Someone from @piersmorgan's staff asked if I would like to come onto Pier's show, Piers Morgan Uncensored, to talk about the state of his attire. Since he invited feedback, I thought I'd do a thread comparing his style to menswear icon Kermit the Frog. 🧵 



Let's again start with the basics.
The core of any outfit is fit and silhouette. Pier's suit jackets often have lapels that buckle away from his chest and a collar that floats from his neck. This suggests his jackets may be too small.


The core of any outfit is fit and silhouette. Pier's suit jackets often have lapels that buckle away from his chest and a collar that floats from his neck. This suggests his jackets may be too small.


No such issues for Kermit the Frog. His clothes hang beautifully and smoothly while still giving a distinctive, flattering silhouette. 

Piers knows that he looks best in a tailored jacket, so he wears them to social functions. However, he relies too much on formal tailoring, such as dark worsted suits in sober colors.
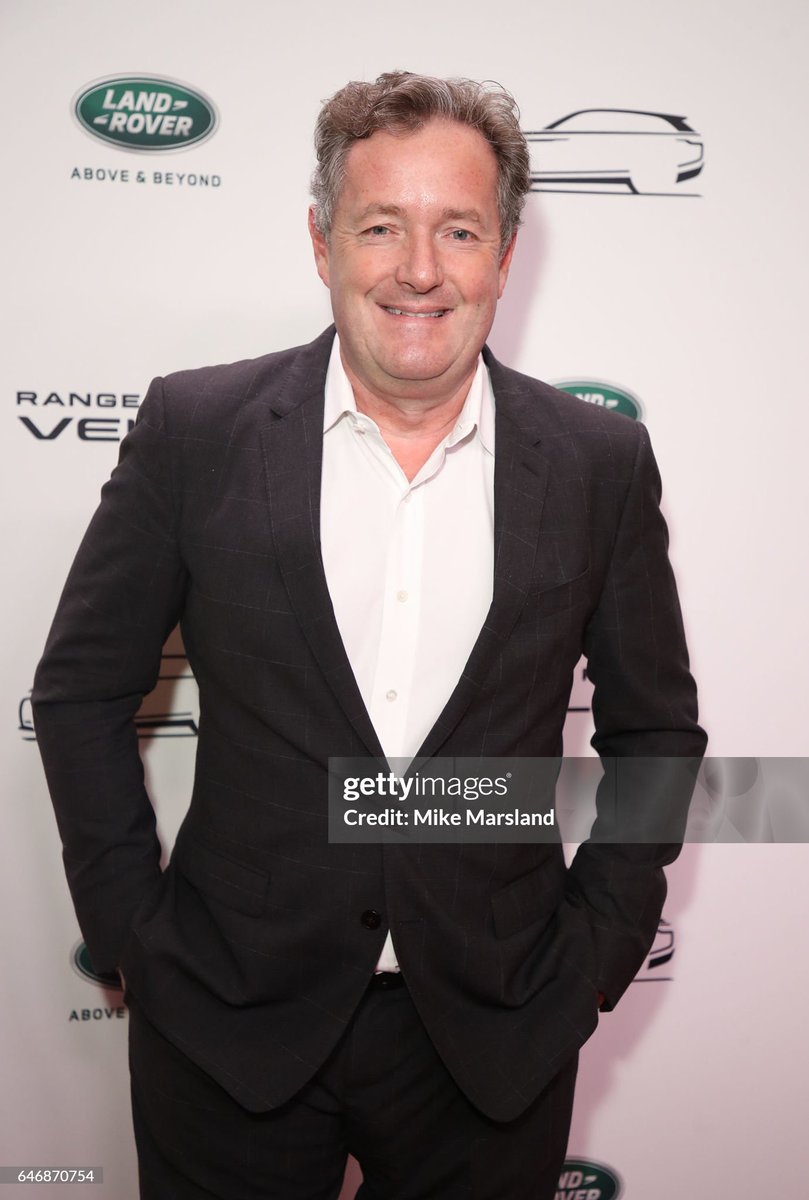




This puts him in a somewhat awkward position of trying to find ways to dress them down. He knows that people at the event may not be wearing suits, but he also doesn't know what else to wear. So he ditches the tie or wears a suit jacket with jeans to look "kinda casual."
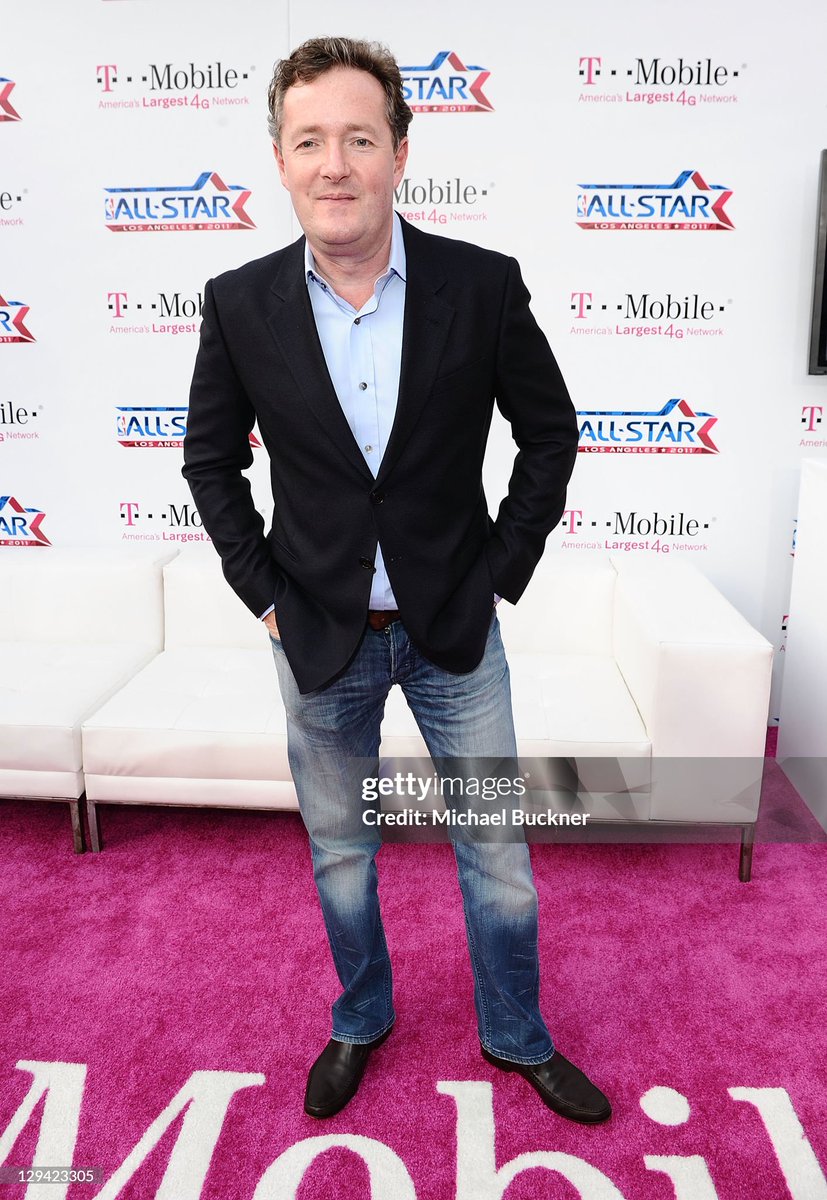




A dark worsted suit without a tie is like the night sky without stars. Kermit the Frog understands this, so he always makes sure he has something—sheen, color, or pattern—between his jacket's front edges. This adds a bit of visual interest to what's a very sober ensemble. 

Kermit also knows that if he doesn't want to wear a tie, he should opt for a more casual top. He often reaches for a charcoal turtleneck. Since turtlenecks aren't meant to be worn with ties, he doesn't look like he's missing something.




Since Piers seemingly only has dark worsted suits in colors such as black, navy, or grey, he often looks like he's just come out of a business meeting, even when he's at social functions.




No such issue for Kermit the Frog. He has a wider variety of options, such as tweeds, checked sport coats, and casual suits made from materials like linen and available in colors like cream. This allows him to look put together without seeming corporate.








For a more casual look, Piers often wears these plain, smooth Merino sweaters in solid colors. These sweaters can sometimes be fine under a tailored jacket, but on their own, they lack something.




No such issue for Kermit the Frog. He knows that if you're going to wear a sweater on its own, the knit needs something like a pattern or texture to make it interesting. Good options include spongey Shetlands, chunky Arans, Fair Isles, and ribbed Shaker knits.




The biggest issue with Piers' casualwear is that it has no direction. It's sort of a mishmash of generic clothes: polos and button-up shirts with pre-washed blue jeans or flat-front beige chinos, sometimes layered with a plain Merino sweater.
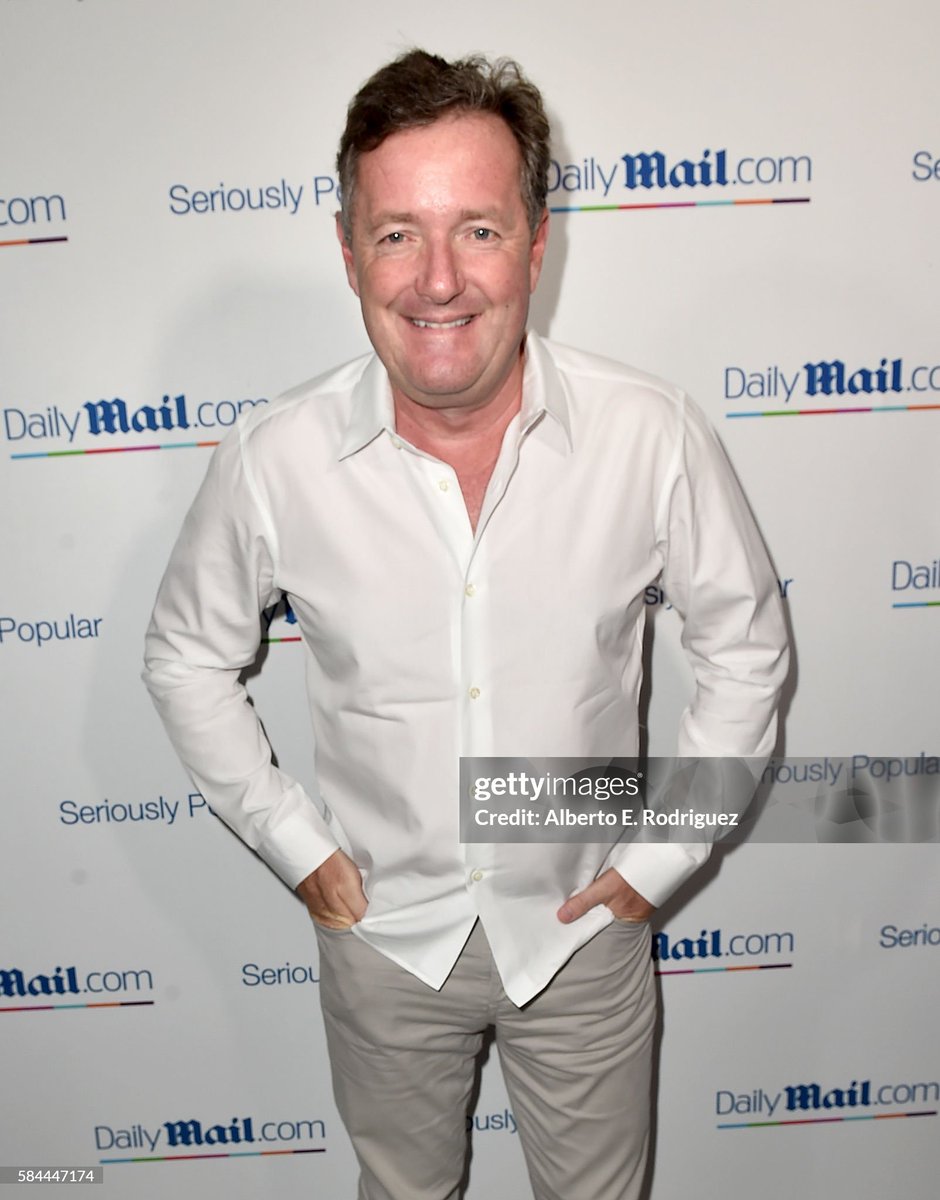




When he layers, the outfits lack cultural meaning or coherency (e.g., topcoat with polo and sweatpants). When he tries to look a bit cooler, he thinks only in terms of single items (e.g., the black dress shirts popular with divorced men hitting the club).




Kermit doesn't think of outfits in parts or as a pseudo-science (e.g., black goes with blue), but as cultural language. He thinks of the *total* outfit and what it conveys. The rebel look with a biker jacket and jeans. Or the time he wore white suits with gold chains in the '70s
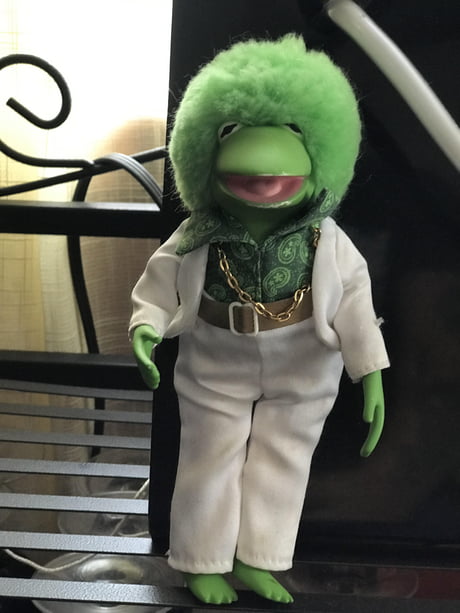




Here, we see him taking chances with a beautifully patterned serape and a safari jacket worn with a neckerchief and beret.




Men often struggle with this because their identity may be rooted in just being a "normal dude," so they see any outfit that deviates from some middle-class uniform as "cosplay."
But do you think a frog actually herds cattle?
But do you think a frog actually herds cattle?

By thinking of clothes as cultural language, Kermit is able to put together cooler outfits. Here, he's channeling 1980s Miami Vice energy with a lightweight jacket, pink mock neck, striped pants, white horsebit loafers, and giant sunglasses. 

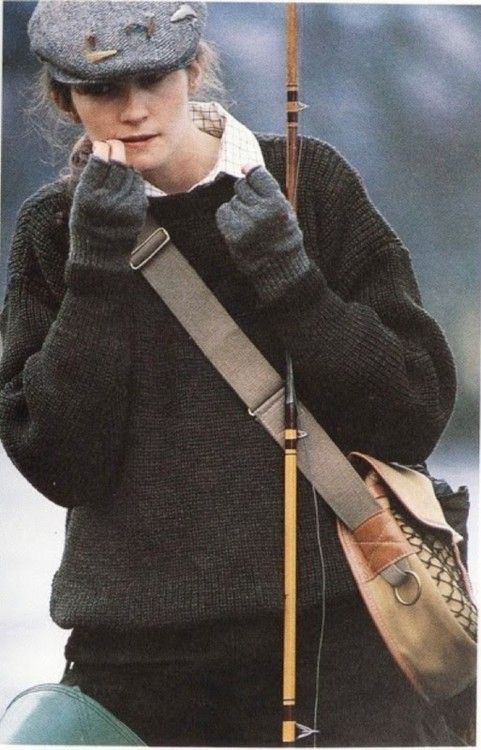
Compare these two outfits. Piers' black polo with checked knee-length shorts and bad sneakers says nothing. But Kermit's cargo shorts with an Aloha shirt, fishing bag, and straw hat says: "I'm a mid-century sportsman on vacation."




To develop your visual vocabulary, you have to pay attention to culture. Think about how clothes were worn in the past by various cultural groups. Here we see all the references for Kermit's outfit above.








You can see how the same language is channeled in Aime Leon Dore's spring/ summer lookbook. The outfit on the right is a little better because the man is wearing a jacket (outfits often need a finishing layer). But perhaps Kermit was hot that day.




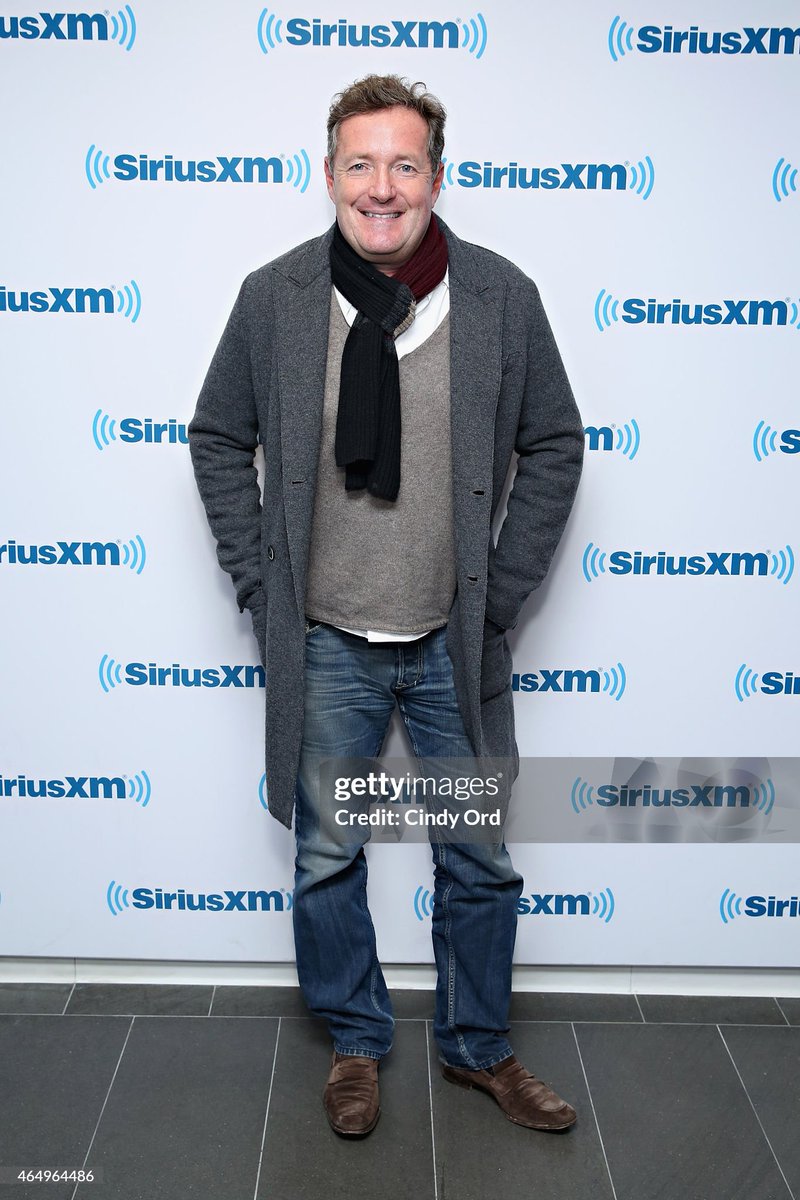
We see the same issues here. Piers is wearing a slim, shapeless topcoat with a stretched-out V-neck, a white dress shirt, a scarf, bad jeans, and suede loafers (confusing, no cultural message, aesthetically unappealing). 

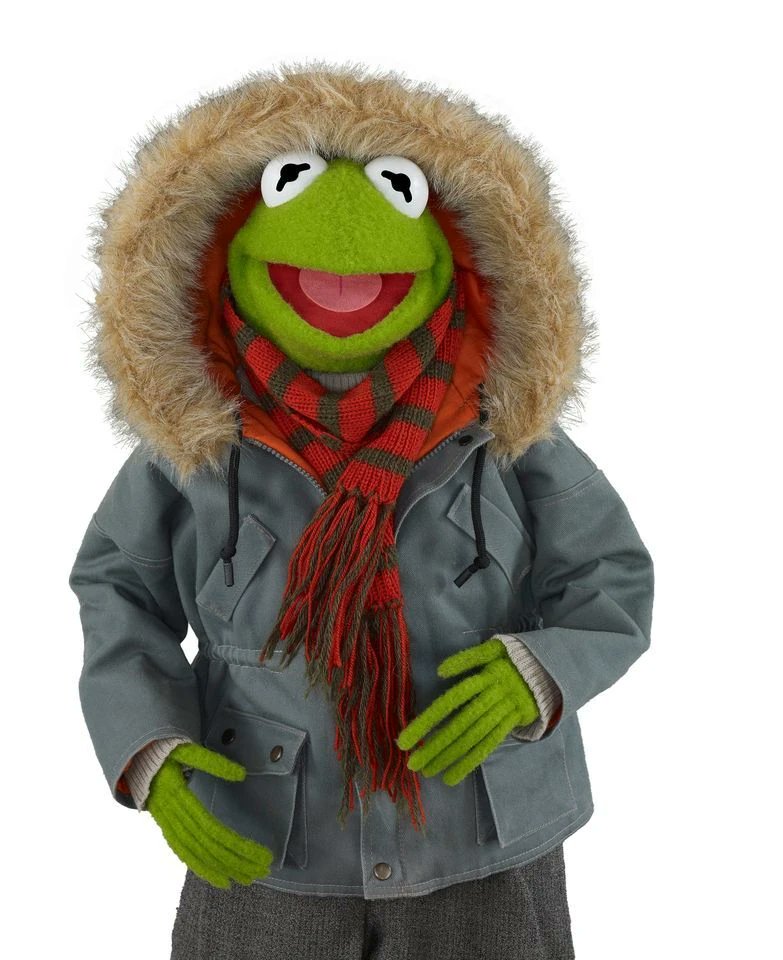
Kermit wears a similar outfit but employs a field parka, a Fair Isle knit, and a scarf. The coat gives him a distinctive silhouette. The sweater is visually more interesting. All the elements in the outfit make sense in terms of weather and cultural language.




Again, the same issue here. Piers is wearing generic clothes (no cultural message, lack of a finishing layer, visually uninteresting). Kermit improves on this by aligning the materials (chambray with denim) and using an open shirt as a lightweight layer. Has a workwear vibe.




Finally, Kermit knows that dinner suits (aka tuxedos) should be worn with black bow ties made from the same material as the jacket's facings, not long black ties, which should be reserved for business meetings, court appearances, and funerals.




Piers looks best on his TV show, where he employs a visual language he knows (dark suit, light shirt, dark tie). He just needs to learn a few more languages for when he's off the show and perhaps pay attention to Kermit the Frog. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh