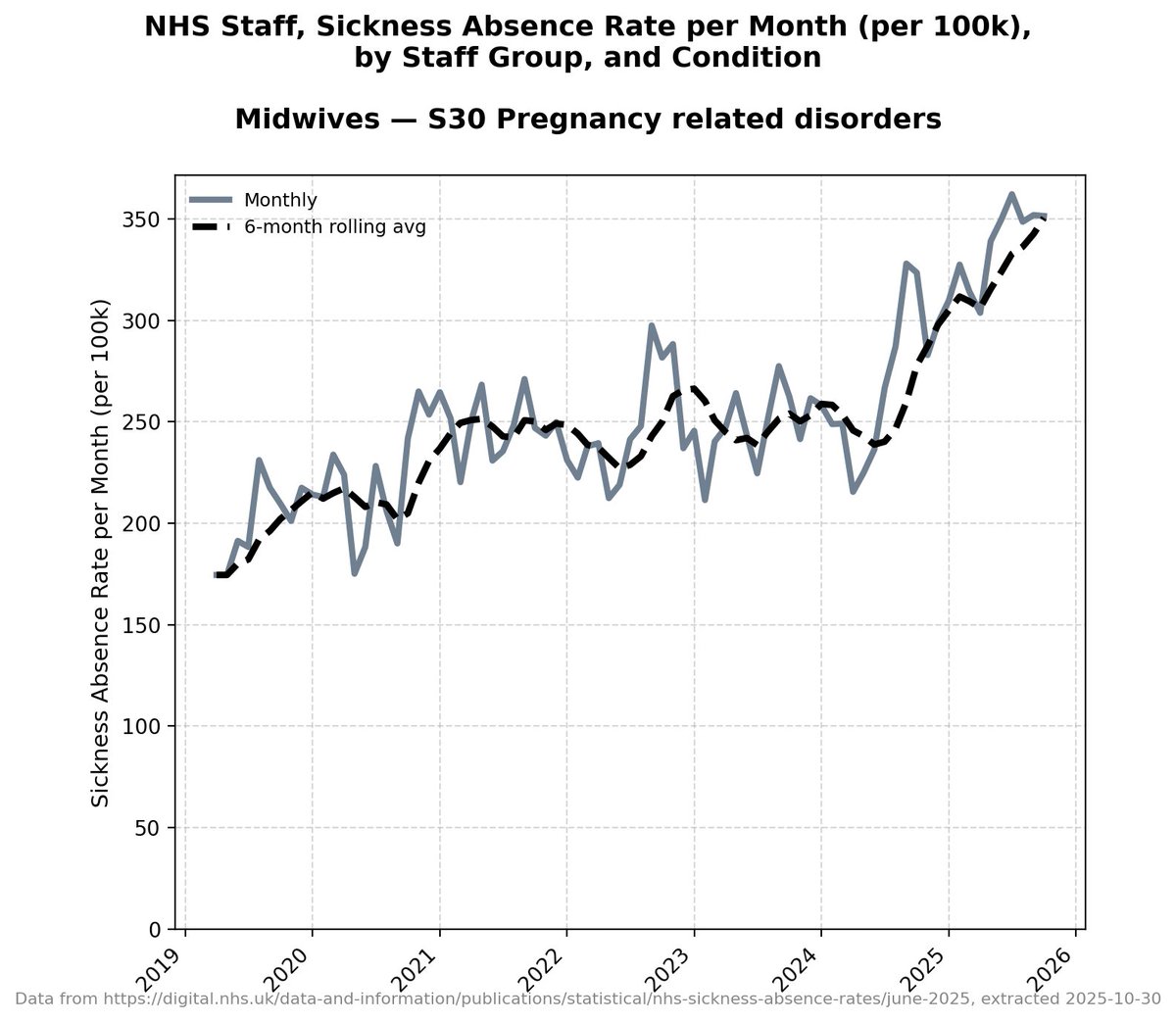
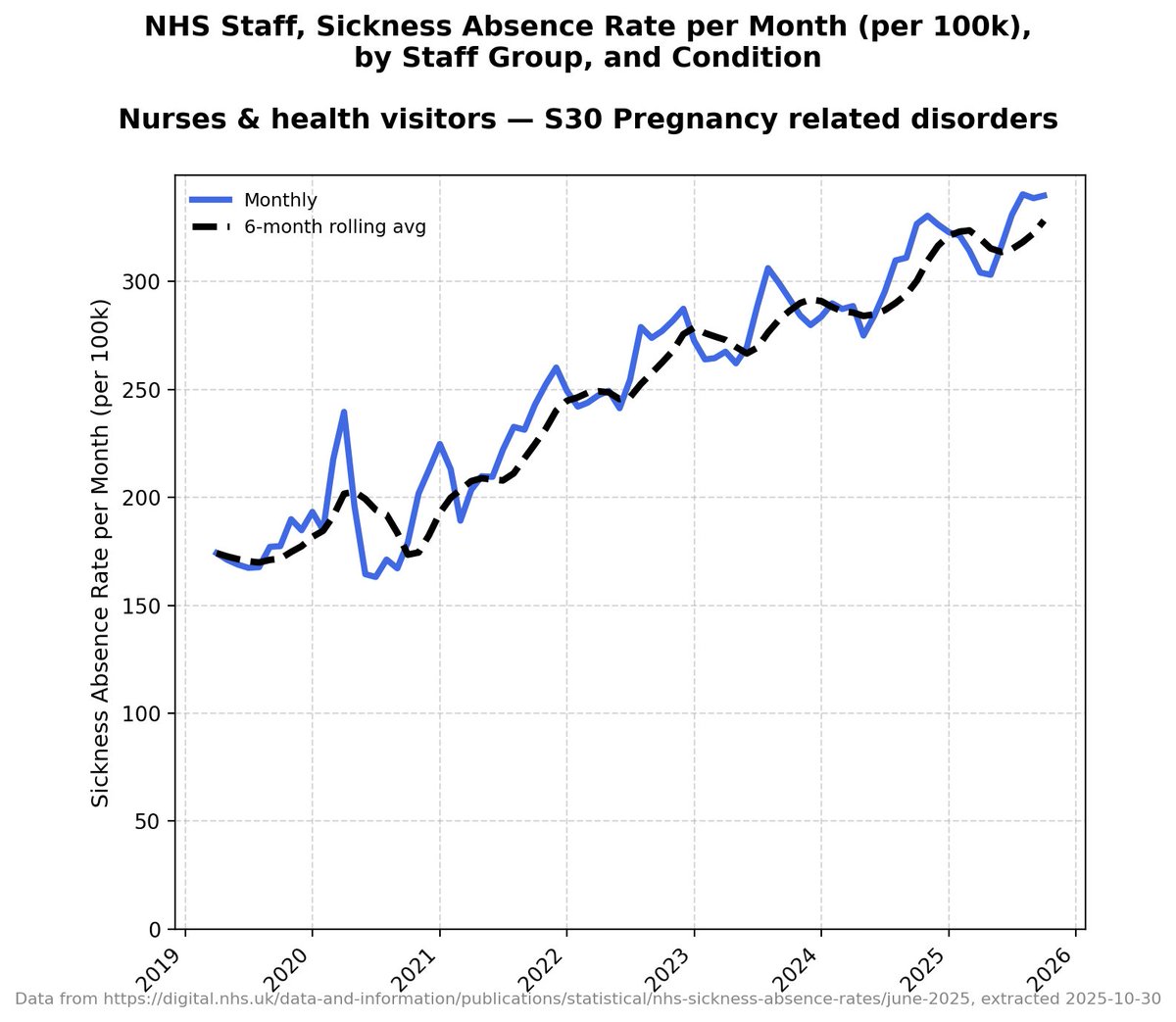
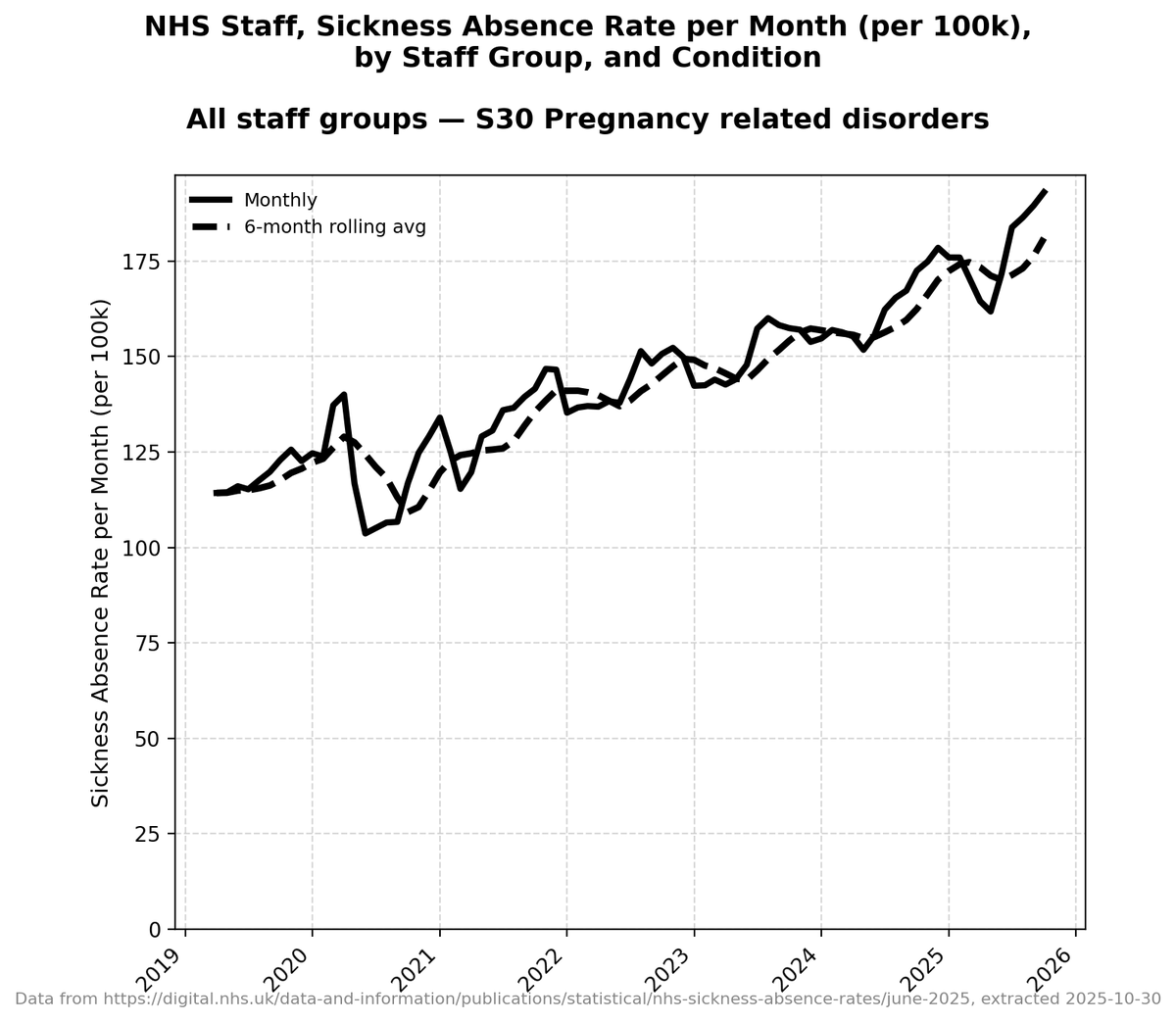
Wow.
Let's work through *all* the slides Yale School of Public Health shared...
🌎"What we know (and don't) know about Covid's effect on the immune system"
🧵

Let's work through *all* the slides Yale School of Public Health shared...
🌎"What we know (and don't) know about Covid's effect on the immune system"
🧵
https://twitter.com/fitterhappierAJ/status/1782126201387000152

(just the immune system, though, nothing here about cardio or lung or liver or nerve, or other stuff, OK?)
LASTING IMPACT.
"Growing research shows infection with SARS-CoV-2 can create lasting differences in some people's immune systems."
"Growing research shows infection with SARS-CoV-2 can create lasting differences in some people's immune systems."

THIS LOOKS LIKE (1)
"Altered immune system cells
Severe cases of COVID-19 can change the parent stem cells that generate immune cells. These altered stem cells create cells that are more inflammatory."
"Altered immune system cells
Severe cases of COVID-19 can change the parent stem cells that generate immune cells. These altered stem cells create cells that are more inflammatory."

THIS LOOKS LIKE (2)
"Viral reservoirs and fragments
Proteins and fragments that have been found in people with Long COVID can set off a continuing immune response and amplify inflammation."
"Viral reservoirs and fragments
Proteins and fragments that have been found in people with Long COVID can set off a continuing immune response and amplify inflammation."

THIS LOOKS LIKE (3)
"Immune dysregulation and chronic inflammation
Dysregulation = when some immune cells are working hard, and others are exhausted. How long it can last is unknown."
"Immune dysregulation and chronic inflammation
Dysregulation = when some immune cells are working hard, and others are exhausted. How long it can last is unknown."

THIS LOOKS LIKE (4)
"Triggered autoimmune conditions, blood clots, and latent viruses
COVID-19 infections can trigger autoantibodies that lead to autoimmune disorders."
"Triggered autoimmune conditions, blood clots, and latent viruses
COVID-19 infections can trigger autoantibodies that lead to autoimmune disorders."

"5-20% of people develop lingering symptoms or new health conditions after infection, called Long COVID.
As of the CDC's latest count in March 2024, 30% of all American adults who've had COVID have experienced Long COVID."
👀🚨
As of the CDC's latest count in March 2024, 30% of all American adults who've had COVID have experienced Long COVID."
👀🚨

"The more COVID-19 vaccine doses you get, the lower the risk of Long COVID. The more reinfections you have, the higher the risk." 

"172% INCREASED RISK
The risk of developing an autoimmune disease rose by up to 172% after infection, per a study following people from 2020 to 2022.
Up-to-date COVID-19 vaccination can reduce the likelihood of developing an autoimmune condition after infection."
The risk of developing an autoimmune disease rose by up to 172% after infection, per a study following people from 2020 to 2022.
Up-to-date COVID-19 vaccination can reduce the likelihood of developing an autoimmune condition after infection."

"OTHER ILLNESSES
SARS-CoV-2 can also activate other viruses that have been lying dormant, like Epstein-Barr and herpes viruses.
Studies have found kids with prior COVID-19 infections had a greater risk of RSV infections."
SARS-CoV-2 can also activate other viruses that have been lying dormant, like Epstein-Barr and herpes viruses.
Studies have found kids with prior COVID-19 infections had a greater risk of RSV infections."

Notice the little bit at the bottom?
"Always feel run-down? Practice harm reduction and learn how you can protect yourself from more damage."
Good idea.
"Always feel run-down? Practice harm reduction and learn how you can protect yourself from more damage."
Good idea.

"49% OF COVID INFECTIONS ARE ASYMPTOMATIC,
which means you may not know if you are actually sick. This is why it's important to take a multilayered approach (one or more of the following) to protect yourselves and others:"
which means you may not know if you are actually sick. This is why it's important to take a multilayered approach (one or more of the following) to protect yourselves and others:"

"N95 and KN95 masks
Up-to-date vaccinations
HEPA air filtration
Rapid tests before gathering
Good ventilation (carbon dioxide <800 parts per million)
Attention to wastewater levels of COVID-19"
Up-to-date vaccinations
HEPA air filtration
Rapid tests before gathering
Good ventilation (carbon dioxide <800 parts per million)
Attention to wastewater levels of COVID-19"

WHAT WE DON'T KNOW (1)
"The long-term impact on other illnesses
Outside of the influence on RSV and reactivated viruses, it's TBD whether altered immune systems predispose people to conditions like other infectious diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, or cancer."
"The long-term impact on other illnesses
Outside of the influence on RSV and reactivated viruses, it's TBD whether altered immune systems predispose people to conditions like other infectious diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, or cancer."

WHAT WE DON'T KNOW (2)
"Why some people's conditions persist
We don't yet know why some people recover and their immune system restores, and why others continue to decline."
"Why some people's conditions persist
We don't yet know why some people recover and their immune system restores, and why others continue to decline."

WHAT WE DON'T KNOW (3)
"What diagnostics and therapies can help restore the immune system
More identifiers like viral load tests and biomarker tests, plus treatments for Long COVID, are needed to help the millions living with the condition."
"What diagnostics and therapies can help restore the immune system
More identifiers like viral load tests and biomarker tests, plus treatments for Long COVID, are needed to help the millions living with the condition."

Wow.
And you might think that was an extensive deep dive into what Covid does to you...
BUT IT WAS ONLY ABOUT YOUR IMMUNE SYSTEM.
Covid does that to every bodily system.
That thread was only a glimpse of what we know about what Covid does.
Don't catch it.
Don't spread it.
Don't spread it.
Whole fb thread here.
https://twitter.com/BradSiroky/status/1782142309750001892?t=CRCoCB841TI78B_42Moxtw&s=19
But, of course, your immune system can then *also* affect every other bodily system, so the cycle continues.
https://twitter.com/1goodtern/status/1782302140091756891?t=K5fn6Z5YY_GU6eZCYM-E9g&s=19
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh