𝙃5𝙉1 𝘼𝙑𝙄𝘼𝙉 𝙄𝙉𝙁𝙇𝙐𝙀𝙉𝙕𝘼 :
𝙃𝙤𝙬 𝙃5𝙉1 𝙞𝙨 𝙏𝙍𝘼𝙉𝙎𝙈𝙄𝙏𝙏𝙀𝘿 ?
𝙒𝙝𝙖𝙩 𝙖𝙧𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙍𝙄𝙎𝙆 𝙛𝙤𝙧 𝙃𝙐𝙈𝘼𝙉𝙎 ?
(1𝘴𝘵 𝘱𝘢𝘳𝘵)
... qnd why the nb of humans cases are underestimated, and consequently the fatality rate overestimated ?
𝙃𝙤𝙬 𝙃5𝙉1 𝙞𝙨 𝙏𝙍𝘼𝙉𝙎𝙈𝙄𝙏𝙏𝙀𝘿 ?
𝙒𝙝𝙖𝙩 𝙖𝙧𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙍𝙄𝙎𝙆 𝙛𝙤𝙧 𝙃𝙐𝙈𝘼𝙉𝙎 ?
(1𝘴𝘵 𝘱𝘢𝘳𝘵)
... qnd why the nb of humans cases are underestimated, and consequently the fatality rate overestimated ?

2) We would first like to take a step back, and remember that the circulation of H*N* is an ancient story :
Fig. Possible origins of pandemic influenza viruses. Phylogenetic studies suggest that an avian influenza virus was transmitted to humans, leading to the 1918 pandemic
Fig. Possible origins of pandemic influenza viruses. Phylogenetic studies suggest that an avian influenza virus was transmitted to humans, leading to the 1918 pandemic

3) For the H5N1 that we have been following for a long time, the clade we are currently talking about emerged in 2021 ! 

4) To understand how we got here, I recommend also the very well done document from the CDC :
cdc.gov/flu/avianflu/t…




cdc.gov/flu/avianflu/t…




5) For those like me, who are passionate about zoonoses, we recommend also this reference work
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/cm…

journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/cm…

6) ...with very well done graphics on structure of influenza A virus virions or the models for the generation of pandemic influenza virus strains in pigs.



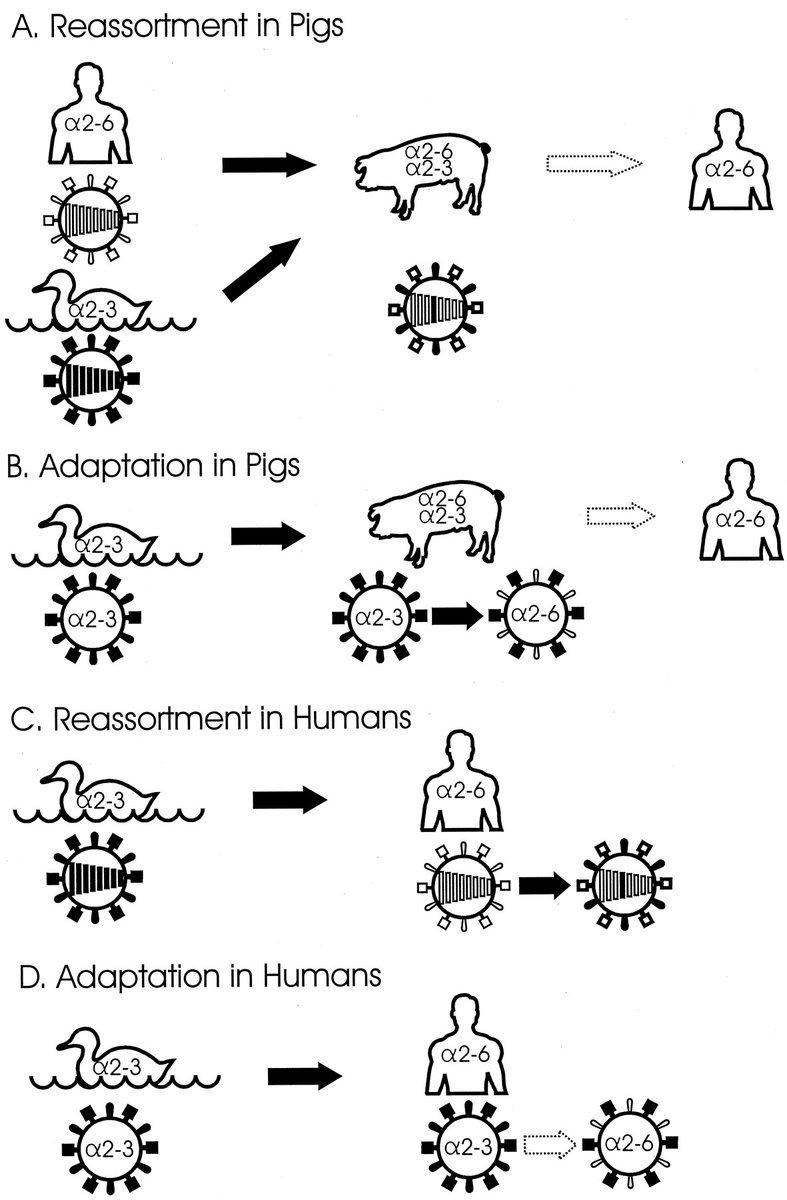
7) Contrary to what we have read recently, the risk is not in the transmission of the virus from animals to humans, but in a mutation of the virus allowing transmission between humans.
Except we are only 1 mutation away from this happening 🤔
Except we are only 1 mutation away from this happening 🤔
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1631157629765517313?t=ISHMhf_y0hXLEJN8dxOpQA&s=19
8) It is very likely that this could happen with the PB2 protein, which is one of the 3 polymerase proteins (PB2, PB1, PA) that make up the influenza virus.
A mutation in this protein could help compensate for insufficient human adaptation of H5N1
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jv…

A mutation in this protein could help compensate for insufficient human adaptation of H5N1
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jv…

9) It is this PB2 adaptation that we must follow closely
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1784075563222655485?t=neY5rDBu18mMlKshaIoI_A&s=19
10) ...knowing that the virus spread all over the world quickly
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1757980770872815875?t=XZfU33I1a5j9ttHusdu1Jw&s=19
11) ... including in big cities
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1784065136858214869?t=iyyZyNHMLb5egNXt6Wi0yw&s=19
12) and of course, recently in the cows
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1780973198063861797?t=kdvxc8EwVL_5lQYy3n4eww&s=19
13) In conclusion of this 1st part, for my friends @0bj3ctivity
@GourlaySyd @DavidJoffe64
@Alitis__ who pushed me to write this thread 🤗 and for those who follow me,
𝙨𝙤𝙢𝙚 𝙜𝙤𝙤𝙙 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙗𝙖𝙙 𝙣𝙚𝙬𝙨:
▶️ Good news : Egypt, for example, succeeded to manage in 2014 ...
@GourlaySyd @DavidJoffe64
@Alitis__ who pushed me to write this thread 🤗 and for those who follow me,
𝙨𝙤𝙢𝙚 𝙜𝙤𝙤𝙙 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙗𝙖𝙙 𝙣𝙚𝙬𝙨:
▶️ Good news : Egypt, for example, succeeded to manage in 2014 ...
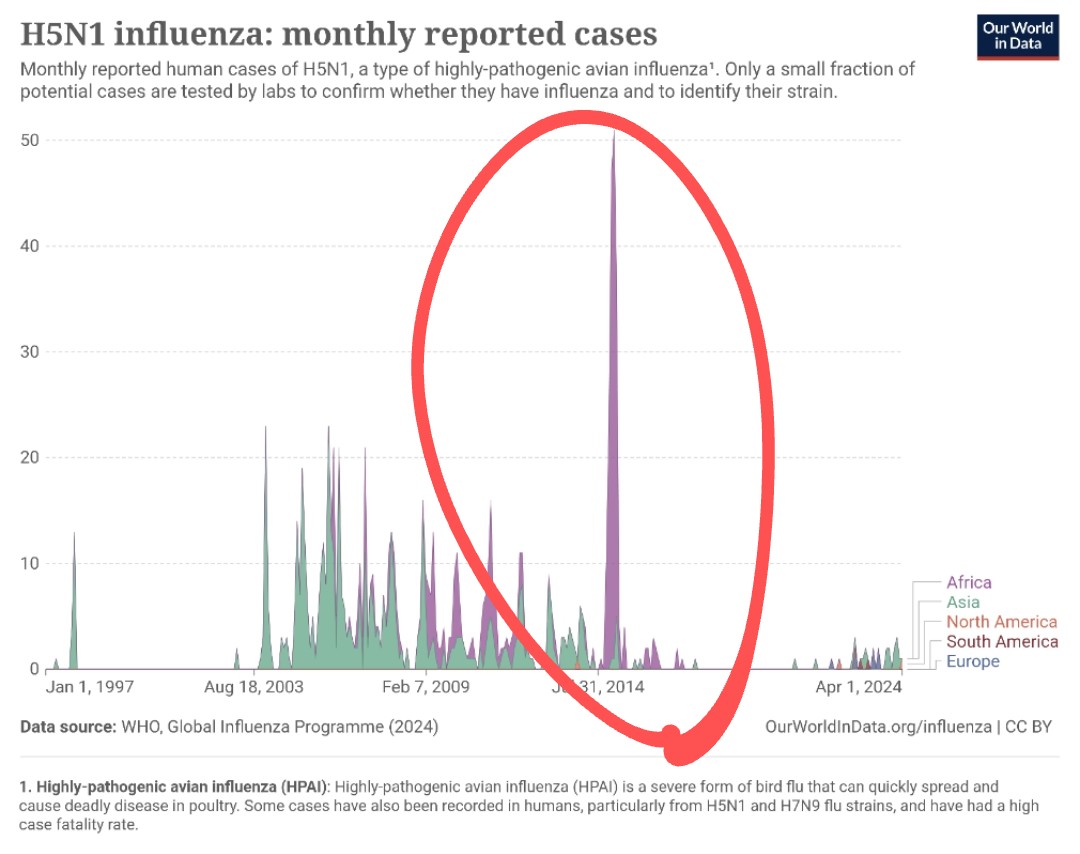
@0bj3ctivity @GourlaySyd @DavidJoffe64 @Alitis__ 14) ...by eliminating all contaminated animals (sorry for animal lovers). This was possible because the infectivity rate is similar to other influenza viruses.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…

ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…

@0bj3ctivity @GourlaySyd @DavidJoffe64 @Alitis__ 15) ▶️ Bad news : A study that has just been published despite many limitations, shows that cats have died after drinking contaminated milk. If it is confirmed (and I would have been wrong as I didn't believe it) we will no longer have to drink raw milk.
wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/30…
wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/30…
@0bj3ctivity @GourlaySyd @DavidJoffe64 @Alitis__ 16) ▶️ Good news : we haven't yet found the mutation, that would allow the transmission between humans has not been found
▶️ Bad news : If mortality rate is lower, it is because the nb of cases is underestimated. It means H5N1 already circulates already in humans.
A bientot 🙋♂️
▶️ Bad news : If mortality rate is lower, it is because the nb of cases is underestimated. It means H5N1 already circulates already in humans.
A bientot 🙋♂️
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh


















