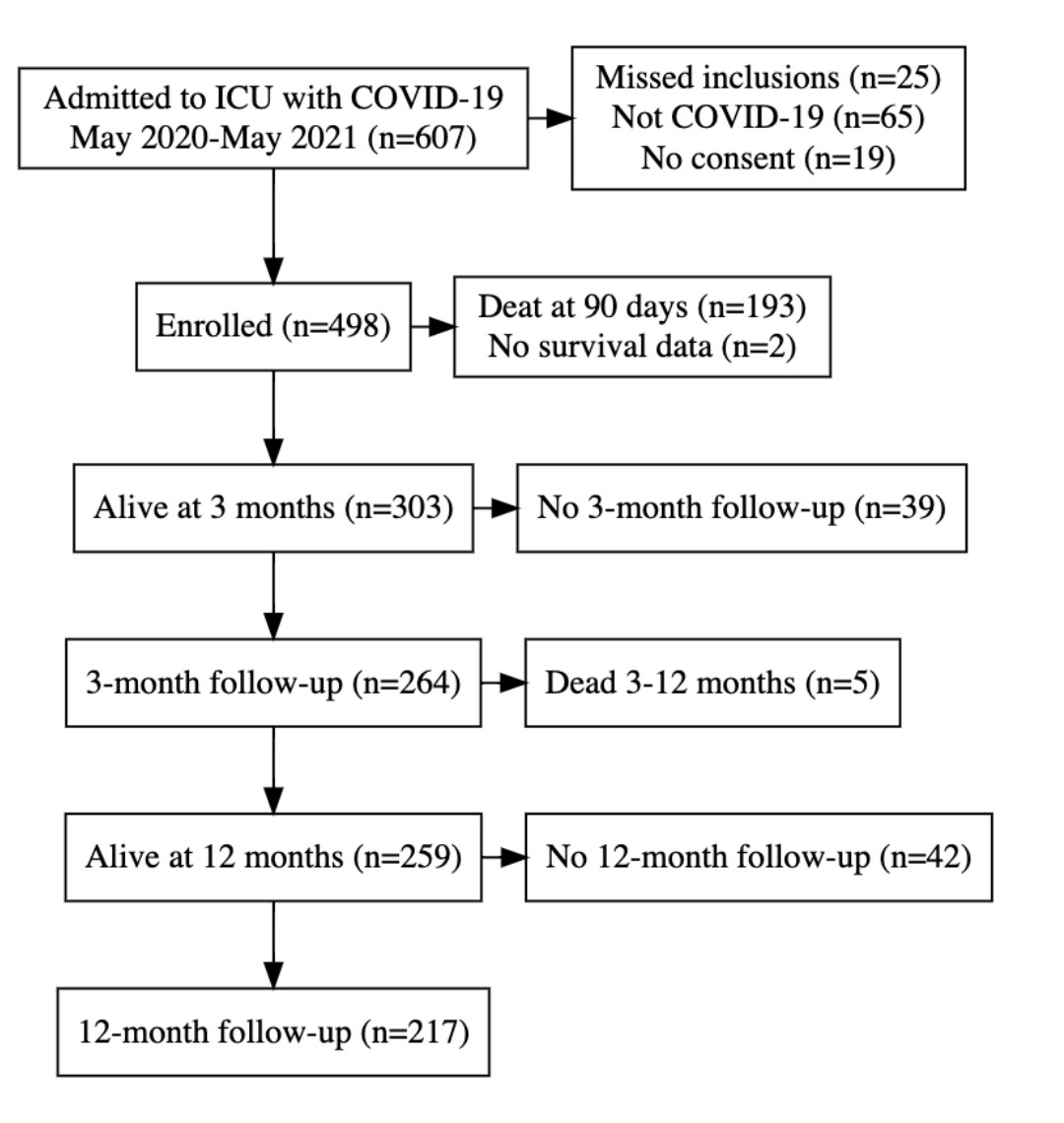
𝙒𝙃𝙀𝙉 𝙒𝙄𝙇𝙇 𝙒𝙀 𝙁𝙄𝙉𝘼𝙇𝙇𝙔 𝙀𝙉𝘿 𝙁𝘼𝙇𝙎𝙀 𝘿𝙄𝘾𝙃𝙊𝙏𝙊𝙈𝙄𝙀𝙎?
▶️ Is the TRANSMISSION of the virus AIRBORNE or by DROPLETS ?
BOTH, even, if it is essentially airborne, due to the constraints of droplet transmission.
▶️ Is there a "relative" IMMUNITY ...
▶️ Is the TRANSMISSION of the virus AIRBORNE or by DROPLETS ?
BOTH, even, if it is essentially airborne, due to the constraints of droplet transmission.
▶️ Is there a "relative" IMMUNITY ...

2) ... post-infection or post-vaccination ?
BOTH, even if reinfections must absolutely be avoided, and if the concept of hybrid immunity is dead, since there are almost no more vaccines administered
▶️ Is a WAVE caused by a VARIANT or by WANING IMMUNITY?
BOTH plus ...
BOTH, even if reinfections must absolutely be avoided, and if the concept of hybrid immunity is dead, since there are almost no more vaccines administered
▶️ Is a WAVE caused by a VARIANT or by WANING IMMUNITY?
BOTH plus ...

3) ...population behavior, environmental factors, population density, transportation, ...
A wave is multifactorial.
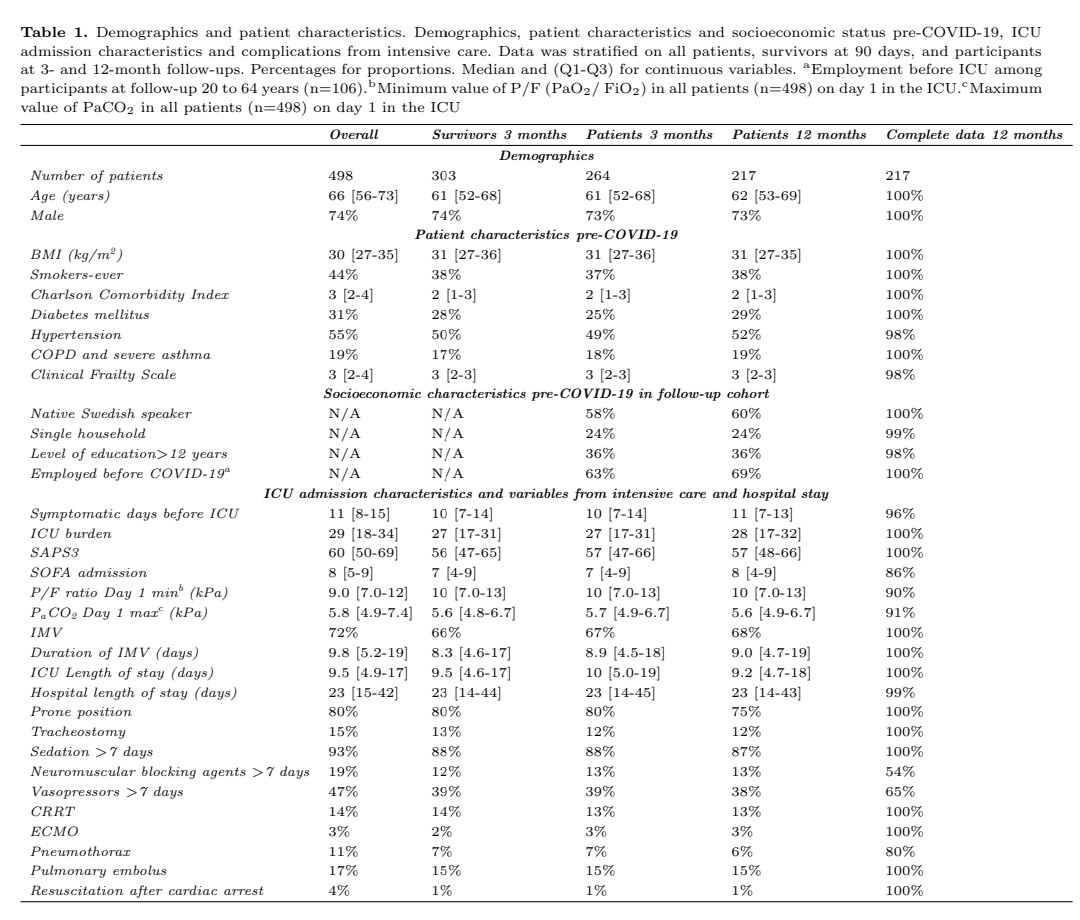
▶️ Is there 10% or more than 40% long COVID?
BOTH, because it depends, on whether the definition, refers to 1 or more symptoms, 3 months after the infection
A wave is multifactorial.
▶️ Is there 10% or more than 40% long COVID?
BOTH, because it depends, on whether the definition, refers to 1 or more symptoms, 3 months after the infection
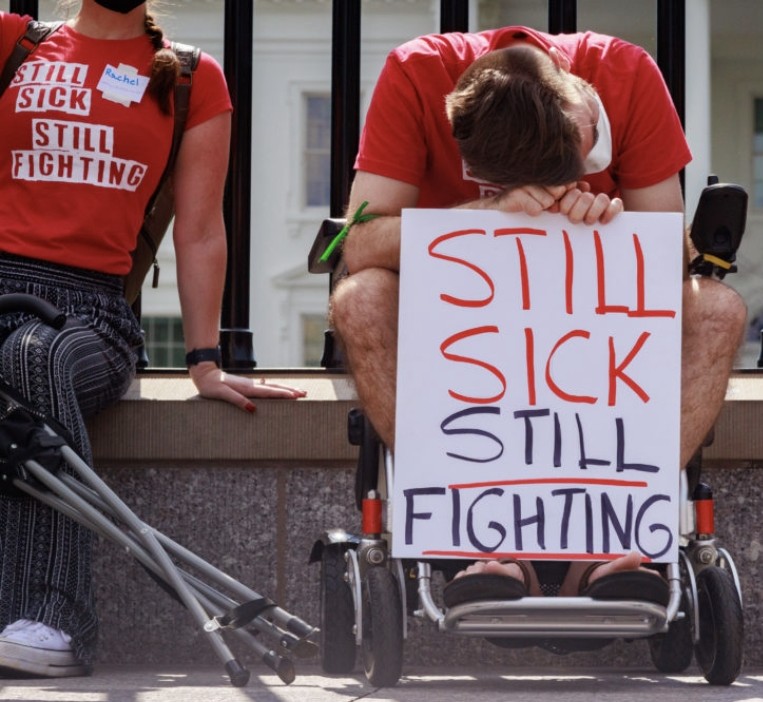
4) ▶️ Is Avian Influenza H5N1 transmissible to MAMMALS or HUMANS?
BOTH, and actually only by birds, because mammal-human or human-human transmission has still not been established
▶️ Is the fatality rate of H5N1 for humans <10% or close to 50%?
BOTH, as it depends ...
BOTH, and actually only by birds, because mammal-human or human-human transmission has still not been established
▶️ Is the fatality rate of H5N1 for humans <10% or close to 50%?
BOTH, as it depends ...

5) ...on the baseline chosen, hospitalized or symptomatic.
If we take into account asymptomatic people we could have rates close to human influenza.
The science, especially of viruses, is not a black or white world ...
(H5N1 before 2019 and after)
If we take into account asymptomatic people we could have rates close to human influenza.
The science, especially of viruses, is not a black or white world ...
(H5N1 before 2019 and after)
6) ... but requires a lot of nuances due to its complexity. There is no room for simplistic dichotomies.
Thanks for reading 🙏
Thanks for reading 🙏

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh