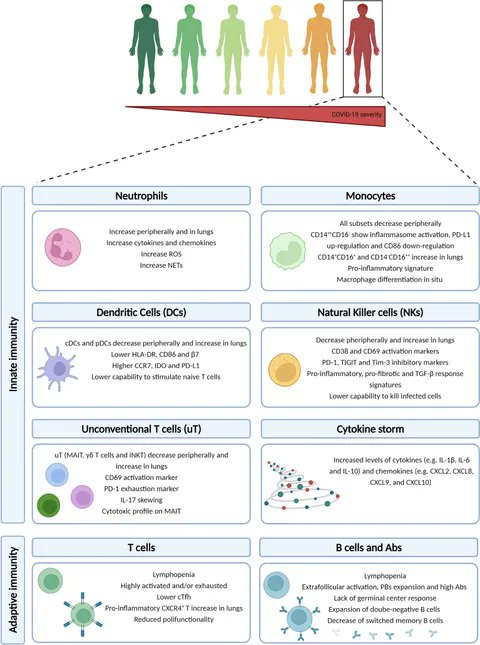
15) We would like to end this thread, with a very good study which summarizes the action of the immune system including others immune cells.
Thanks for reading 🙏
"Hallmarks of Severe COVID-19 Pathogenesis: A Pas de Deux Between Viral and Host Factors"
frontiersin.org/journals/immun…

Thanks for reading 🙏
"Hallmarks of Severe COVID-19 Pathogenesis: A Pas de Deux Between Viral and Host Factors"
frontiersin.org/journals/immun…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh