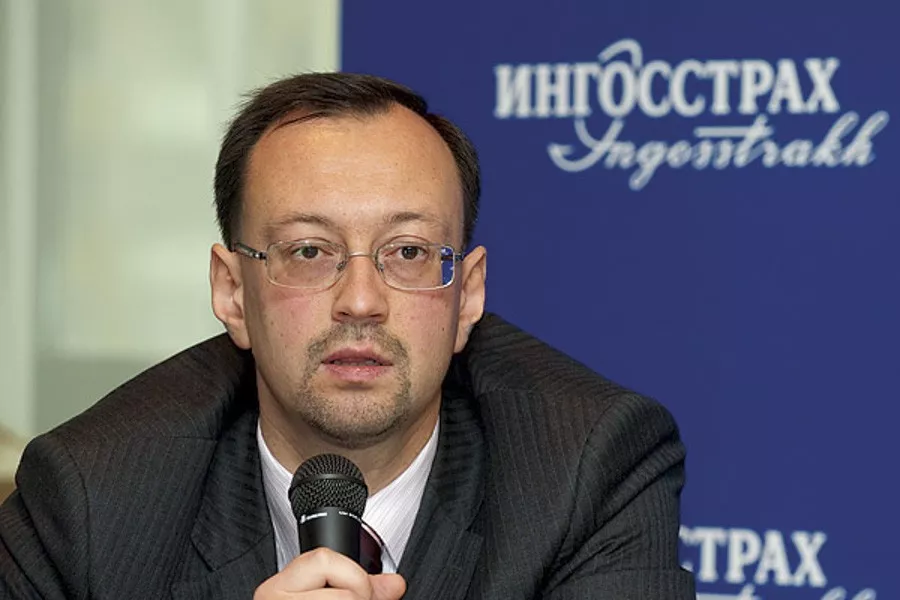
There is now a lot of discussion about the arrest of Deputy Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation Timur Ivanov on charges of bribery. This is the second person in the ministry after Shoigu. No matter how funny it may sound for Russia, yes. Precisely for bribes. But
1/12
1/12
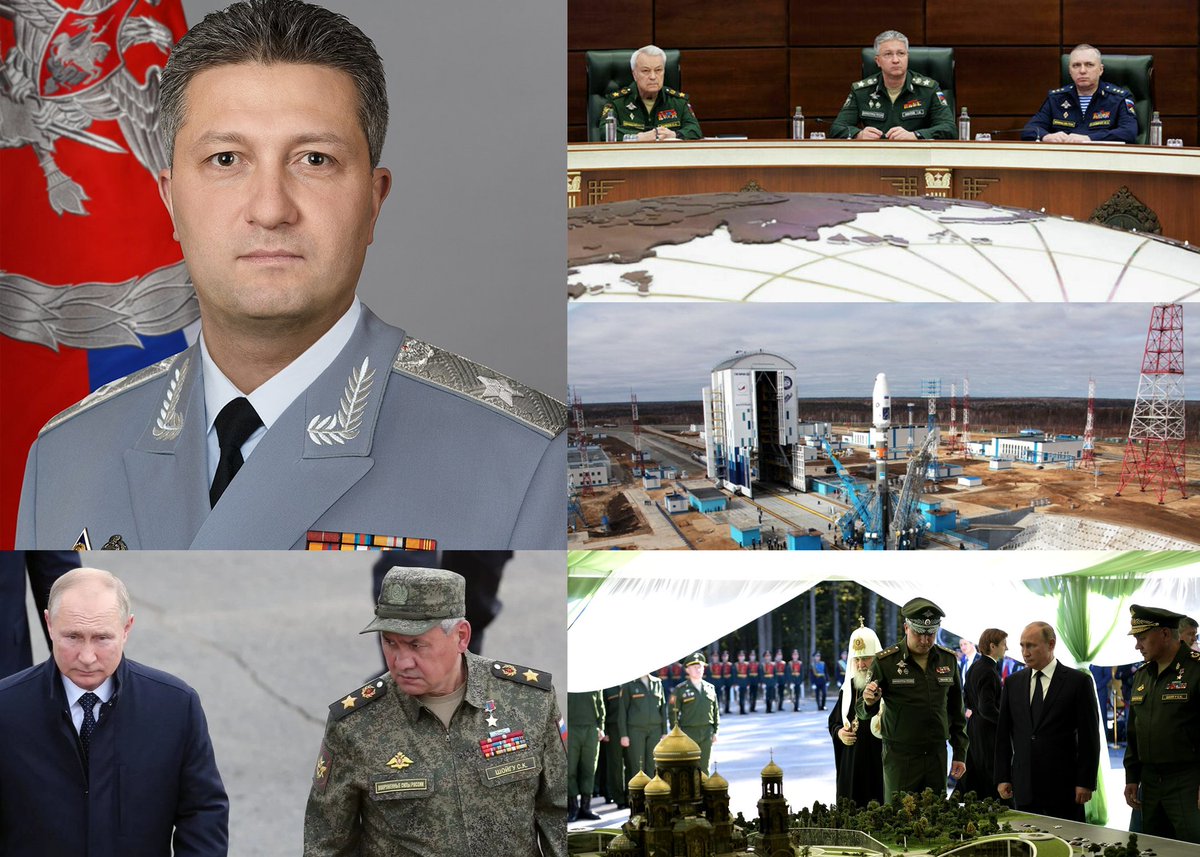

the detention of Timur Ivanov is a strong blow to Shoigu. Apparently, Shoigu himself did not know about the upcoming arrest, because the day before he held a meeting where Ivanov also took part. It was Shoigu who brought Ivanov to the ministry and covered for him more than
2/12
2/12

once in previous cases. Ivanov’s arrest is in no way a fight against corruption - in Russia everyone steals as much as they can. In the Russian system, each official has a separate folder in the FSB, and when a signal comes from above that a person needs to be processed,
3/12
3/12
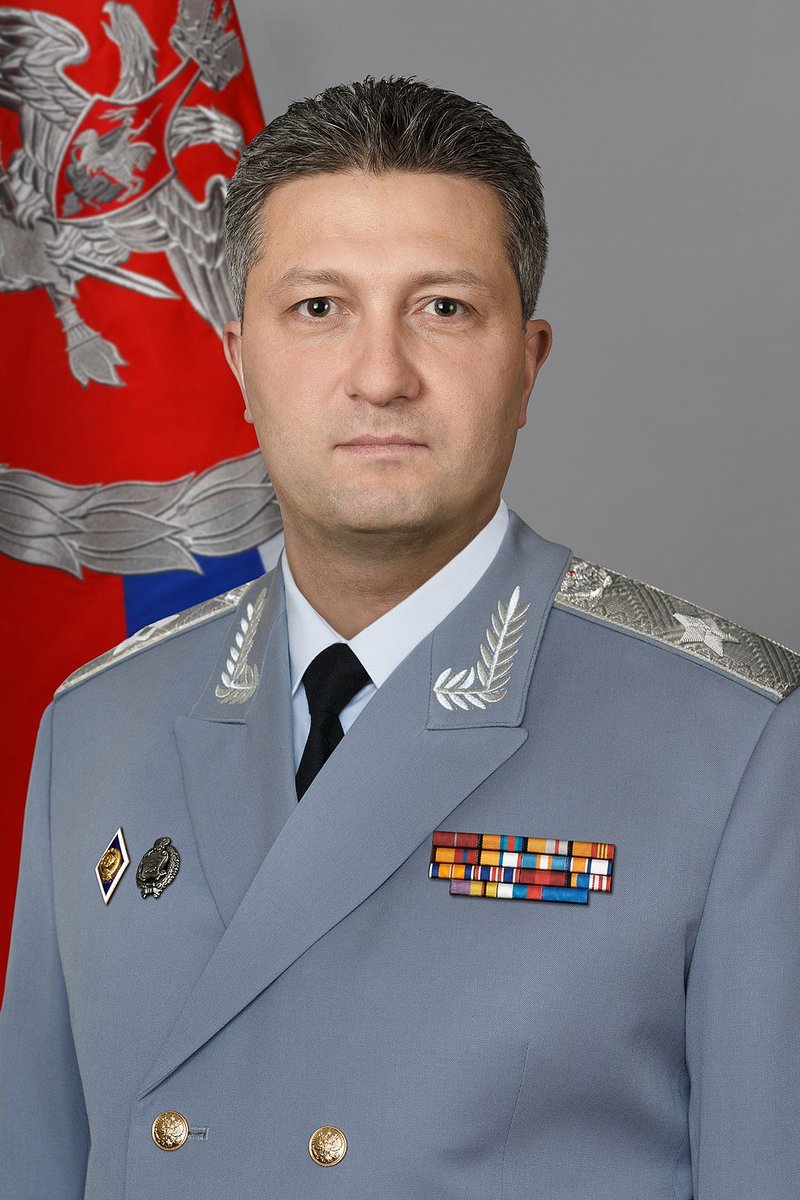

they take it off the shelf and put it into action. A person working for the Russian government, even if he has palaces, yachts and expensive cars, actually does not possess any of this. It does not belong to him and can be taken away at any moment, and he is sent to prison.
4/12
4/12

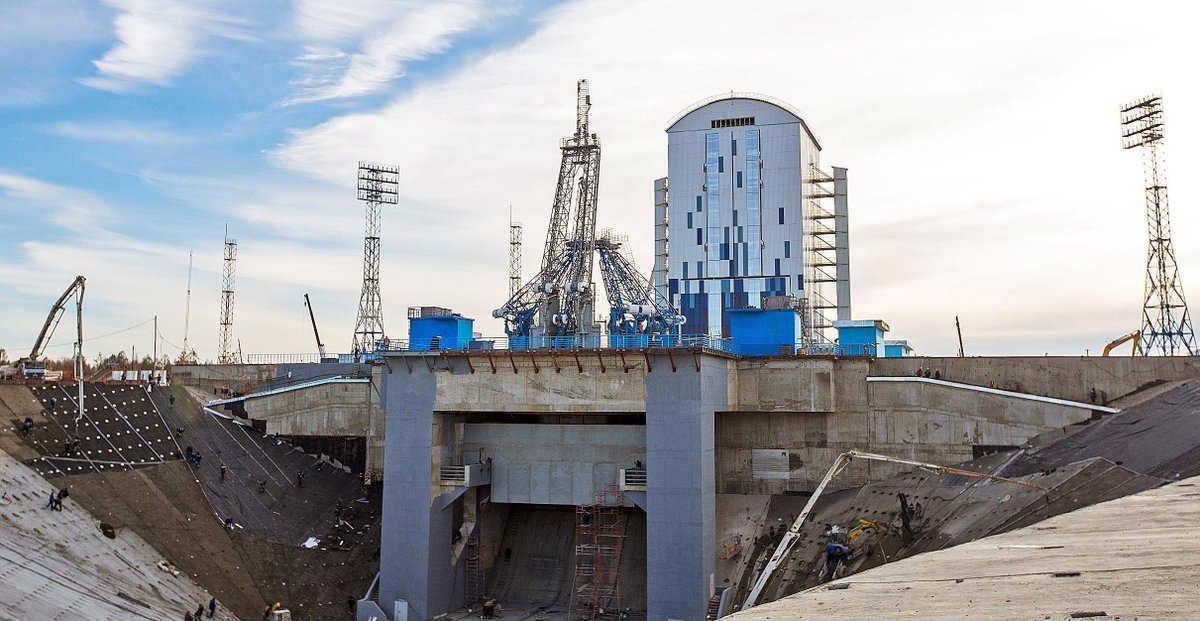
The reasons why he was removed from his post are not yet clear, but most likely it will be known later. Artur Ivanov was not a military man, although he wore a uniform. He was involved in the construction of military and other facilities. For example, he was responsible for
5/12
5/12

the construction of the Vostochny cosmodrome, where record amounts were stolen. He was responsible for the construction of the Patriot Park and construction in Mariupol, destroyed by the Russians. He held the civil position of Acting State Councilor of the Russian
6/12
6/12

Federation, 1st class. In the army this would correspond to a general's post. That’s why there were all these uniforms with medals. His arrest actually indicates that a serious intra-clan struggle has begun in Putin’s system. Ivanov’s place is very profitable, because during
7/12
7/12

construction there are some of the largest kickbacks. Now the struggle for this place will begin and all the contenders will now rush to compromise and snitch on each other in the fight for this place. Putin created a system, like any dictator, where he pits everyone against
8/12
8/12

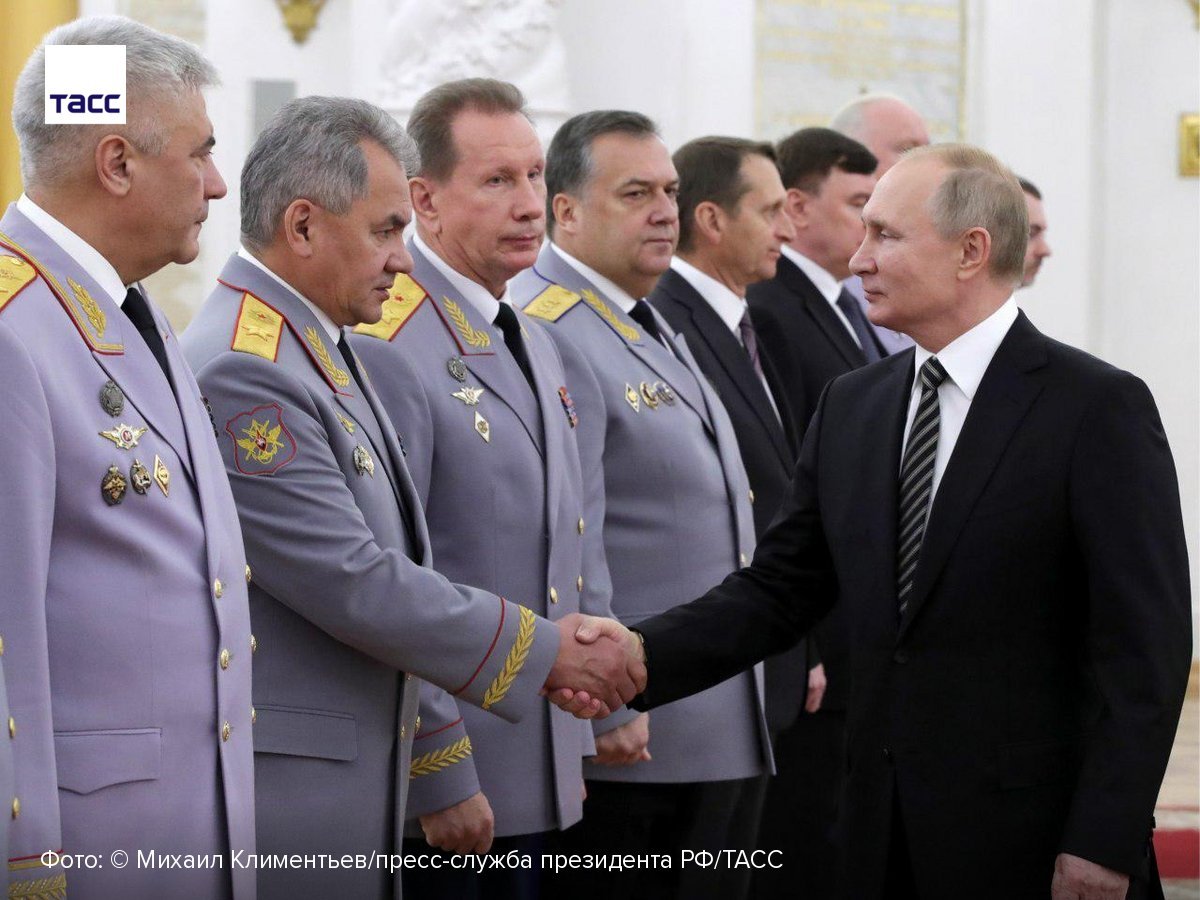
each other and forces one to fight with another. His task is to ensure that no one can unite so much as to become a threat to his own power. Whether clouds are gathering over Shoigu himself is also difficult to say now. After Prigozhin’s rebellion, Putin does not risk
9/12
9/12

introducing new players, relying on old, proven and loyal people, albeit absolutely useless. In this system, such people are actually allowed almost everything. Steal, send soldiers in batches to their deaths, but the main thing is to remain loyal. But failures at the
10/12
10/12

front may force Putin to make some personnel decisions. So it’s now difficult to vouch for Shoigu’s safety. But no matter what happens there, it’s all for the benefit of Ukraine, because the Russian system is devouring itself in this way, begins to collapse from the inside
11/12
11/12

and weakens, and with it, naturally, Putin’s power. The list of Russia's problems is only growing every day. Kadyrov is also preparing to kick the bucket, and if the struggle for power begins in Chechnya, it will explode significantly.
12/12
12/12

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh