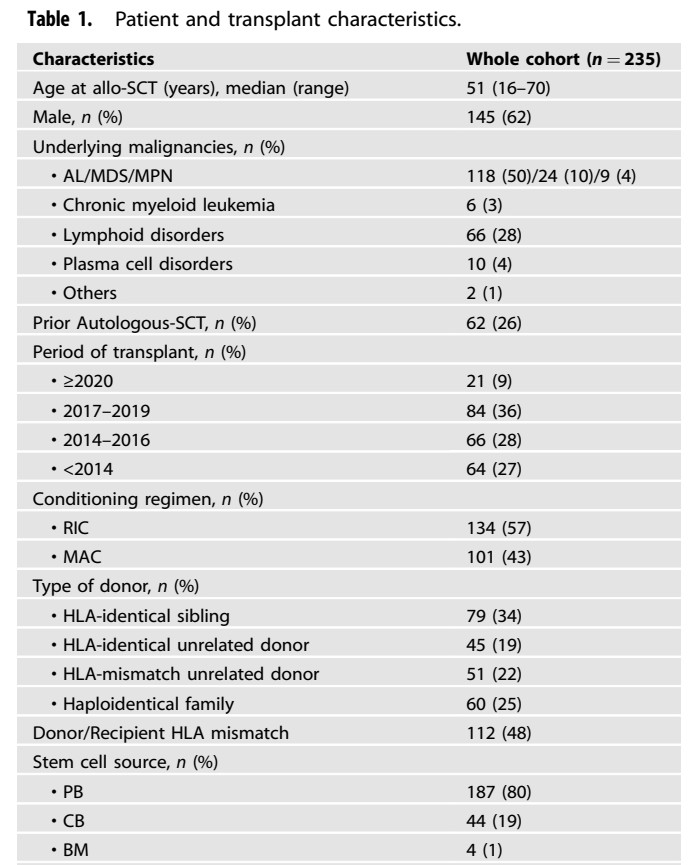
𝗪𝗛𝗢𝗢𝗣 !
𝗧𝗵𝗲 𝗪𝗛𝗢𝗢𝗣𝗜𝗡𝗚 𝗖𝗢𝗨𝗚𝗛 (𝗽𝗲𝗿𝘁𝘂𝘀𝘀𝗶𝘀) 𝗶𝘀 𝗕𝗔𝗖𝗞 !
(𝘮𝘦𝘨𝘢-𝘵𝘩𝘳𝘦𝘢𝘥 🧵)
Thanks to @1goodtern who alerted about this topic in UK, this disease is back.
𝙒𝙃𝙀𝙍𝙀 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙒𝙃𝙔 ?
𝗧𝗵𝗲 𝗪𝗛𝗢𝗢𝗣𝗜𝗡𝗚 𝗖𝗢𝗨𝗚𝗛 (𝗽𝗲𝗿𝘁𝘂𝘀𝘀𝗶𝘀) 𝗶𝘀 𝗕𝗔𝗖𝗞 !
(𝘮𝘦𝘨𝘢-𝘵𝘩𝘳𝘦𝘢𝘥 🧵)
Thanks to @1goodtern who alerted about this topic in UK, this disease is back.
𝙒𝙃𝙀𝙍𝙀 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙒𝙃𝙔 ?
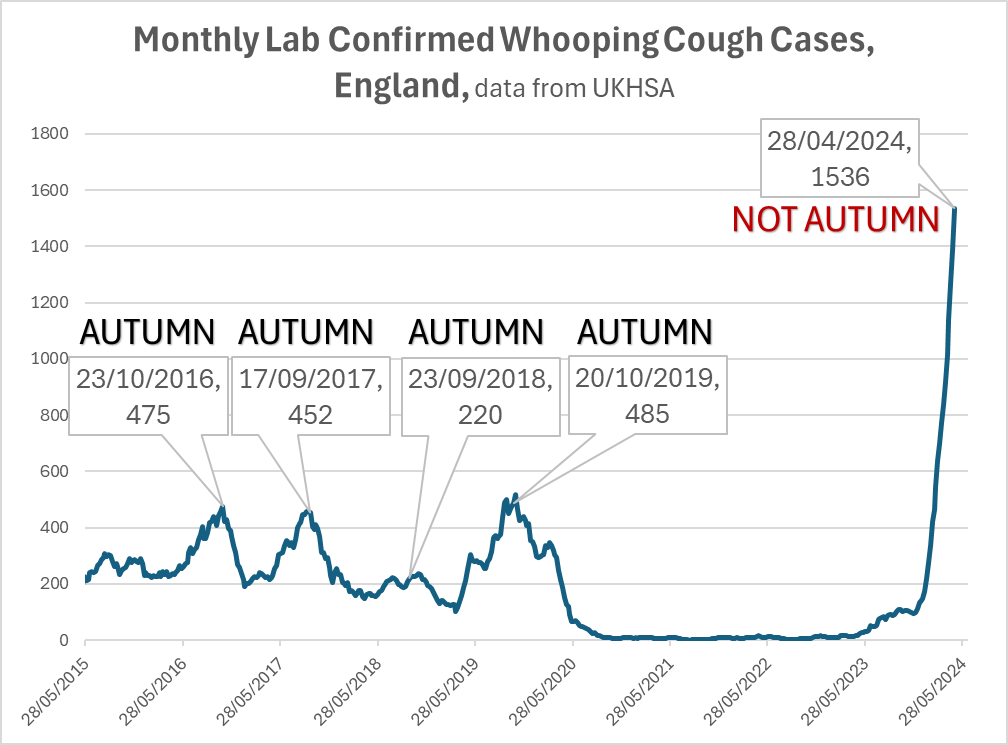
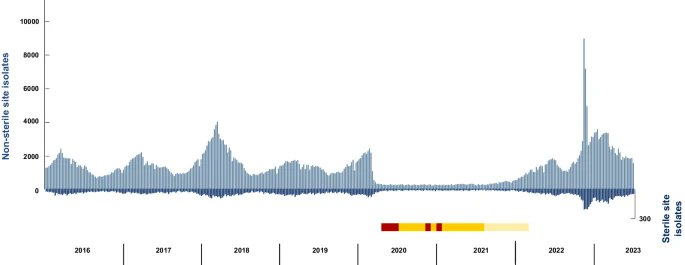
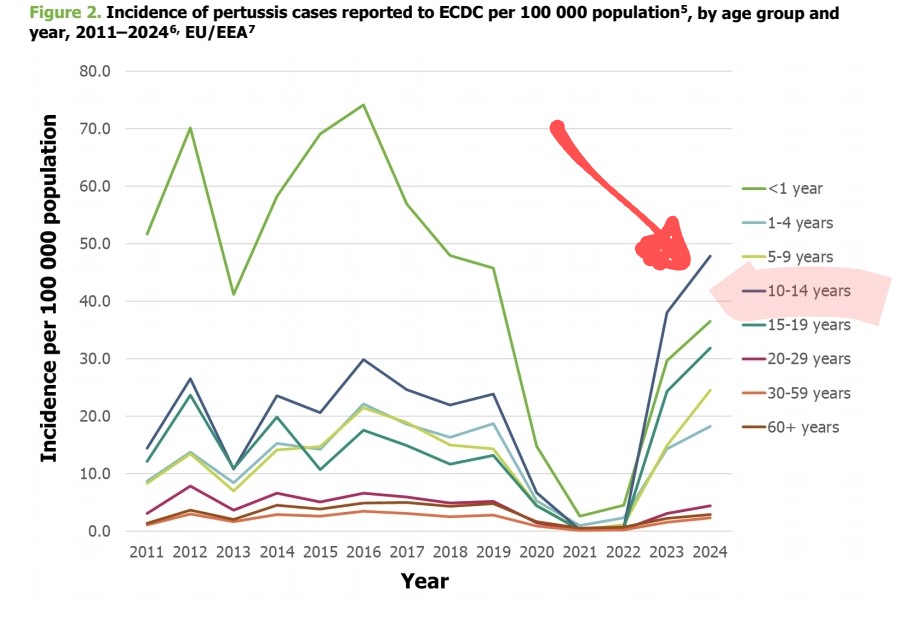
2) Back, not only in UK but also in Europe. 25 000 cases for the all year 2023, 32 000 just from January to March 2024 !!! 
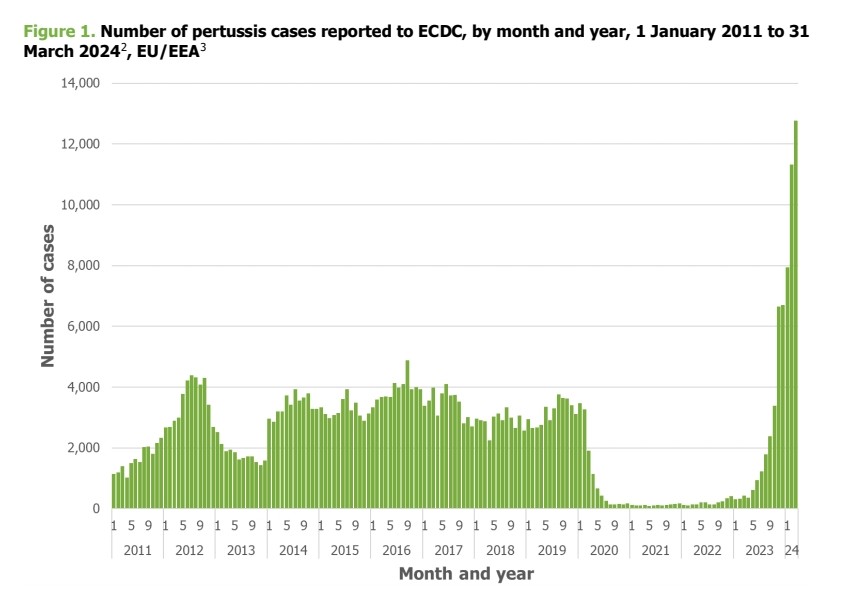
3) For the situation in Europe, we recommend the excellent report of ECDC
"Increase of pertussis cases in the EU/EEA"
ecdc.europa.eu/en/publication…

"Increase of pertussis cases in the EU/EEA"
ecdc.europa.eu/en/publication…

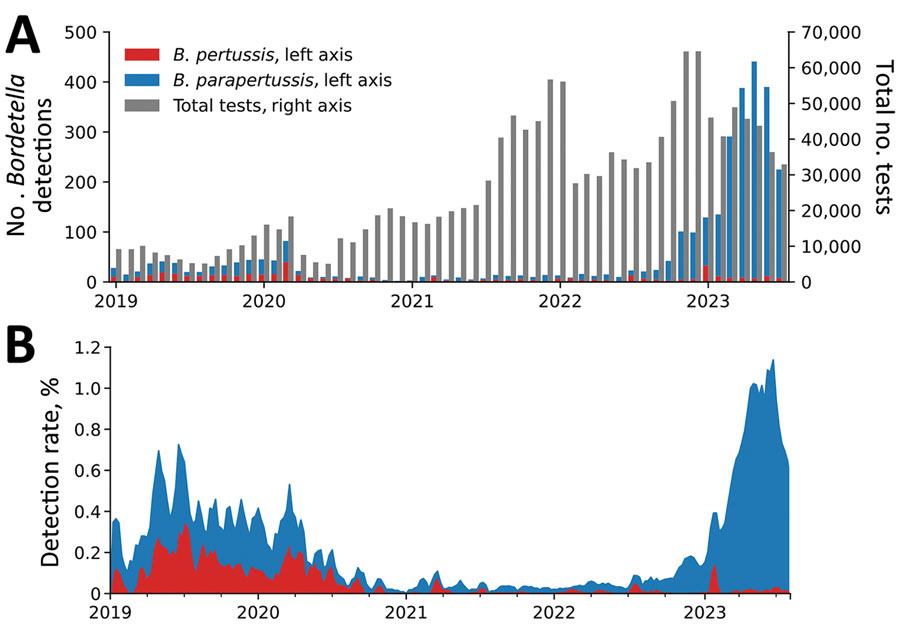
4) We have the same situation in US.
"Reemergence of Bordetella parapertussis, United States, 2019–2023"
wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/30…

"Reemergence of Bordetella parapertussis, United States, 2019–2023"
wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/30…
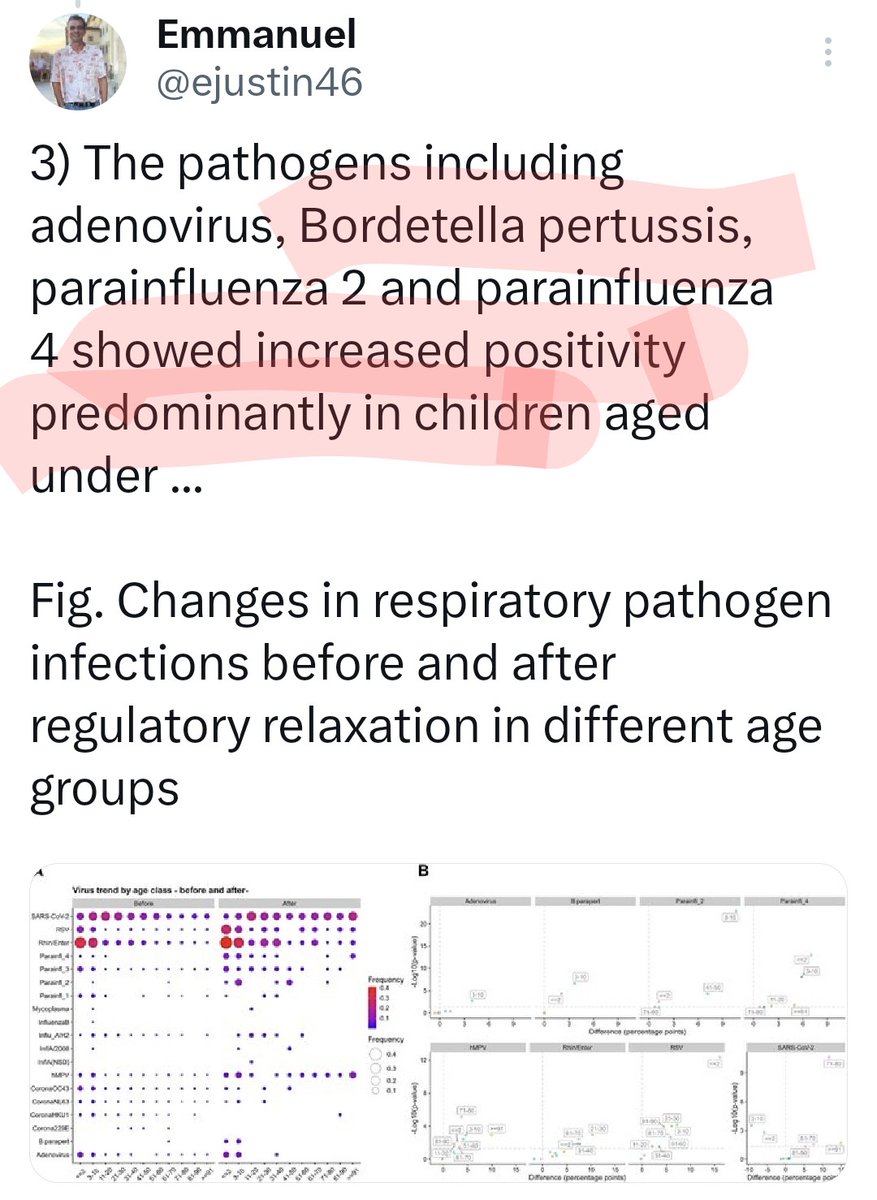
5) In China also, as we posted it few days ago.

https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1788593973461717208?t=IS1sRDi1AJXVz1b9BqGpxw&s=19

6) In Japan :

https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1771418588894867865?t=R-kEv_ynL5byZMbEHPElog&s=19
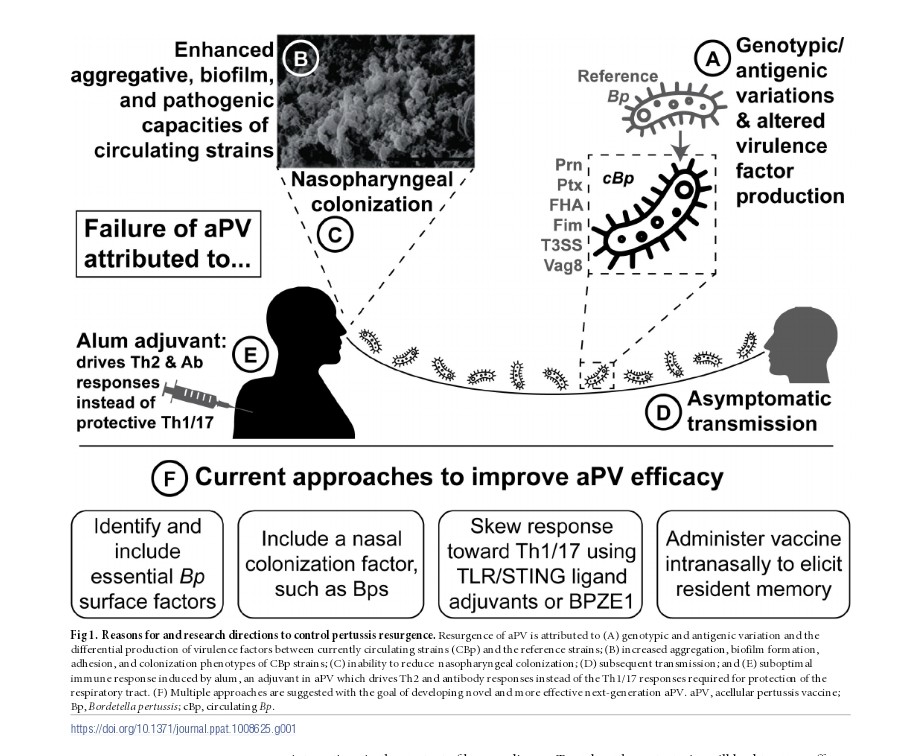
7) One of the main reason seems to be the decrease, or lack of vaccination, as this study showed it.
cambridge.org/core/journals/…

cambridge.org/core/journals/…

8) Another study raised the question of waning immunity after the vaccination ...
cambridge.org/core/journals/…

cambridge.org/core/journals/…

10) But there is something strange in the ECDC report. The strongest progression concerns 10-14 year olds. It is difficult to speak of "immunity debt" (or even immunity gap), or even a drop in vaccinations in this age group.
There may be other hypotheses to explain this increase.
There may be other hypotheses to explain this increase.
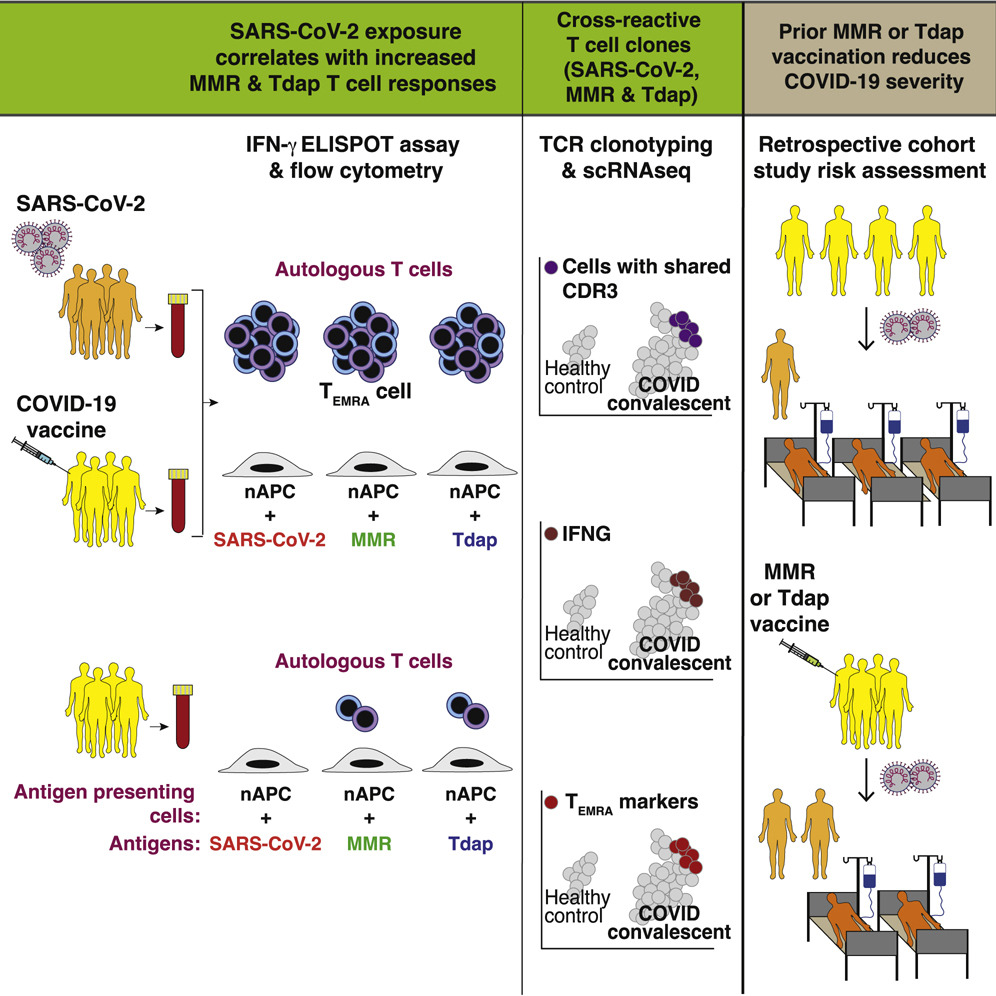
11) 1st hypothesis that we would like to propose without being able to develop it.
There is a protective heterologous T cell immunity in COVID-19 induced by the Tdap vaccine antigens.
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…

There is a protective heterologous T cell immunity in COVID-19 induced by the Tdap vaccine antigens.
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…

12) However, the T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Tdap vaccine proteins are highly correlated. Does the weakening of T cells following a COVID-19 infection contribute in the opposite direction to a reduction in the defenses in children facing pertussis? 
13) 2nd hypothesis. SARS-CoV-2 has bacteriophage behavior.
Does this have an impact on the bordella pertusis bacteria which is the cause of whooping cough?
Carlo Brogna @carlobrogna1 sent us a lot of studies on this subject today. We will come back to this topic very soon.
Does this have an impact on the bordella pertusis bacteria which is the cause of whooping cough?
Carlo Brogna @carlobrogna1 sent us a lot of studies on this subject today. We will come back to this topic very soon.
@carlobrogna1 14) Thanks for reading 🙏
and see you soon
FYI
@DrEricDing @DavidJoffe64 @C_A_G0101 @LauraMiers @RWittenbrink
and see you soon
FYI
@DrEricDing @DavidJoffe64 @C_A_G0101 @LauraMiers @RWittenbrink
15) The correct reference in the post 8 is here 👇
Thanks to @jorgenponder to tell me and sorry for the mistake 🙏researchgate.net/publication/34…
Thanks to @jorgenponder to tell me and sorry for the mistake 🙏researchgate.net/publication/34…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh