𝗟𝗼𝗻𝗴𝗶𝘁𝘂𝗱𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗙𝗲𝗰𝗮𝗹 𝗦𝗵𝗲𝗱𝗱𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗼𝗳 𝗦𝗔𝗥𝗦-𝗖𝗼𝗩-2, 𝗣𝗲𝗽𝗽𝗲𝗿 𝗠𝗶𝗹𝗱 𝗠𝗼𝘁𝘁𝗹𝗲 𝗩𝗶𝗿𝘂𝘀, 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗛𝘂𝗺𝗮𝗻 𝗠𝗶𝘁𝗼𝗰𝗵𝗼𝗻𝗱𝗿𝗶𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗡𝗔 𝗶𝗻 𝗖𝗢𝗩𝗜𝗗-19 𝗣𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…

medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
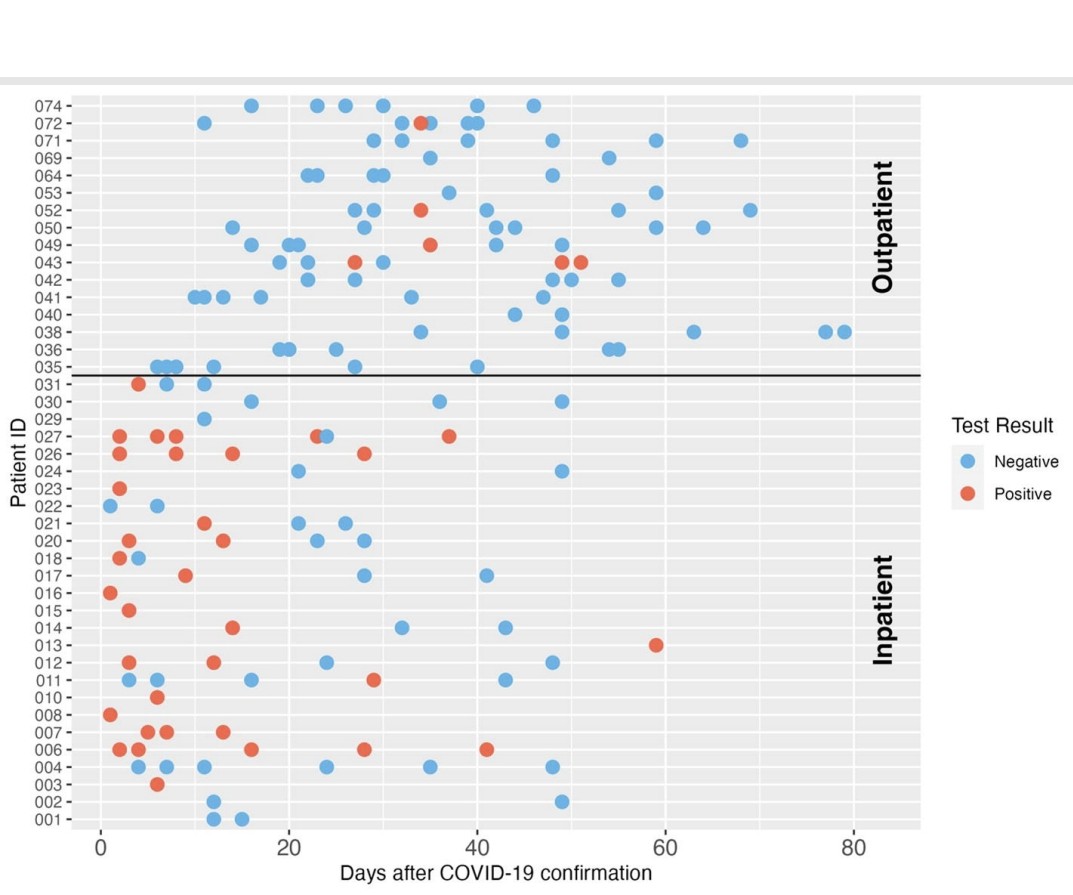
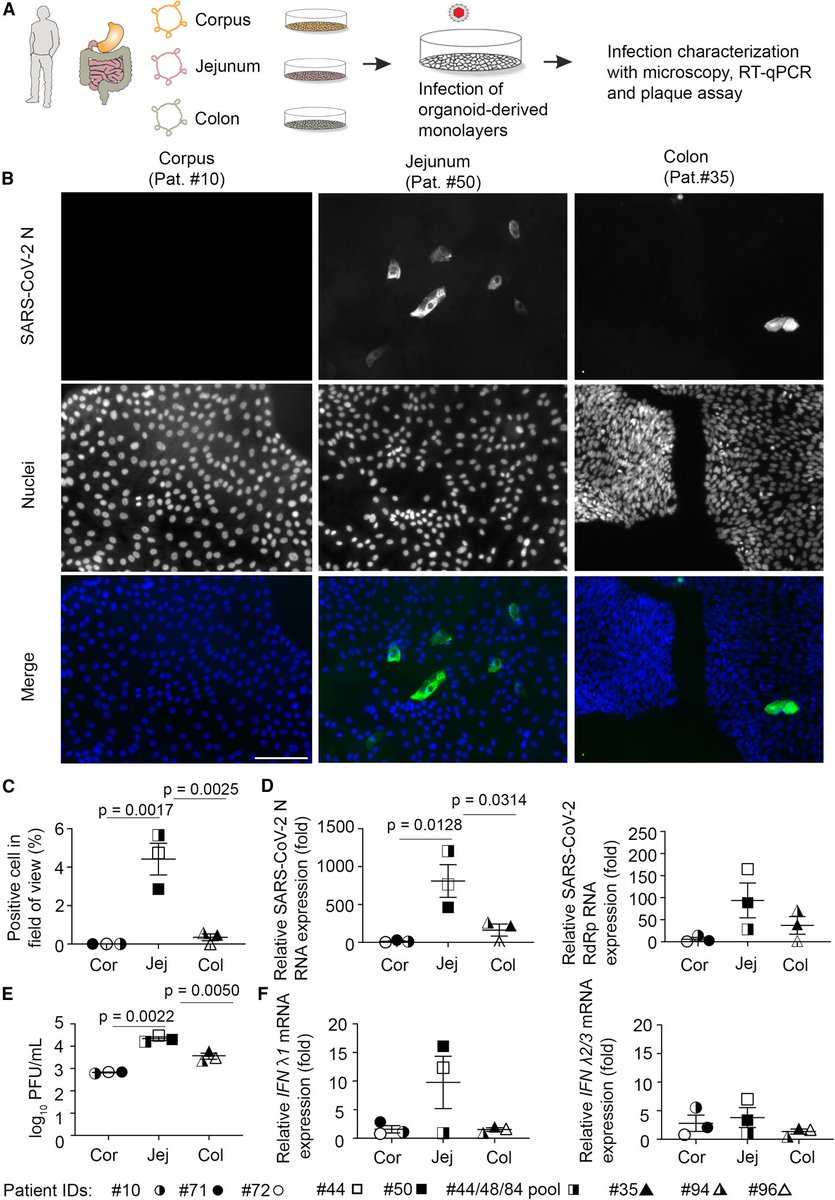
2)The study analyzed longitudinal fecal samples collected from 42 COVID-19 patients over 42 days to examine shedding dynamics of SARS-CoV-2, pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV), and human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). 

3) 73.1% of inpatients shed SARS-CoV-2 in stool, most within 3 weeks of diagnosis but some up to 60 days. Only 7.1% of outpatients tested positive, all past 3 weeks.
Median SARS-CoV-2 concentration in positive inpatient samples was higher than outpatients.
Median SARS-CoV-2 concentration in positive inpatient samples was higher than outpatients.
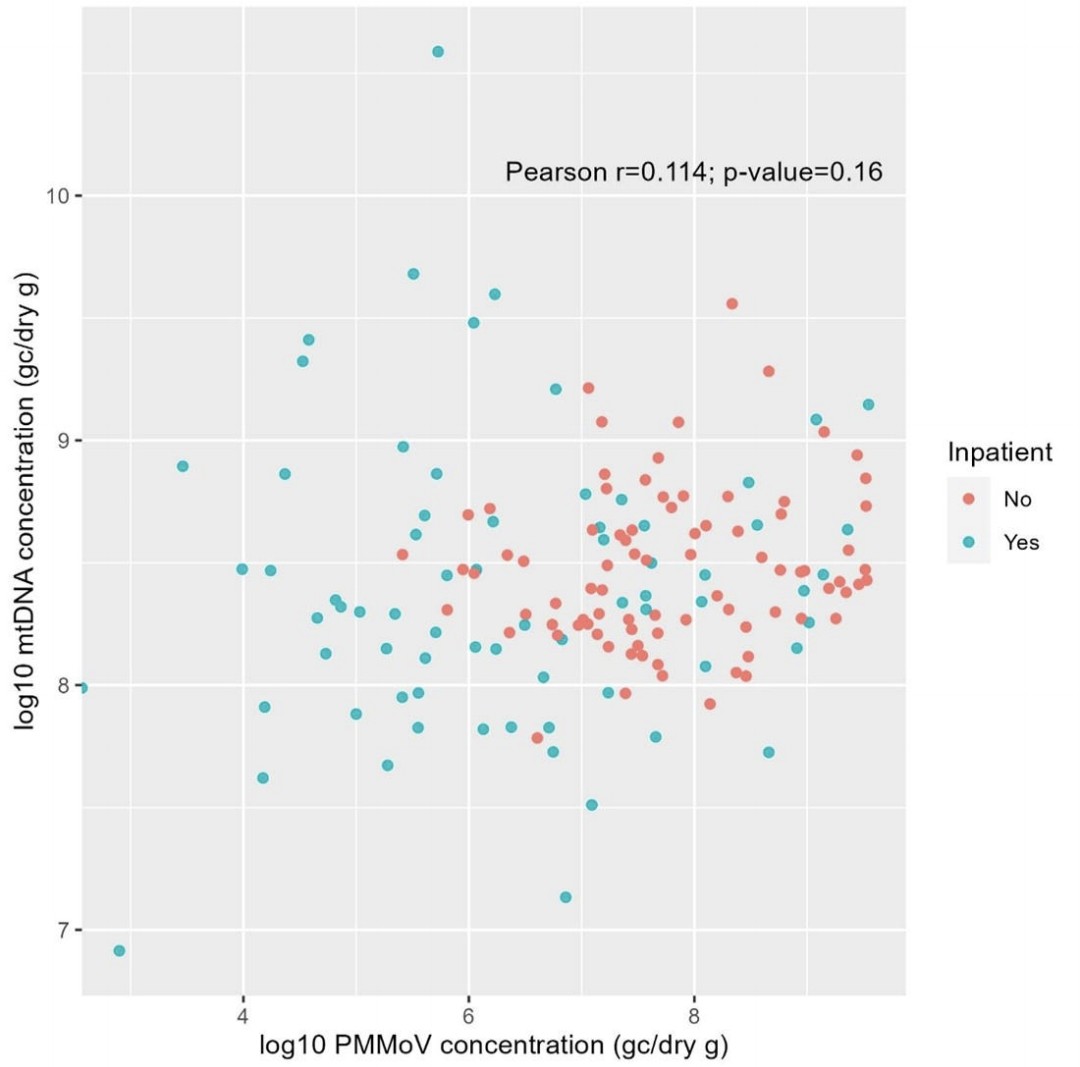
4) Detection rates and concentrations differed between inpatients and outpatients. PMMoV was detected in 99.4% of samples and mtDNA in 100%, with median concentrations of 1.73x107 and 2.49x108 genome copies/gram respectively. PMMoV levels varied more within/between individuals. 
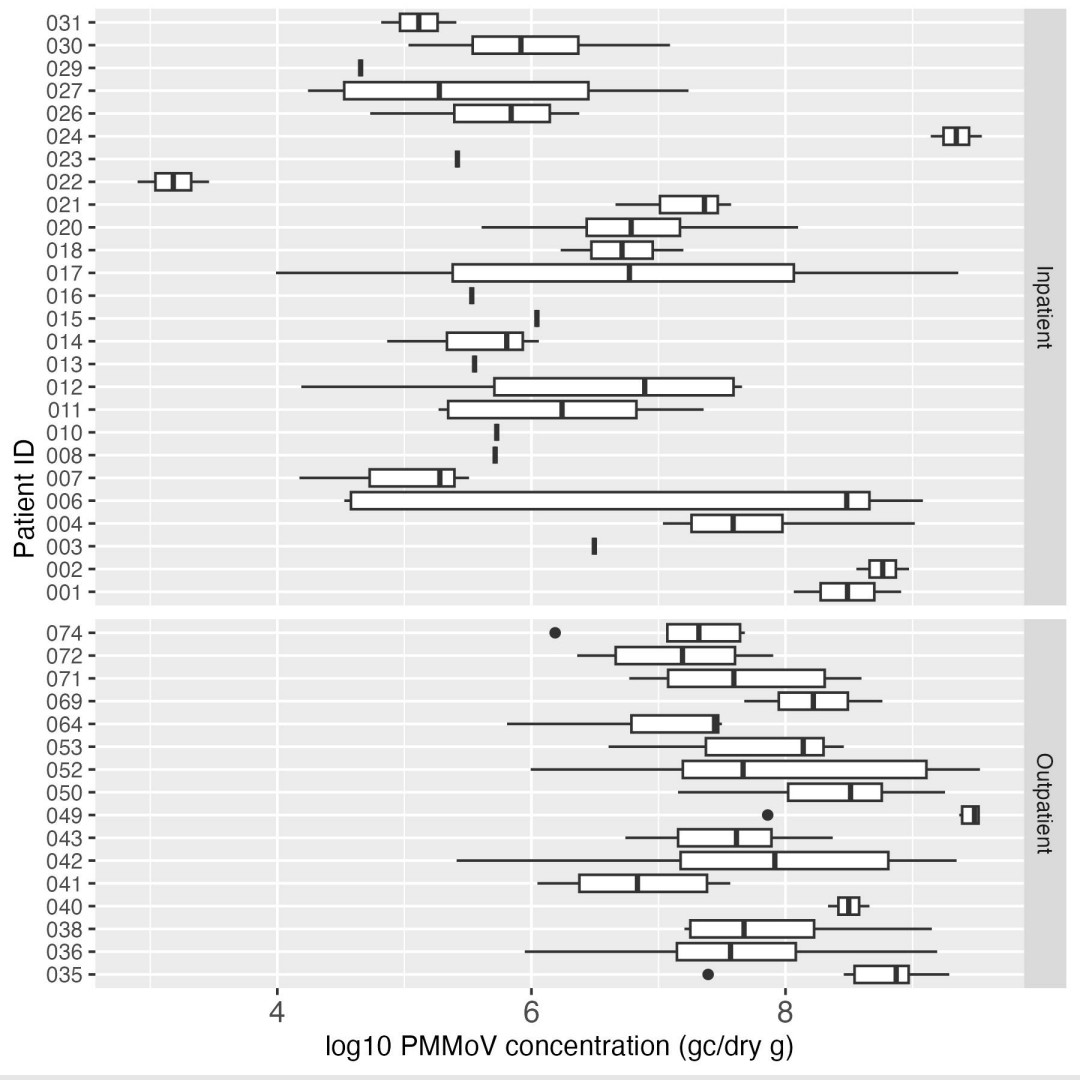
5) mtDNA showed higher positive rates, concentrations and less variability than PMMoV, suggesting it could be a better normalization factor for wastewater-based epidemiology results. 
6) Results provide important information on SARS-CoV-2 and indicator shedding dynamics, addressing a key knowledge gap for advancing wastewater monitoring and using data to estimate COVID-19 prevalence.
Thanks for reading 🙏
Others references :
Thanks for reading 🙏
Others references :
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1740989947362841069?t=CKDs49hATLhQYs9LRpEWGg&s=19
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh