𝙎𝙚𝙫𝙚𝙧𝙚 𝙣𝙚𝙪𝙧𝙤𝙡𝙤𝙜𝙞𝙘𝙖𝙡 𝙢𝙖𝙣𝙞𝙛𝙚𝙨𝙩𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣 𝙖𝙨𝙨𝙤𝙘𝙞𝙖𝙩𝙚𝙙 𝙬𝙞𝙩𝙝 𝘾𝙊𝙑𝙄𝘿-19 𝙞𝙣 𝙘𝙝𝙞𝙡𝙙𝙧𝙚𝙣 𝙙𝙪𝙧𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙊𝙢𝙞𝙘𝙧𝙤𝙣 !
𝘛𝘩𝘢𝘯𝘬𝘴 𝘵𝘰 𝘮𝘺 𝘧𝘳𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘥 𝘋𝘢𝘷𝘪𝘥 @DavidJoffe64
pedneur.com/article/S0887-…

𝘛𝘩𝘢𝘯𝘬𝘴 𝘵𝘰 𝘮𝘺 𝘧𝘳𝘪𝘦𝘯𝘥 𝘋𝘢𝘷𝘪𝘥 @DavidJoffe64
pedneur.com/article/S0887-…
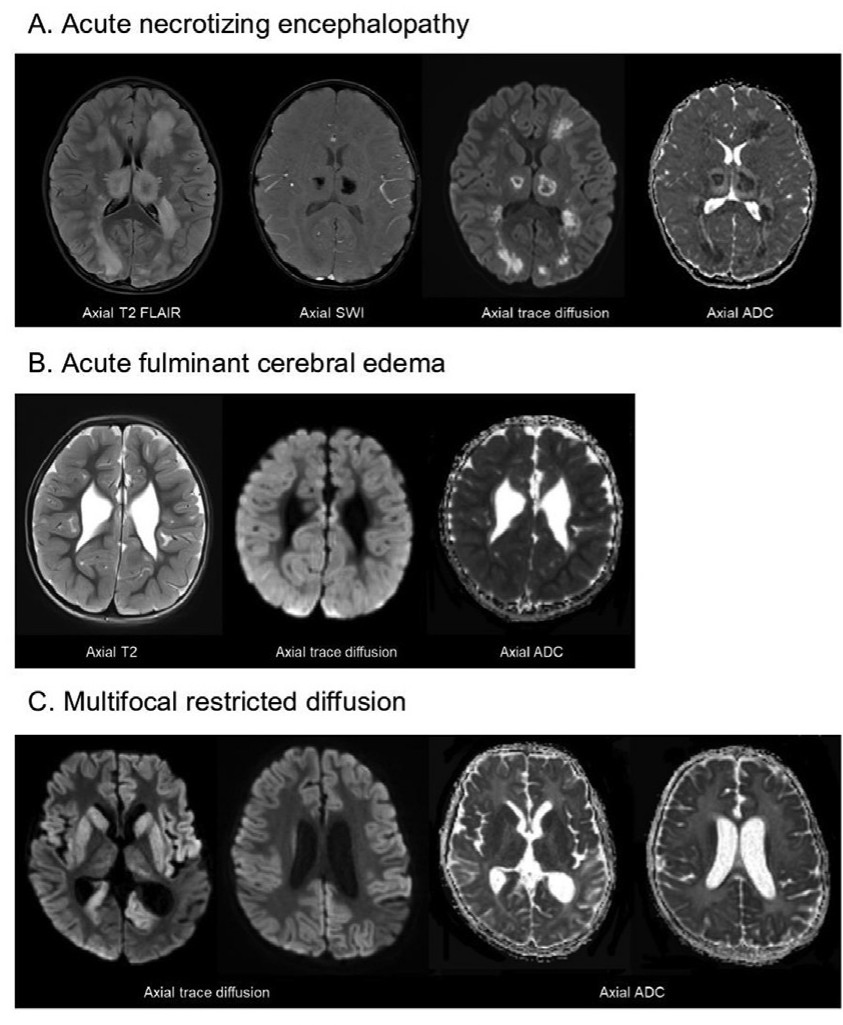
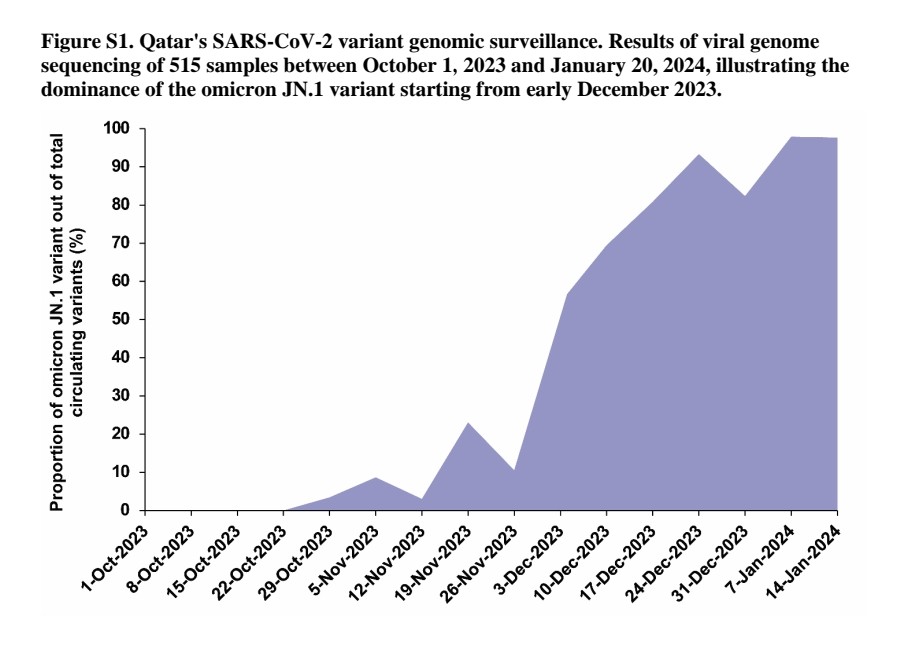
2) The study analyzed 17 pediatric patients in Korea who experienced severe neurological manifestations associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection during the Omicron variant-predominant period from January to April 2022. 

3) Over half (11/17) of the patients had pre-existing neurological disabilities and 9 met the criteria for MIS-C (multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children). Only 1 patient was vaccinated.
Severe neurological manifestations included acute necrotiwezing encephalopathy ...
Severe neurological manifestations included acute necrotiwezing encephalopathy ...
4) ...acute fulminant cerebral edema, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, basal ganglia encephalitis, severe encephalopathy/encephalitis, and refractory status dystonicus.
MRI findings showed various patterns of abnormalities including lesions with restricted diffusion ...
MRI findings showed various patterns of abnormalities including lesions with restricted diffusion ...
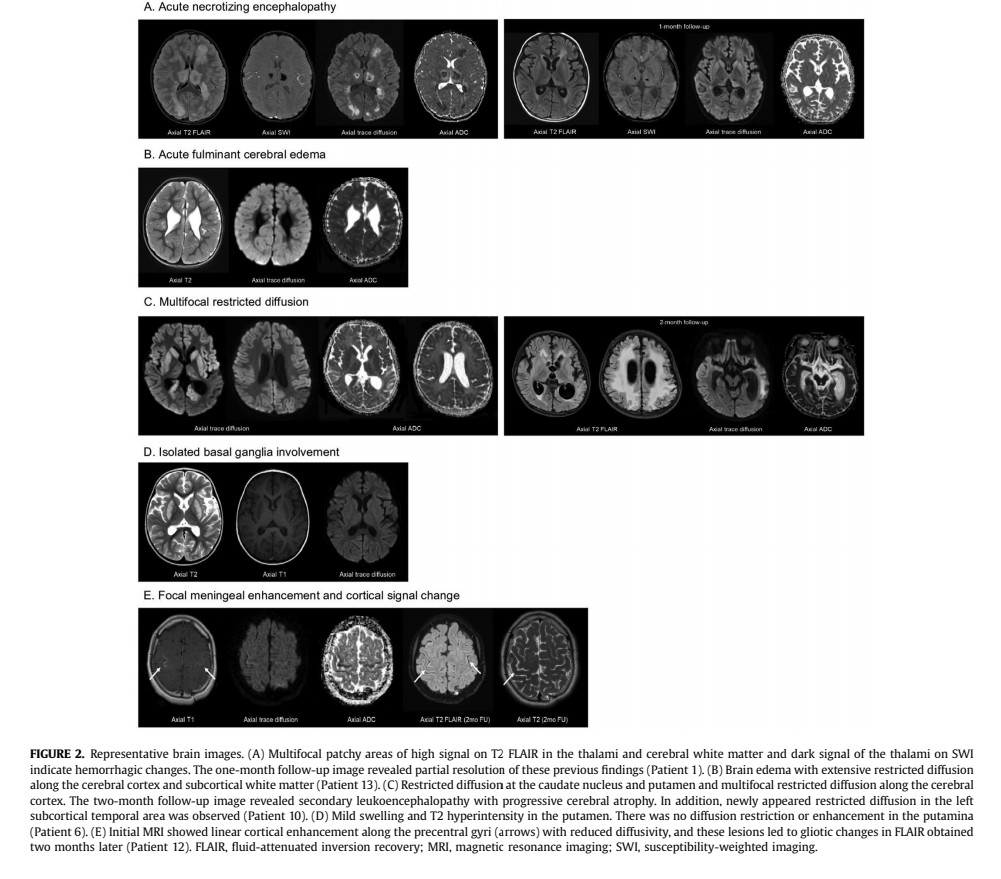
5) ...in the cortex, subcortical white matter, basal ganglia, and thalamus.
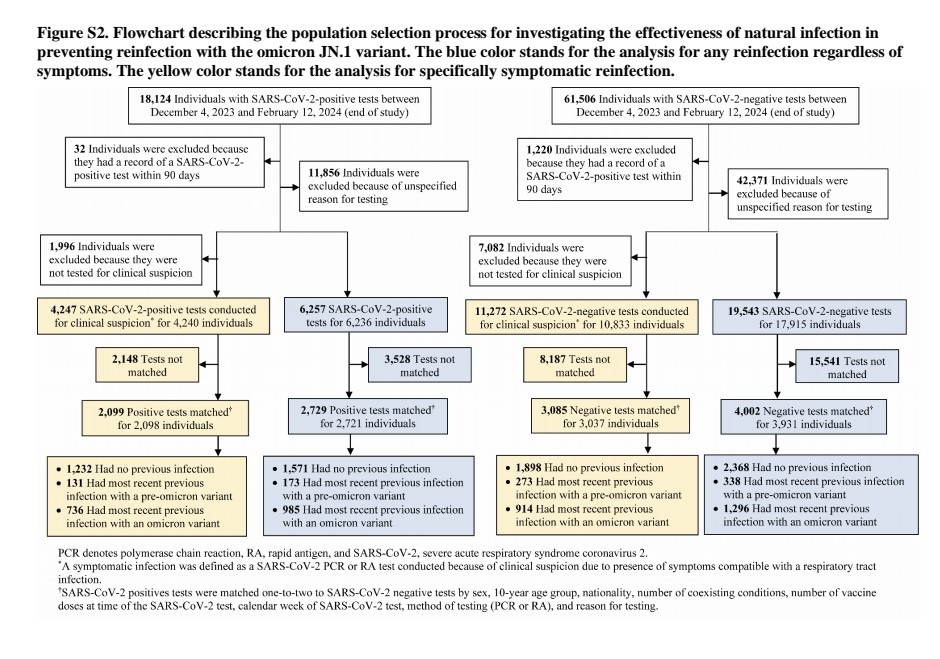
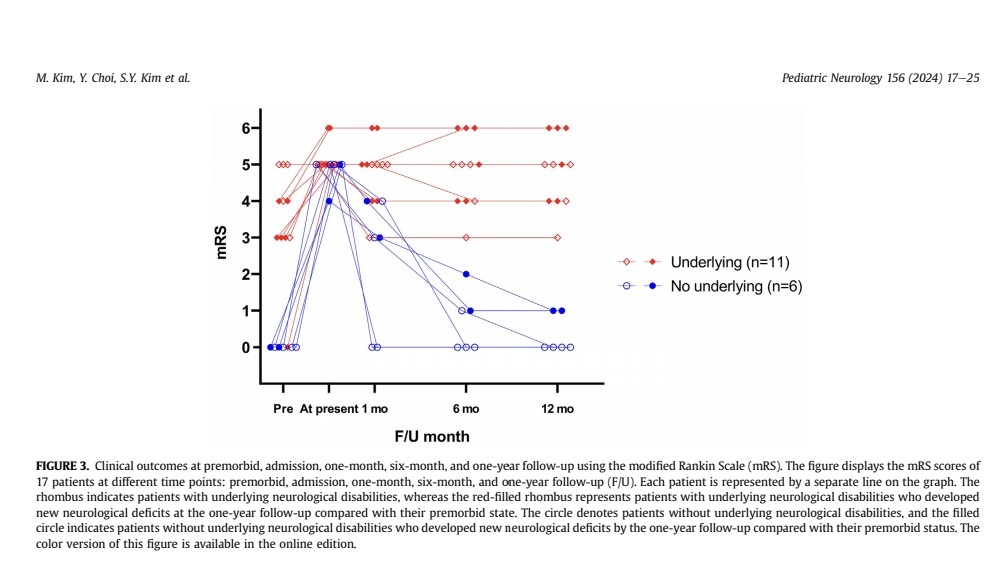
Patients with underlying neurological disabilities or MIS-C had longer hospital and ICU stays compared to those without.
Outcomes were poor - 3 patients died and ...
Patients with underlying neurological disabilities or MIS-C had longer hospital and ICU stays compared to those without.
Outcomes were poor - 3 patients died and ...
6) ...5 had new neurological deficits at 1-year follow-up, and those with pre-existing disabilities generally had worse outcomes.
The study demonstrates that severe neurological complications can occur with Omicron in pediatric patients ...
The study demonstrates that severe neurological complications can occur with Omicron in pediatric patients ...
7) ...especially those with pre-existing conditions or who are unvaccinated. Earlier recognition and management may help improve outcomes.
Thanks for reading 🙏
Thanks for reading 🙏
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh