We have successfully documented the entire Russian missiles industry, mapping 28 of its key enterprises. Read our first OSINT sample focusing on the Votkinsk Plant, a major producer of intercontinental ballistic missiles. How does it make weaponry?

https://twitter.com/rhodusinc/status/1785030605438120351
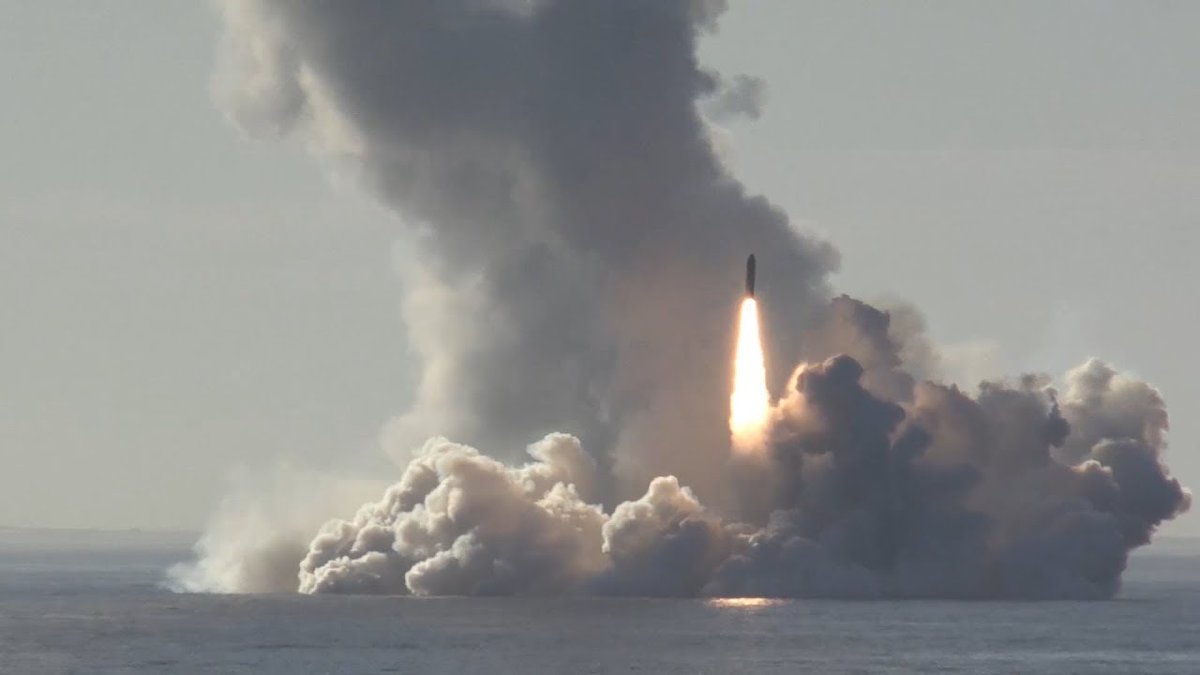

The strategic missiles industry appears to be highly secretive and impenetrable to the observers. And yet, it is perfectly OSINTable, based on the publicly available sources. This investigation sample illustrates our approach and methodology (31 p.)
assets-global.website-files.com/65ca3387040186…

assets-global.website-files.com/65ca3387040186…

Step 1. State Propaganda.
Our first and invaluable source is the state propaganda, such as the federal and regional TV channels, corporate media, social media and so on. It provides abundant visual evidence, particularly on the hardware used in the production of weaponry.

Our first and invaluable source is the state propaganda, such as the federal and regional TV channels, corporate media, social media and so on. It provides abundant visual evidence, particularly on the hardware used in the production of weaponry.


Step 2. Using public procurements data
Our next step is procurements. Aiming to check the managerial corruption, authorities force the military industry to proceed their purchases through the centralised procurements system. Once it was built, it became an invaluable OSINT tool
Our next step is procurements. Aiming to check the managerial corruption, authorities force the military industry to proceed their purchases through the centralised procurements system. Once it was built, it became an invaluable OSINT tool

Step 3. Integrating professional sources
Propaganda may give us a general picture of what equipment stands there. But what is it being used for? This we can learn in professional and academic sources.

Propaganda may give us a general picture of what equipment stands there. But what is it being used for? This we can learn in professional and academic sources.


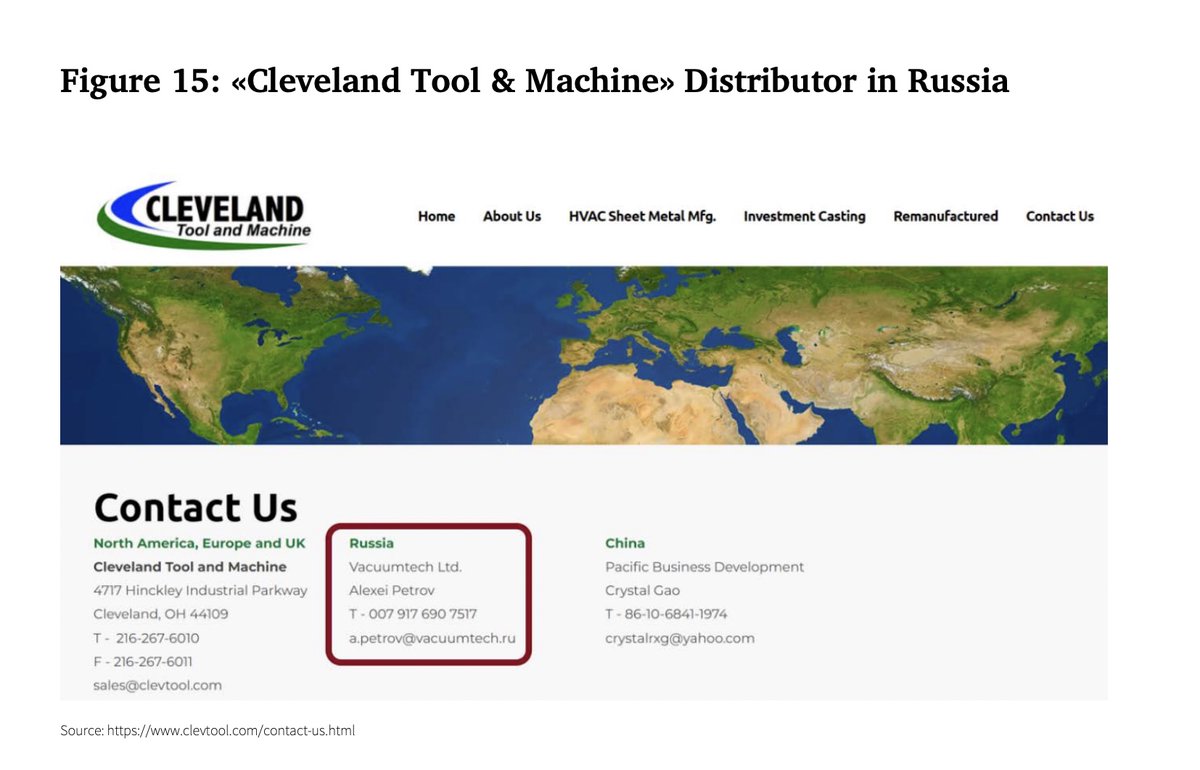
Step 4. Tracking the supply chain
Once we identified the equipment used in the production of weaponry, we can track the entire supply chain. In most cases, it is not even very long.
Once we identified the equipment used in the production of weaponry, we can track the entire supply chain. In most cases, it is not even very long.
Step 5. Surveying the HR sources
HR sources such as resumes and vacancy listings can provide an insight into the hardware used in the military production, and, most importantly, into the structure and competences of the military industrial workforce.
HR sources such as resumes and vacancy listings can provide an insight into the hardware used in the military production, and, most importantly, into the structure and competences of the military industrial workforce.

Our work would be inconceivable without our donors. It started with @mercatus grant (thanks @tylercowen) and continued with private contributions of whom I would like to specifically thank @badita and @BErickson_BIO. There are also outrageously generous anonymous contributors whose names I don't even know.
Thank you.
Thank you.

If you want to support our work, you can:
PayPal:
donations@rhodus.com
Do a card payment:
BTC: bc1qssdxjeazytnqds0s92lsh2nm4t7zq6594q3eyz
ETH: 0xA9FA4454cC3EC0Ff521926BB5F8D4389bA0e665arhodus.com/donations
PayPal:
donations@rhodus.com
Do a card payment:
BTC: bc1qssdxjeazytnqds0s92lsh2nm4t7zq6594q3eyz
ETH: 0xA9FA4454cC3EC0Ff521926BB5F8D4389bA0e665arhodus.com/donations
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





