1/11 Baseless doom and gloom: war is not just a matter of quantity, but also of quality. Analysis by @joni_askola 

2/11 There is a great deal of doom and gloom surrounding russia's purported army regeneration and increased resources. These assessments focus solely on quantity rather than quality. Furthermore, they place trust in russian figures, which are almost always deceitful. 

3/11 The individuals discussing russia's military resurgence overlook the fact that Ukraine has substantially bolstered its armed forces during the same timeframe. As a result, Ukraine's army is now considerably more capable than it was at the beginning of the full-scale war. 

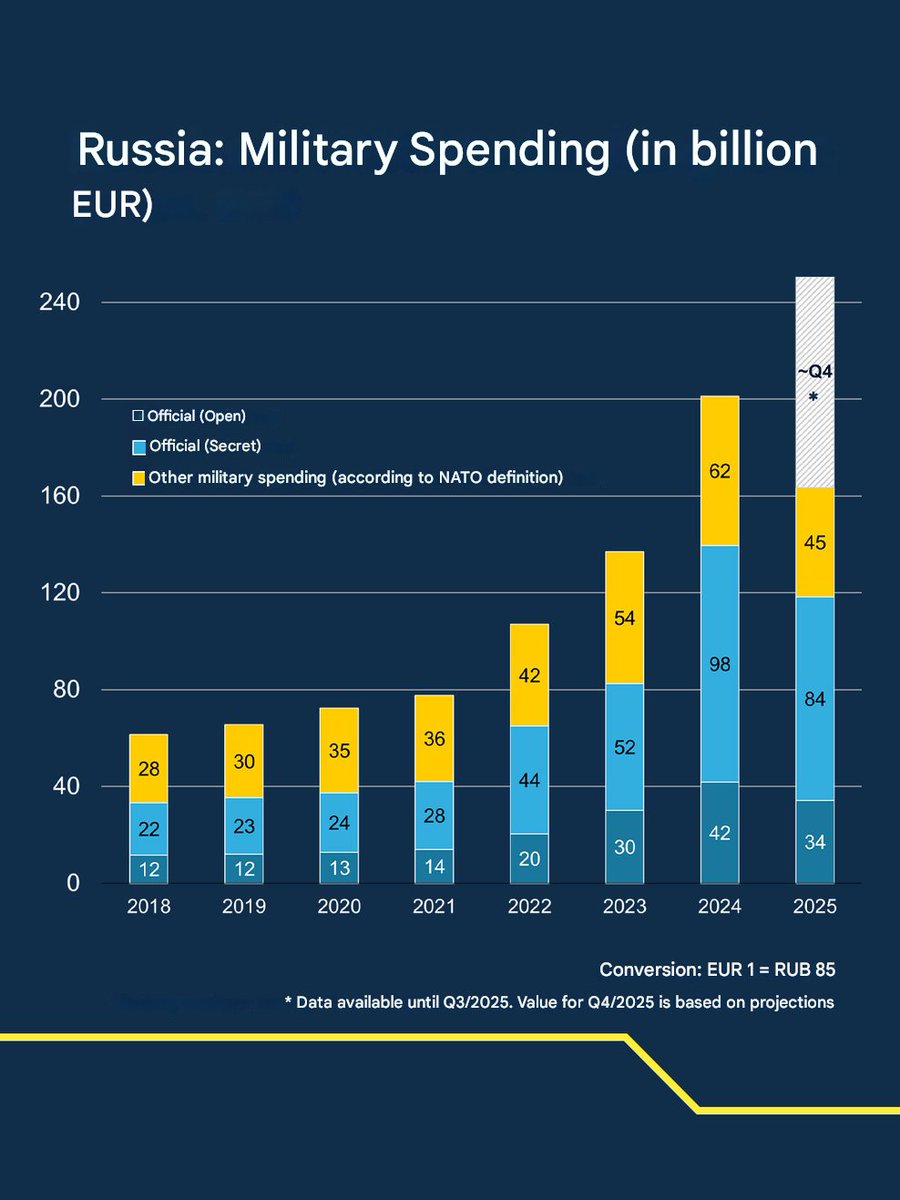
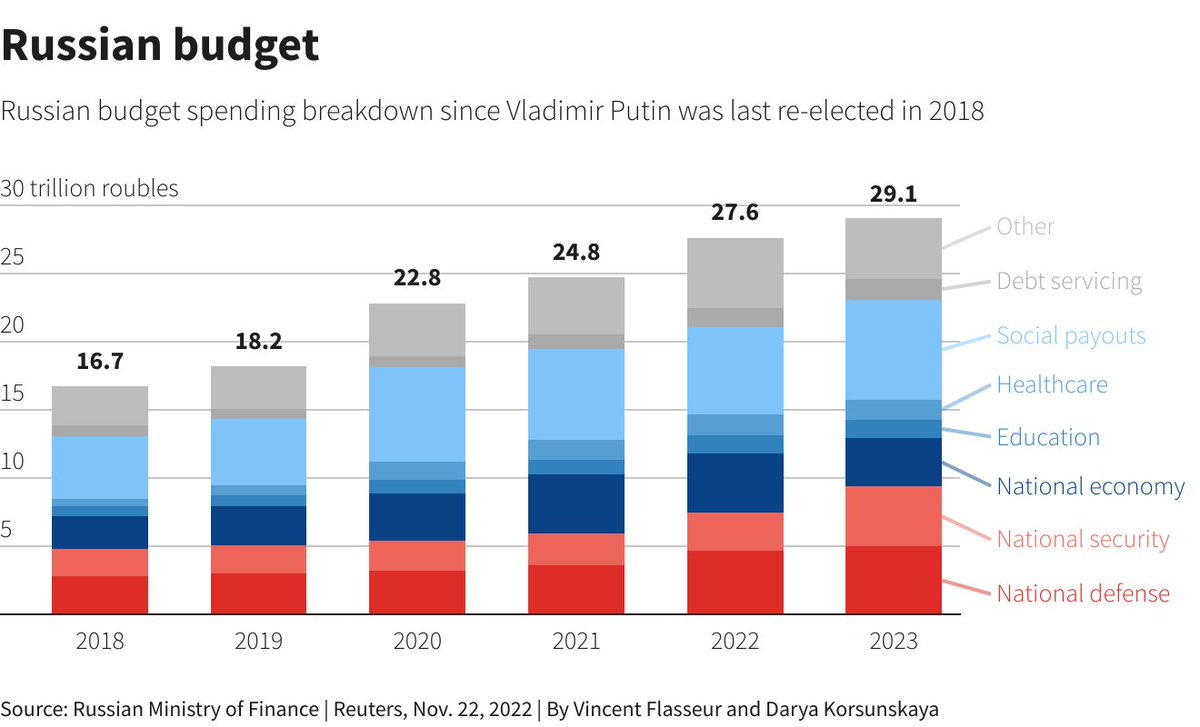
4/11 russia is presently depleting its resources at a rate far exceeding its production capacity. To compensate, it is utilizing older Soviet-era resources from its stockpiles. However, this equipment is outdated and of inferior quality compared to the machinery it is replacing. 

5/11 Within 18 to 24 months, russia will deplete its supply of Soviet-era resources, leading to a highly challenging predicament. It is unfeasible for russian production to ramp up sufficiently within this timeframe. 

6/11 Prior to this depletion, the quality of russia's equipment will continue to decline, while Ukraine's equipment quality will improve through Western assistance. Most Western weapon systems are significantly superior to those of russia. 

7/11 If wars were solely determined by quantity, Russia would have already invaded Ukraine, and the USSR would have conquered Finland in a matter of days. However, quality also plays a significant role. In the case of Ukraine, its Western weapons are of superior quality. 

8/11 russia's invasion of Ukraine has been a dismal failure, as it has not succeeded in capturing any of the 23 regional capitals and special status cities that Ukraine controlled at the onset of the war. 

9/11 The upcoming months will pose significant challenges as Ukraine mobilizes and trains troops, simultaneously defending the front lines, constructing defensive barriers, and awaiting the arrival of military aid. 

10/11 Should Ukraine endure the next few months without substantial territorial or human losses, its situation is poised to improve by the year's end. russia's window of opportunity is gradually narrowing, and the disparity in quantity between russia and Ukraine will diminish. 

11/11 Source: rusi.org/explore-our-re…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh