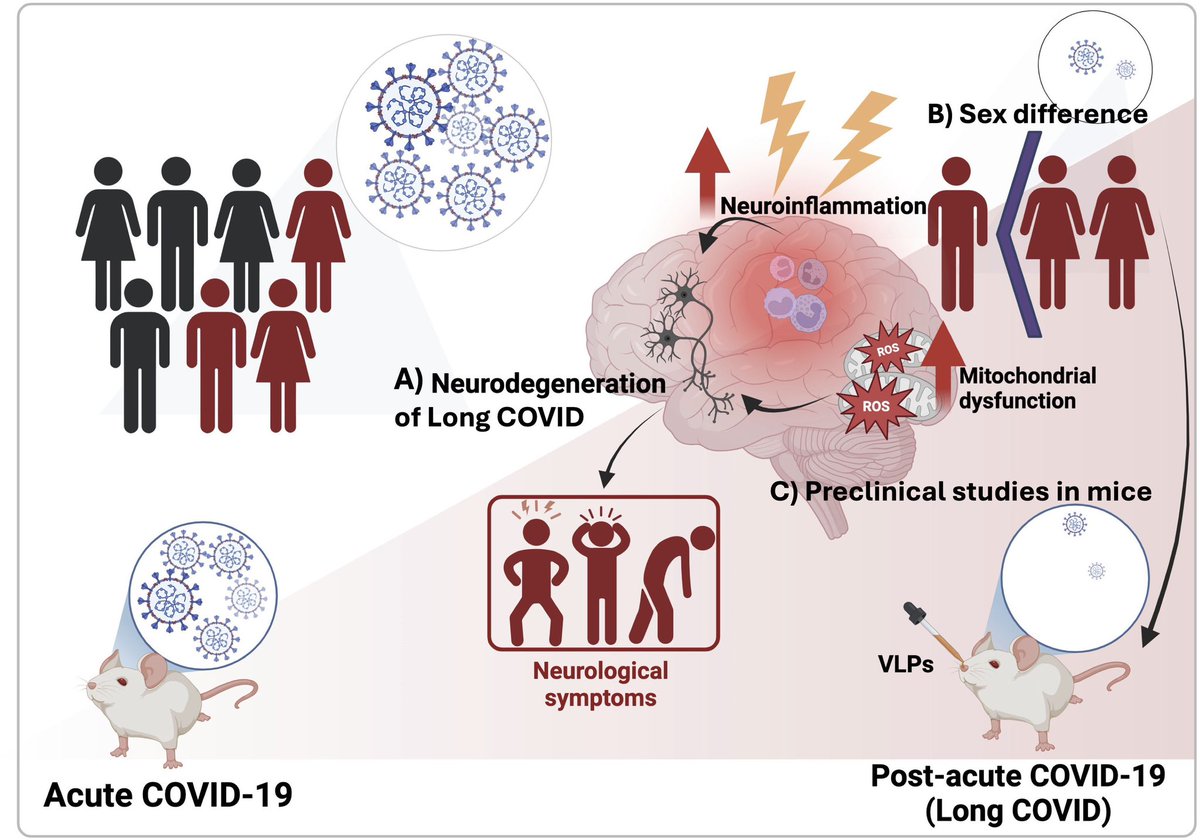
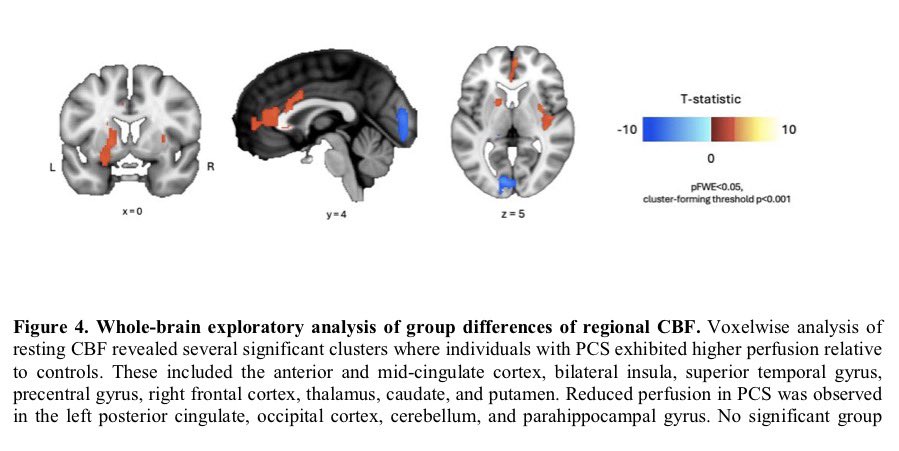
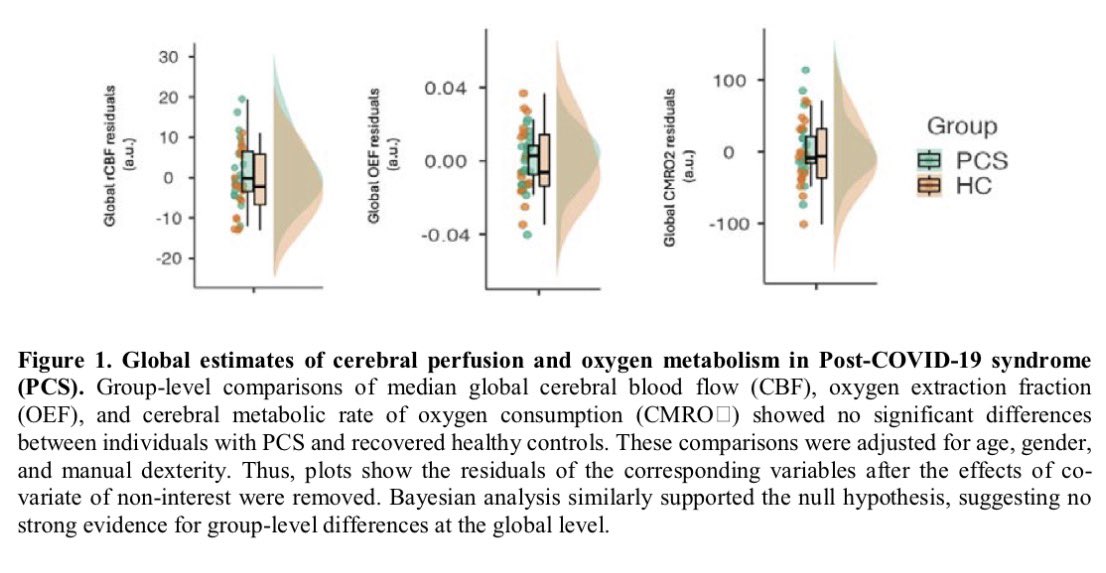
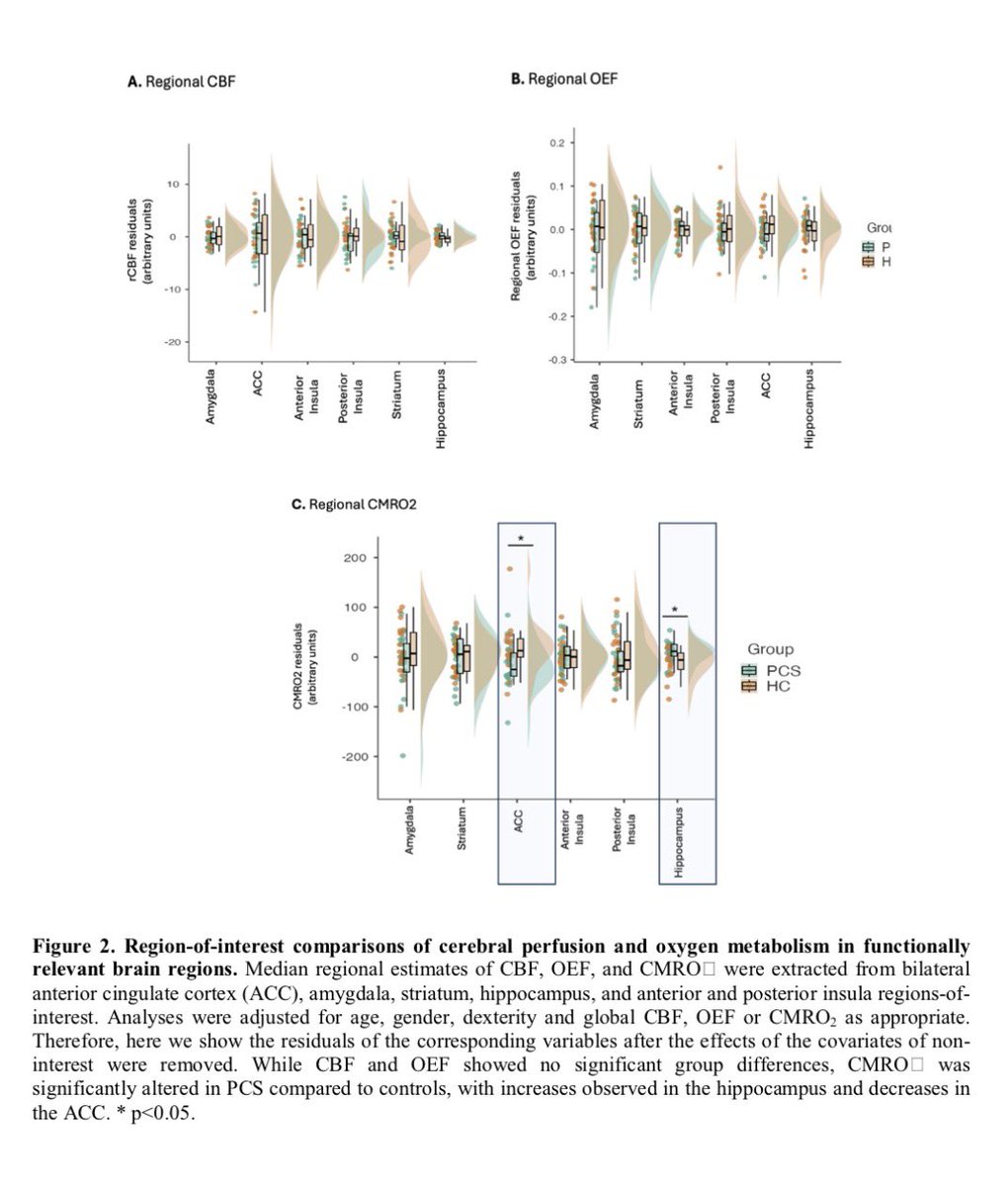
A NEW discovery, akin to a black-swan event-—unexpected but making perfect sense once revealed, would offer an approach to fixing broken immune responses in #LongCovid and some autoimmune diseases! 1/ 

Scientists have long known that brain plays a part in the immune system — but how it does so has been a mystery. Now, scientists have identified cells in brainstem that sense immune cues from the periphery of body & act as master regulators of body’s inflammatory response 2/ 

The results suggest that the brain maintains a delicate balance between the molecular signals that promote inflammation and those that dampen it —a finding that could lead to treatments for autoimmune diseases and other conditions caused by an excessive immune response. 3/ 
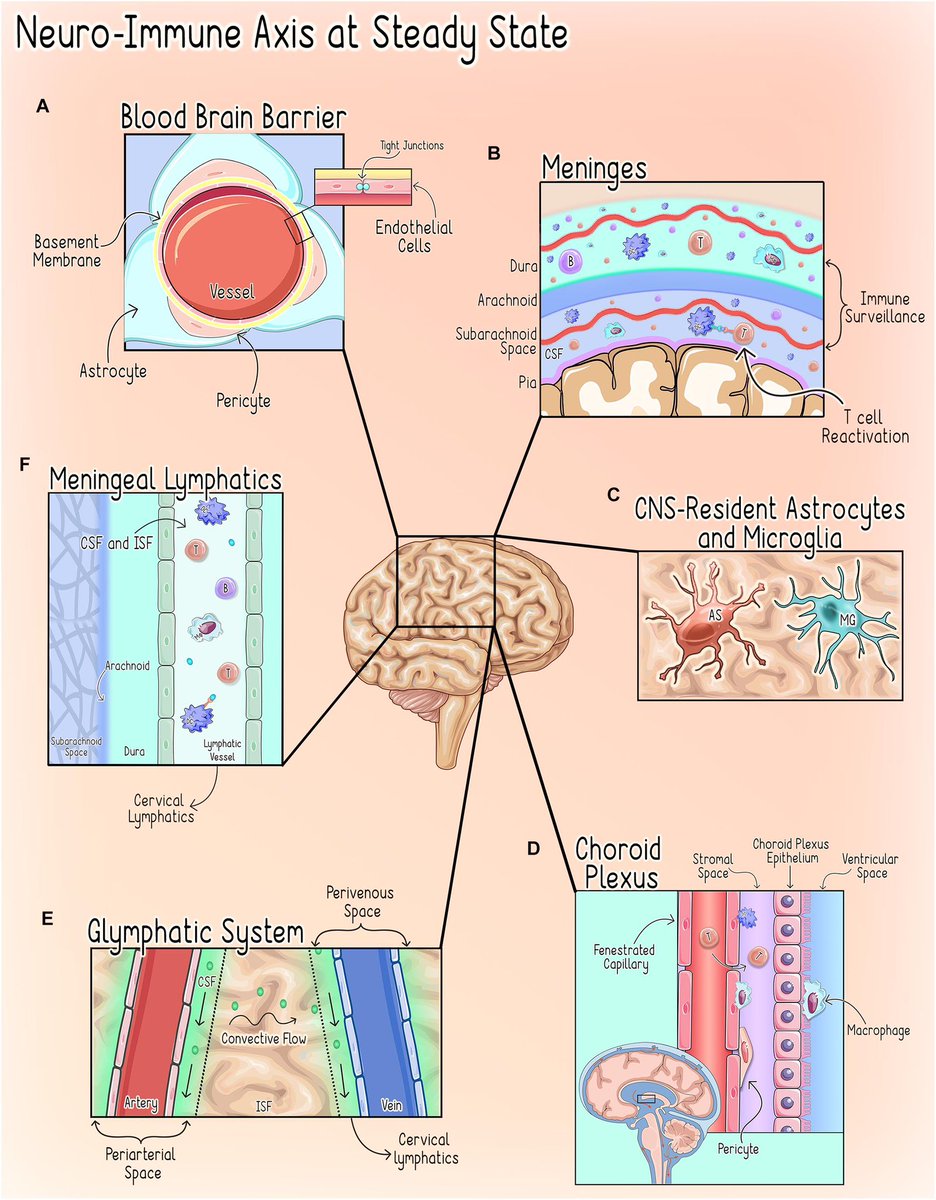
Scientists have known that the brainstem has many functions, such as controlling basic processes such as breathing. However, it shows that there is whole layer of biology that we haven’t even anticipated! 4/ 

After sensing an intruder, the immune system unleashes a flood of immune cells that promote inflammation. This response must be controlled w/ exquisite precision: if it’s too weak, the body is at risk of becoming infected; if it’s too strong, it can damage body’s own tissues 5/ 

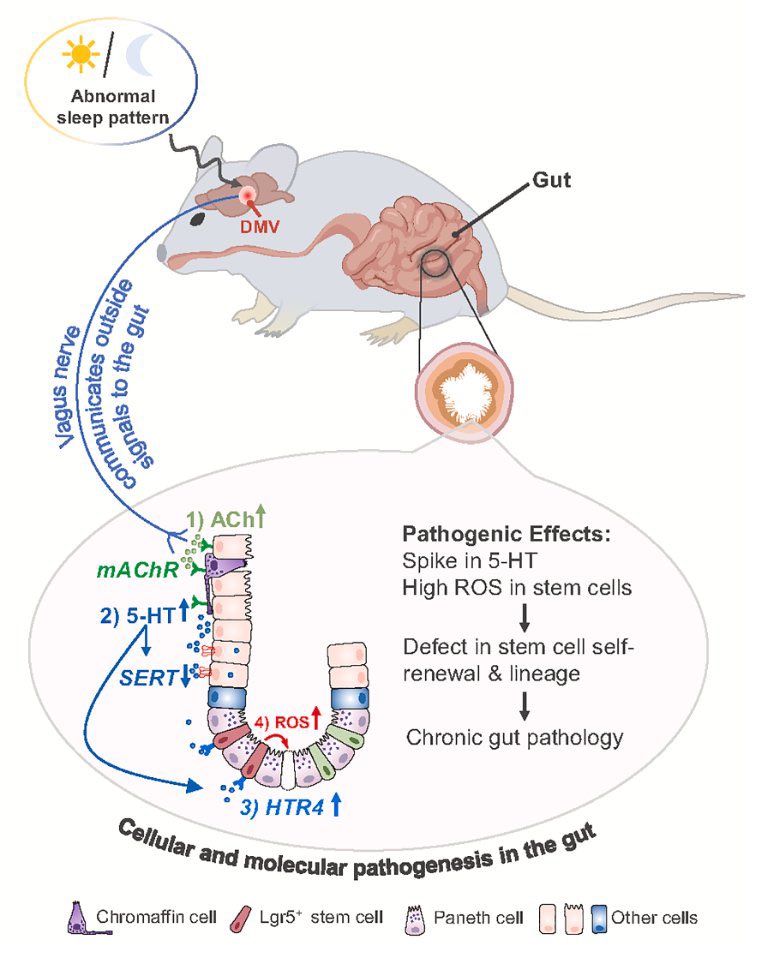
Previous work has shown that the vagus nerve, a large network of nerve fibres that links the body with the brain, influences immune responses. However, the specific brain neurons that are activated by immune stimuli remained elusive. 6/ 

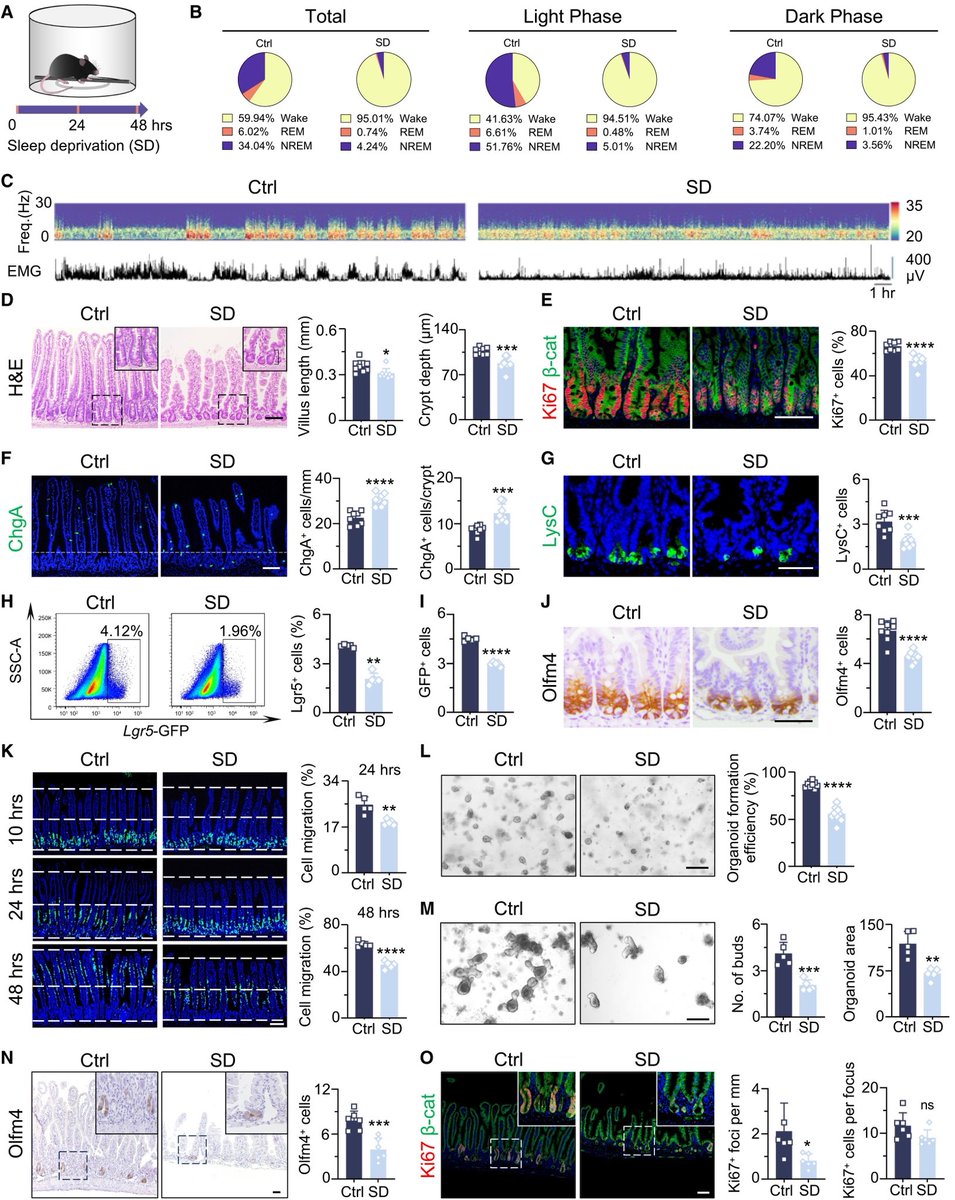
To investigate how the brain controls the body’s immune response, researchers monitored the activity of brain cells after injecting the abdomen of mice with bacterial compounds that trigger inflammation. 7/ 

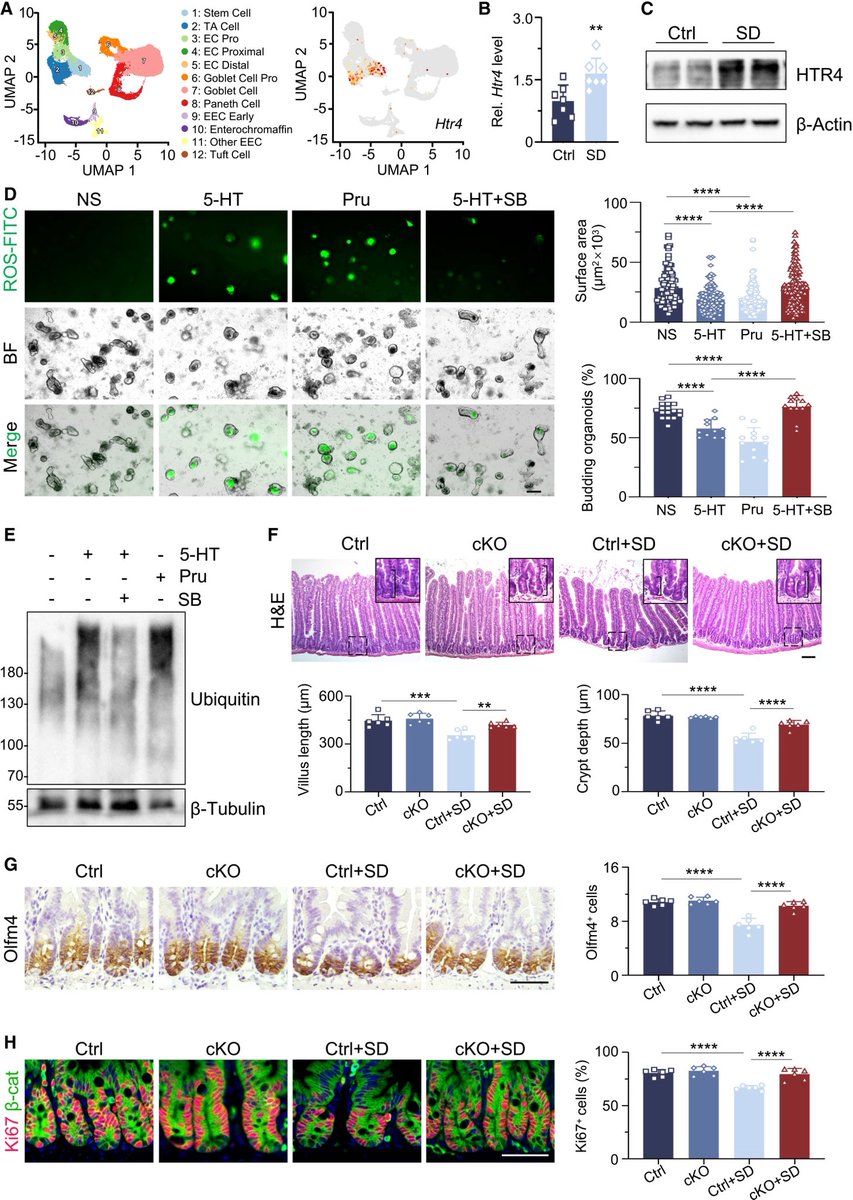
They used single-cell RNA sequencing, combined with functional imaging, to identify the circuit components of this neuro-immune axis. 8/
The researchers identified neurons in the brainstem that switched on in response to the immune triggers. Activating these neurons with a drug reduced the levels of inflammatory molecules in the mice’s blood. 9/
Silencing the neurons led to an uncontrolled immune response, with the number of inflammatory molecules increasing by 300% compared with the levels observed in mice with functional brainstem neurons. 10/
These nerve cells act as a rheostat in the brain that ensures that an inflammatory response is maintained within the appropriate levels. 11/ 

Further experiments showed two discrete groups of neurons in vagus nerve: one that responds to pro-inflammatory immune molecules & another that responds to anti-inflammatory molecules. These neurons relay their signals to the brain, allowing it to monitor the immune response 12/
In mice with conditions characterized by an excessive immune response, artificially activating the vagal neurons that carry anti-inflammatory signals diminished inflammation. 13/
Finding ways to control this newly discovered body–brain network would offer an approach to fixing broken immune responses in various conditions such as autoimmune diseases and even long COVID. 14/
There’s evidence that therapies targeting the vagus nerve can treat diseases such as multiple sclerosisand rheumatoid arthritis, suggesting that targeting the specific vagal neurons that carry immune signals might work in people. 15/15
nature.com/articles/s4158…


nature.com/articles/s4158…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh