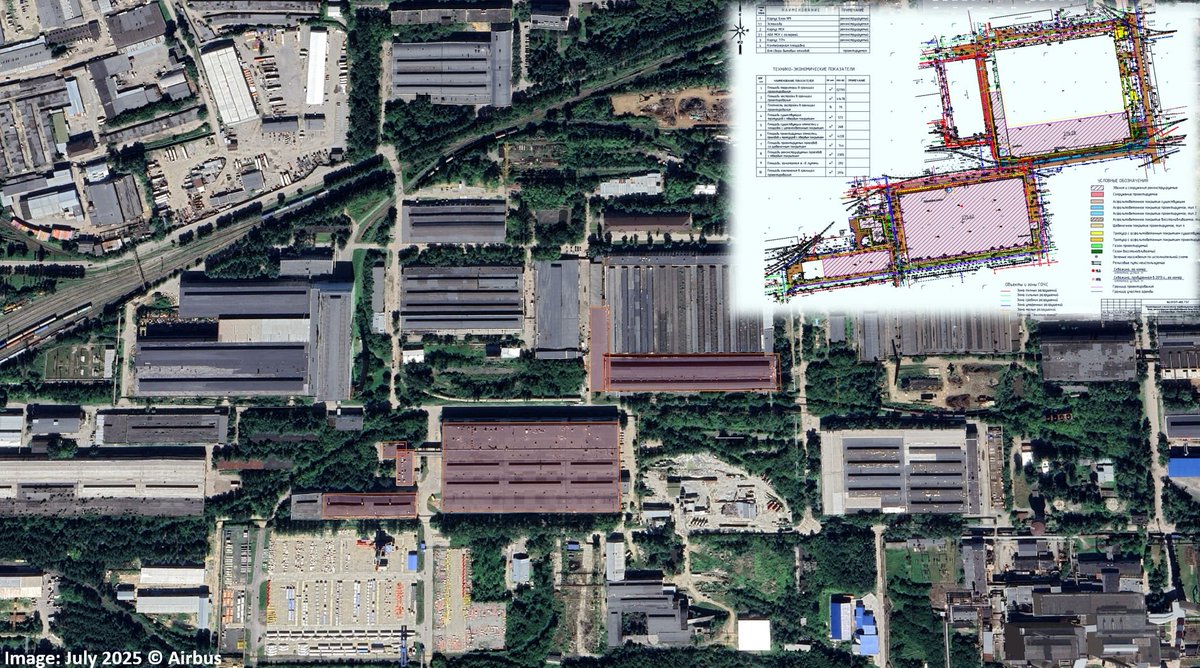
Investigation by Frontelligence Insight reveals that since 2022, despite sanctions, Russian cruise missile manufacturer Raduga has not only continued to operate but also expanded production, thanks to imported Western and Chinese machinery
🧵Thread (Please Like and Share first):
🧵Thread (Please Like and Share first):

2/ "Raduga" is a design bureau located in Dubna, Moscow Oblast, specializing in the production of missile systems, which are now used against Ukraine. This includes various modifications of the Kh-55, Kh-59, and Kh-101 missiles, as well as other missile types and models. 

3/ The Raduga State Machine Building Design Bureau was sanctioned by the U.S. Treasury on March 24, 2022. Despite these sanctions, the enterprise has continued its operations. However, the production of high-precision missiles isn't entirely reliant on domestic resources alone. 

4/ Thanks to the Ukrainian Cyber Resistance @CyberResUa, which provided us with materials from Raduga, we were able to analyze hundreds of conversations and inspect documents containing evidence of the continued acquisition of foreign components for production.
5/ The key document of our investigation is Raduga's Plan for Technical Modernization and Reconstruction for 2023. It provides a detailed description of needs, expansion costs, and goals aimed at meeting the requirements and production volumes set by the Ministry of Defense 

6/ This detailed plan included a budget and a list of specific equipment, along with their country of origin. The following non-Russian companies have been listed: Fagima Jazz R (Italy), Automator (Italy), Hottenger Gmbh (Germany), Hangcha (China), and Hision (China). 

7/ It remains unclear whether this equipment is purchased through third parties or third countries, but in some cases, like with Italian FAGIMA FRESATRICI SRL, business was likely conducted directly with the company. 

8/ Based on the semi-annual report on task progress, most tasks were completed on time, with some even ahead of schedule, suggesting that some of the listed equipment has already been successfully purchased and delivered. 

9/ Based on the same document, it's evident that the finances were allocated towards purchasing new equipment, constructing and modernizing buildings, upgrading laboratory and testing facilities, and developing IT solutions.
10/ While the Frontelligence Insight team cannot determine whether all these companies are fully, partially aware of this, or unaware of it at all, without strict enforcement of sanctions, Russia will find ways to circumvent sanctions and expand its military production.
11/ These companies should undergo additional scrutiny to determine how their equipment ends up in Russian missile production:
- Fagima (Italy)
- Automator (Italy), provided through Атомус
- Hottinger Gmbh (Germany)
- Hangcha (China)
- Hision (China)
- Fagima (Italy)
- Automator (Italy), provided through Атомус
- Hottinger Gmbh (Germany)
- Hangcha (China)
- Hision (China)
12/ Thank you for taking the time to read our investigation.
The full report with more details will be released later this week. Meanwhile, we would greatly appreciate it if you could consider liking and sharing the first message of the thread to help increase its visibility
The full report with more details will be released later this week. Meanwhile, we would greatly appreciate it if you could consider liking and sharing the first message of the thread to help increase its visibility
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh