𝗔𝗡𝗧𝗜𝗕𝗜𝗢𝗧𝗜𝗖𝗦 𝗢𝗩𝗘𝗥𝗨𝗦𝗘 😨
42.1% 𝗼𝗳 𝗖𝗢𝗩𝗜𝗗 𝗣𝗔𝗧𝗜𝗘𝗡𝗧𝗦 𝗵𝗮𝗱 𝗺𝘂𝗹𝘁𝗶𝗱𝗿𝘂𝗴 𝗥𝗘𝗦𝗜𝗦𝗧𝗔𝗡𝗧 𝗕𝗔𝗖𝗧𝗘𝗥𝗜𝗔 𝗜𝗡𝗙𝗘𝗖𝗧𝗜𝗢𝗡𝗦 !
(Global systematic review of 173 studies with 892K+ COVID patients)
42.1% 𝗼𝗳 𝗖𝗢𝗩𝗜𝗗 𝗣𝗔𝗧𝗜𝗘𝗡𝗧𝗦 𝗵𝗮𝗱 𝗺𝘂𝗹𝘁𝗶𝗱𝗿𝘂𝗴 𝗥𝗘𝗦𝗜𝗦𝗧𝗔𝗡𝗧 𝗕𝗔𝗖𝗧𝗘𝗥𝗜𝗔 𝗜𝗡𝗙𝗘𝗖𝗧𝗜𝗢𝗡𝗦 !
(Global systematic review of 173 studies with 892K+ COVID patients)

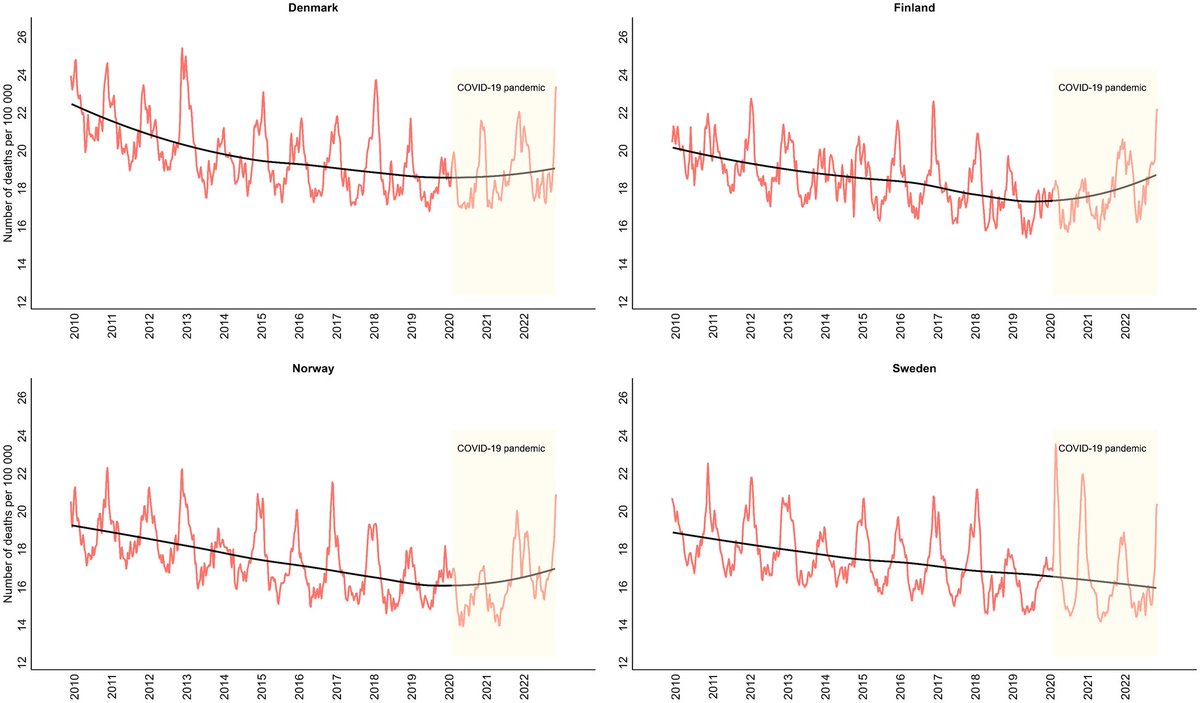
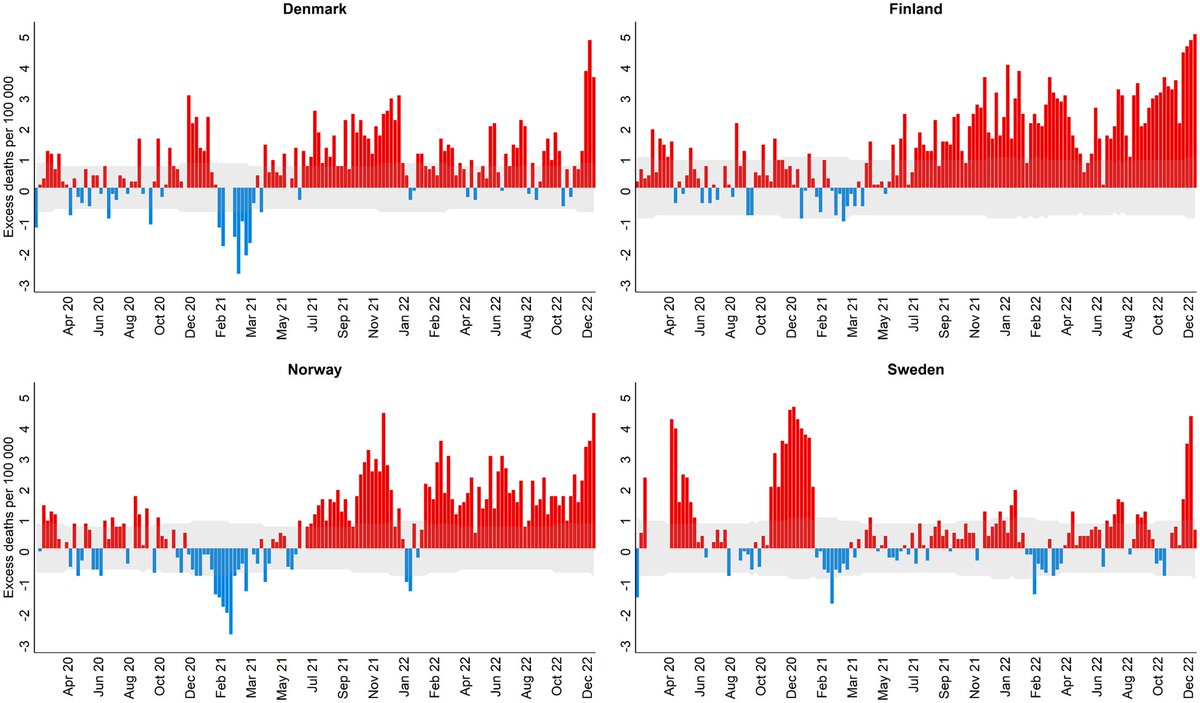
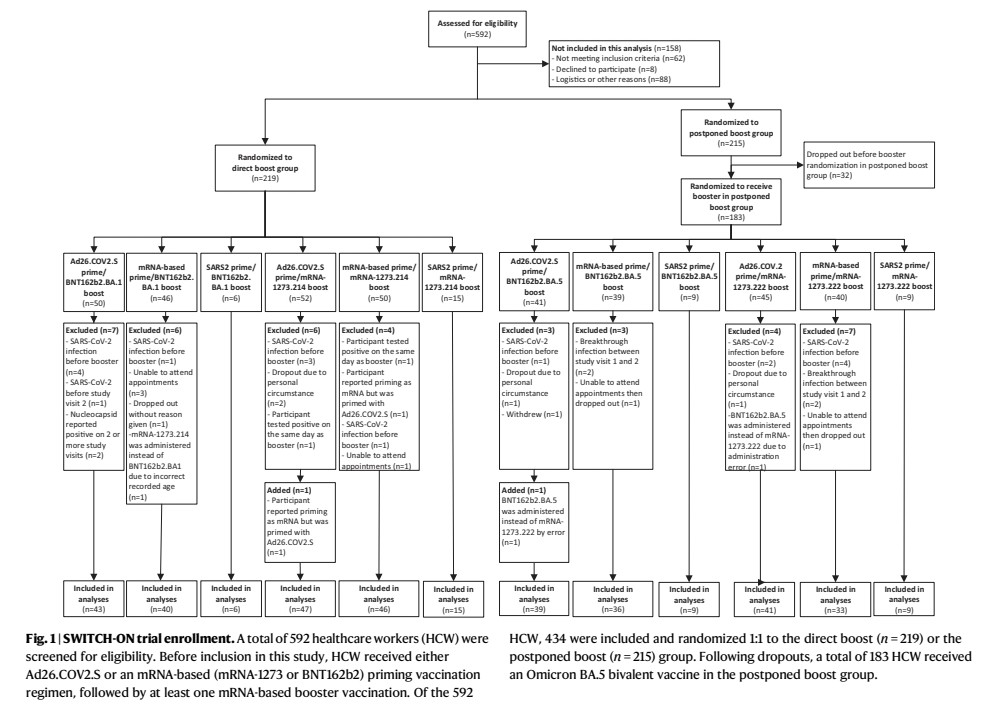
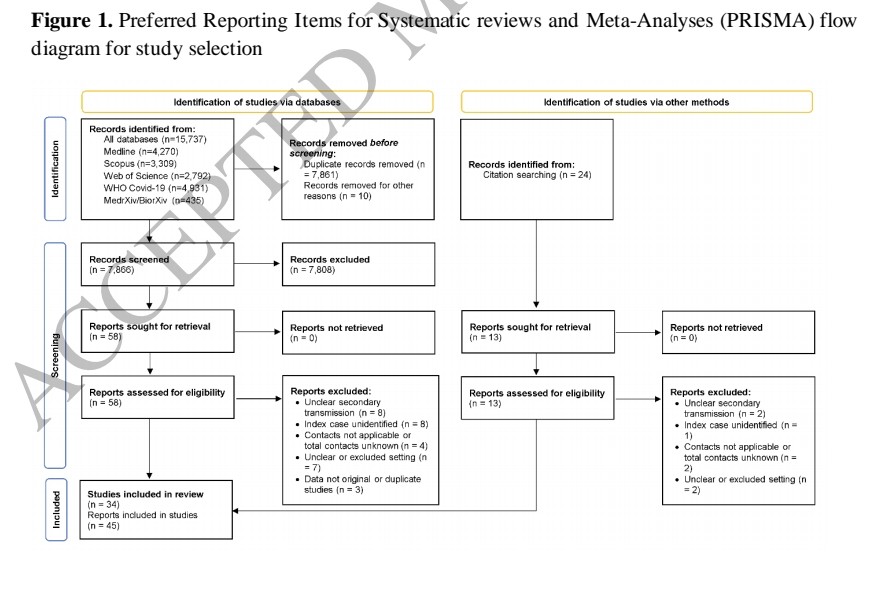
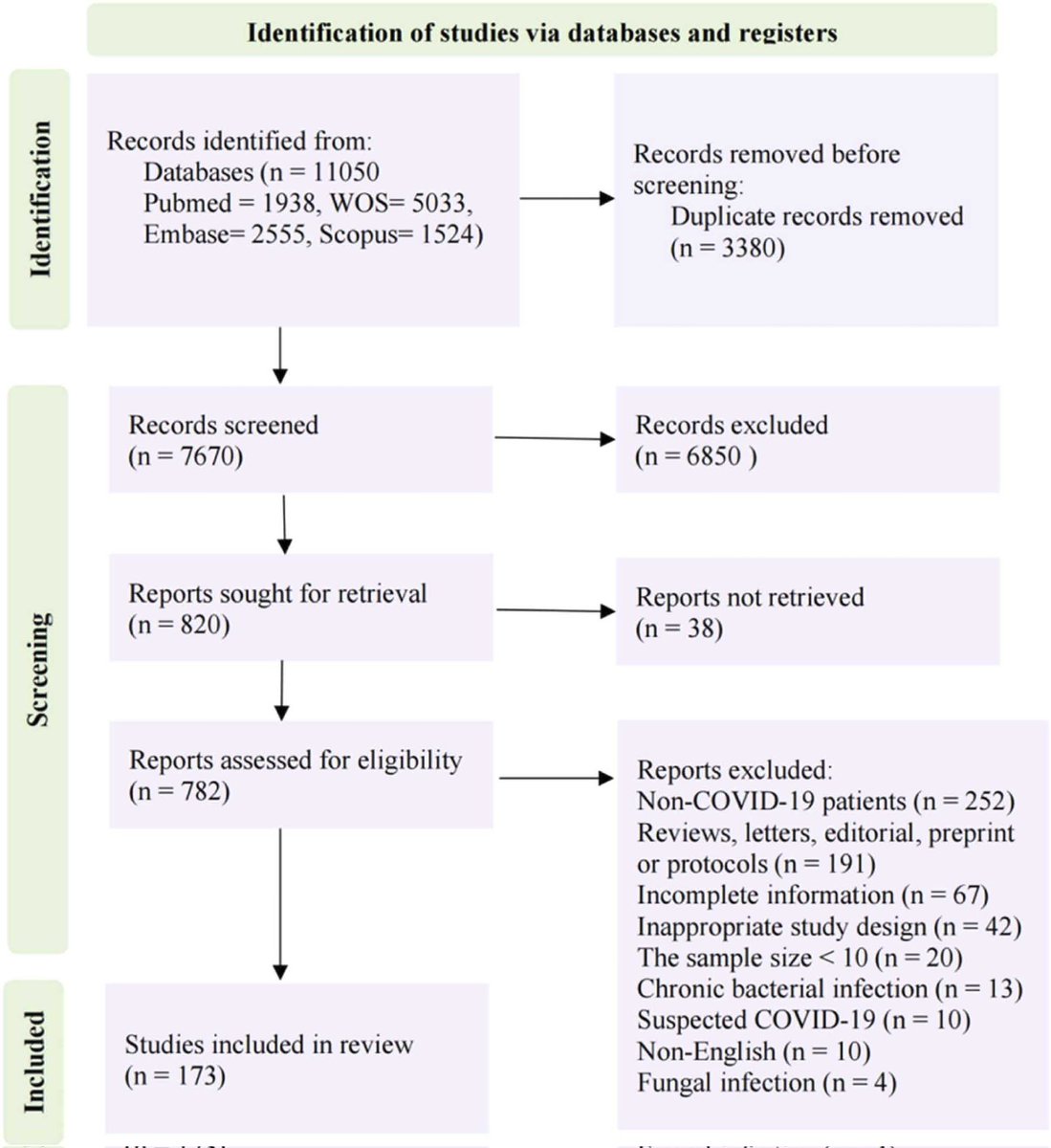
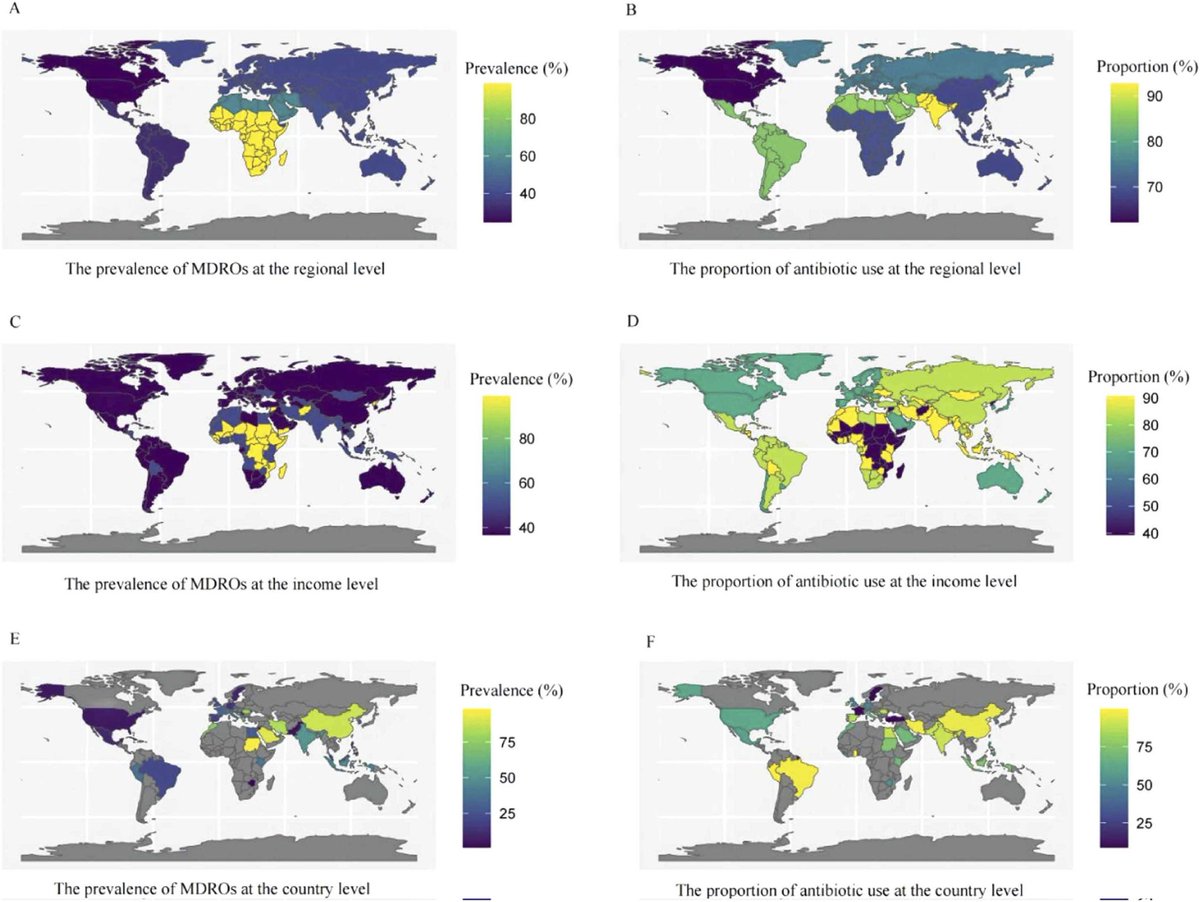
2) This systematic review and meta-analysis of 173 studies with 892,312 COVID-19 patients provided a comprehensive assessment of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and antibiotic usage during the pandemic. It reported a 42.1% prevalence of multidrug-resistant organism infection ... 

3) ...(MDRO) among bacterial co-infected patients and found 76.2% of all COVID patients received antibiotics. Lower-middle and low-income regions faced greater challenges seen by higher antimicrobial resistance prevalence and antibiotic overuse. 
4) Subgroup analyses showed MDRO prevalence and drug usage were highest among severe/critical cases and those admitted to intensive care. 
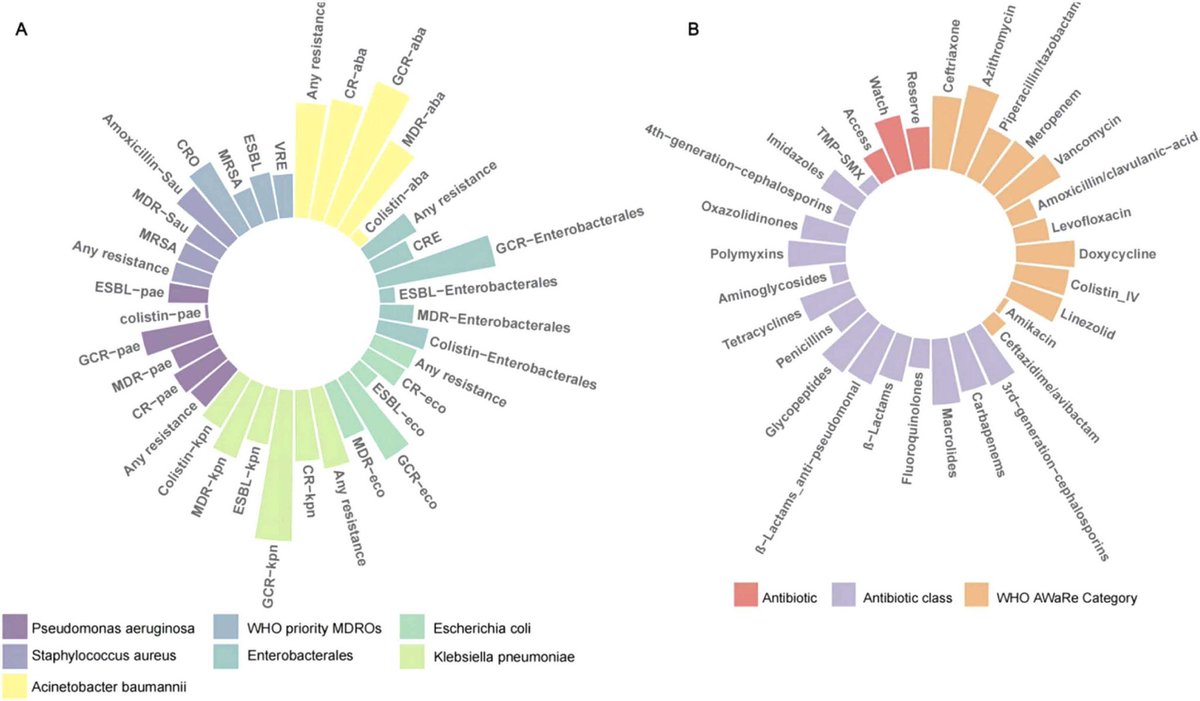
5) The findings underline the urgent need for sustained global efforts to strengthen antimicrobial stewardship in the wake of public health emergencies.
Thanks for reading 🙏
FYI
@1goodtern @C_A_G0101 @DavidJoffe64
Reference :
journalofinfection.com/article/S0163-…

Thanks for reading 🙏
FYI
@1goodtern @C_A_G0101 @DavidJoffe64
Reference :
journalofinfection.com/article/S0163-…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh