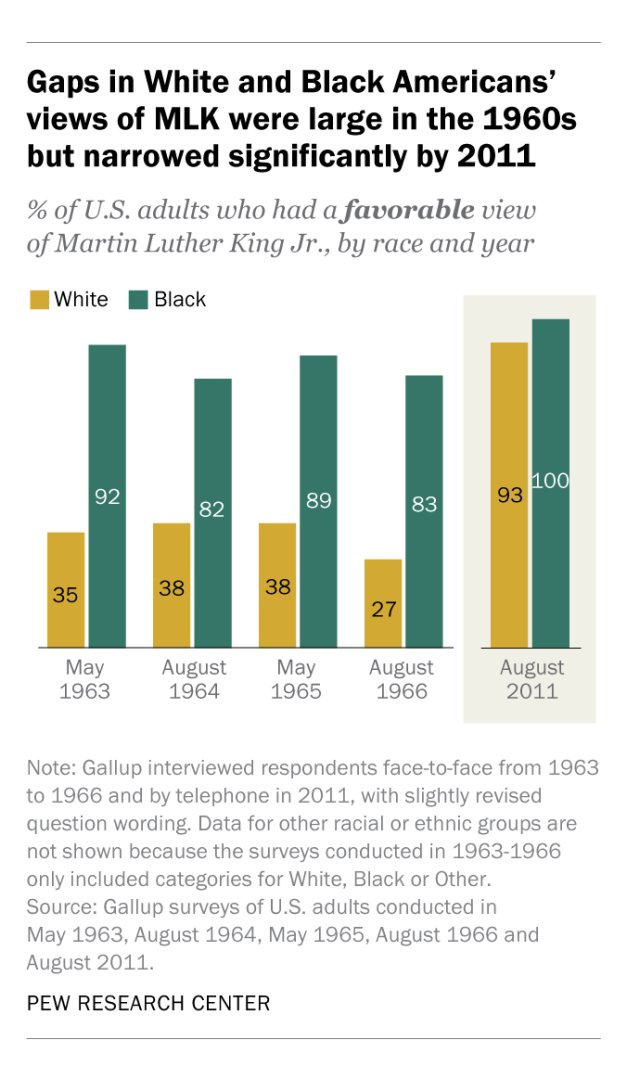
Does diversity make teams work better?
Apparently not!
A new, comprehensive preregistered meta-analysis found that, whether the diversity was demographic, cognitive, or occupational, its relationship with performance was near-zero.
Apparently not!
A new, comprehensive preregistered meta-analysis found that, whether the diversity was demographic, cognitive, or occupational, its relationship with performance was near-zero.
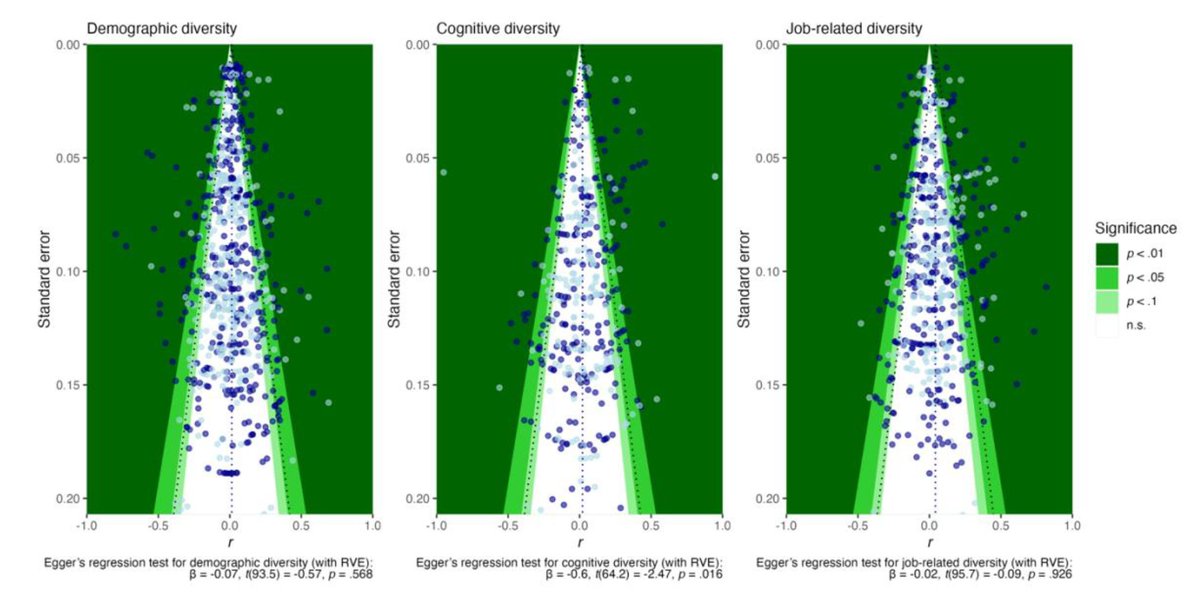
These authors were very thorough
Just take a look at the meta-analytic estimates. These are in terms of correlations, and they are corrected for attenuation
These effect sizes are significant due to the large number of studies, but they are very low, even after blowing them up
Just take a look at the meta-analytic estimates. These are in terms of correlations, and they are corrected for attenuation
These effect sizes are significant due to the large number of studies, but they are very low, even after blowing them up

You may ask yourself: are there hidden moderators?
The answer looks to be 'probably not.' Team longevity, industry sector, performance measures, power distance, year or country of study, task complexity, team interdependence, etc.
None of it really mattered.
Here's longevity:
The answer looks to be 'probably not.' Team longevity, industry sector, performance measures, power distance, year or country of study, task complexity, team interdependence, etc.
None of it really mattered.
Here's longevity:

But let's put this into practical terms.
Using these disattenuated effects, if you selected from two groups you expected to have comparable performance otherwise, but one was more diverse, you'd make the 'correct' (higher-performing) decision in 51% of cases (vs. 50%).
Using these disattenuated effects, if you selected from two groups you expected to have comparable performance otherwise, but one was more diverse, you'd make the 'correct' (higher-performing) decision in 51% of cases (vs. 50%).
That assumes there really hasn't been any bias in what gets published. If there has been, you might want to adjust your estimate downwards towards zero, or upwards if you think the literature was rigged the other way.
The paper paints an unsupportive picture of the idea that diversity on its own makes teams more performant.
I recommend giving it a read.
I recommend giving it a read.
Link: osf.io/preprints/psya…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh