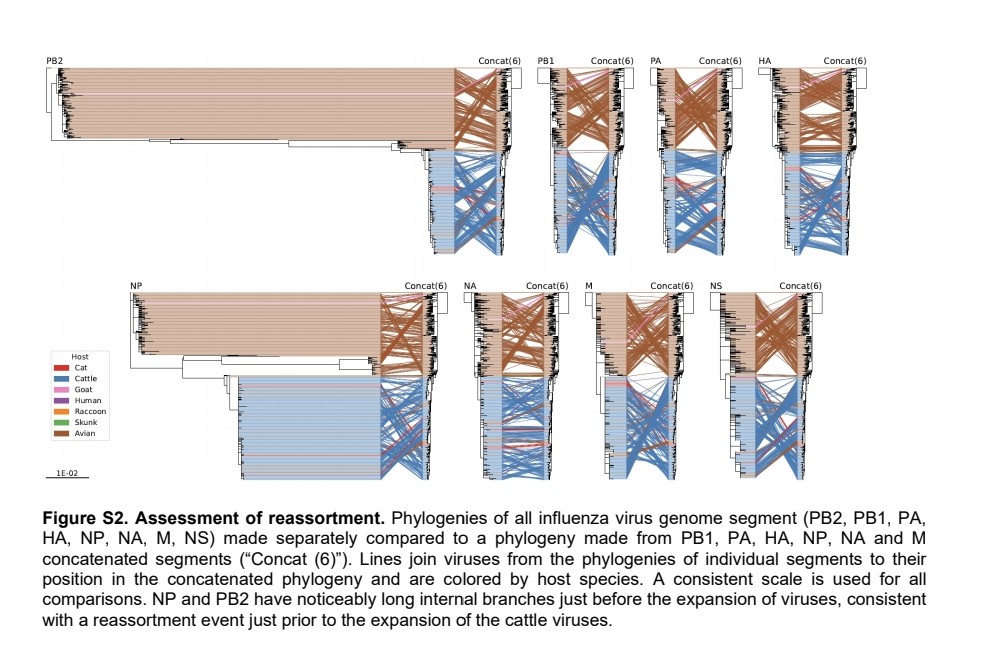
𝗠𝗲𝘁𝗮-𝗮𝗻𝗮𝗹𝘆𝘀𝗶𝘀 𝗮𝗯𝗼𝘂𝘁 𝗜𝗡𝗙𝗟𝗨𝗘𝗡𝗭𝗔 𝗩𝗔𝗖𝗖𝗜𝗡𝗔𝗧𝗜𝗢𝗡 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗖𝗢𝗩𝗜𝗗-19 𝗜𝗡𝗙𝗘𝗖𝗧𝗜𝗢𝗡 𝗥𝗜𝗦𝗞 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗗𝗜𝗦𝗘𝗔𝗦𝗘 𝗦𝗘𝗩𝗘𝗥𝗜𝗧𝗬
ajicjournal.org/article/S0196-…

ajicjournal.org/article/S0196-…

2) This systematic review including 14 prospective studies found no significant association between influenza vaccination and reduced risk of COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, or death. 

3) Meta-analysis showed influenza vaccination was not protective against SARS-CoV-2 infection (SRR 0.95, 95%CI 0.81-1.11) or hospitalization/mortality due to COVID-19 (hospitalization: SRR 0.90, 95%CI 0.68-1.19; mortality: SRR 0.83, 95%CI 0.56-1.23). 
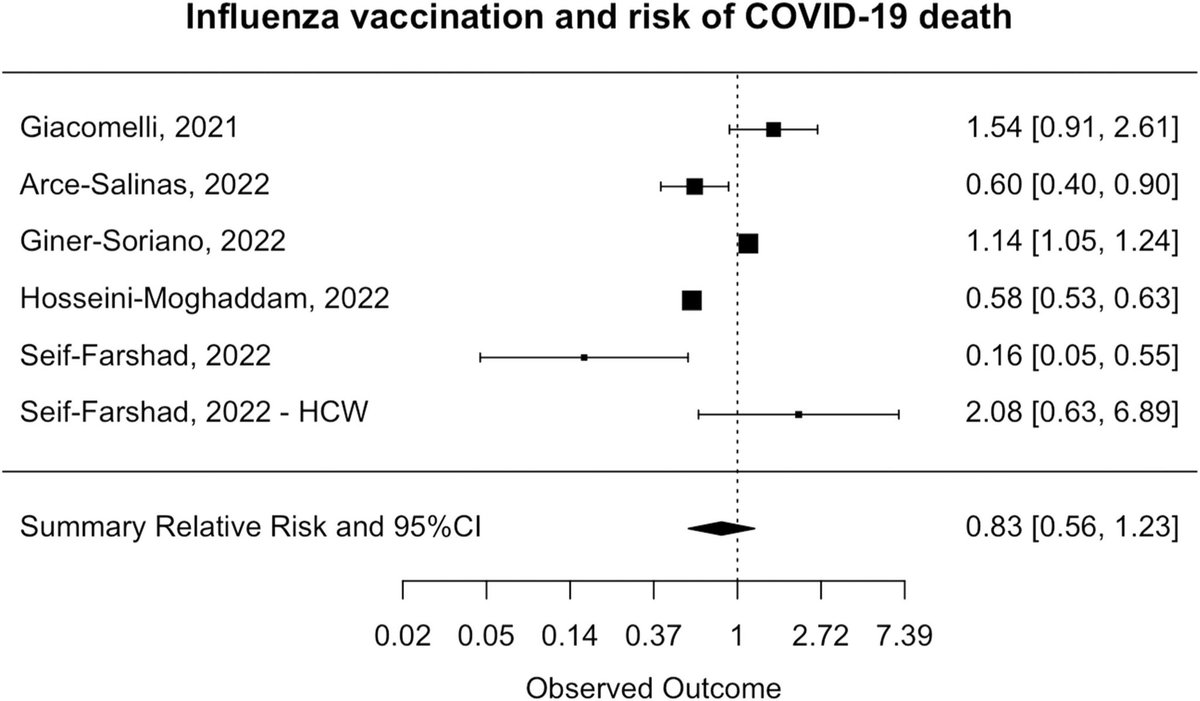
4) Prospective data provided robust evidence that influenza vaccines did not directly reduce COVID-19 burden of disease.
Thanks for reading 🙏
Thanks for reading 🙏
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh