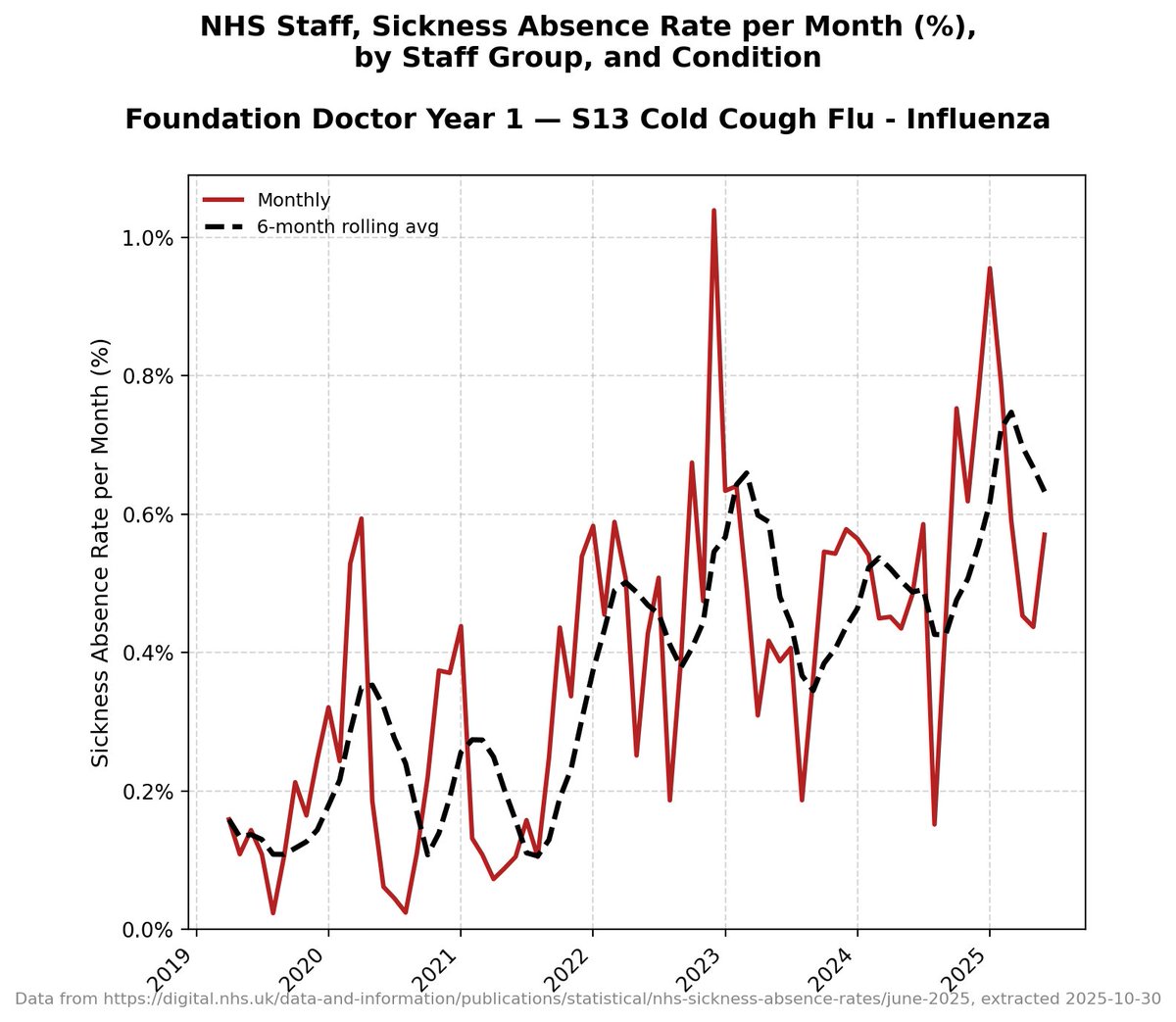
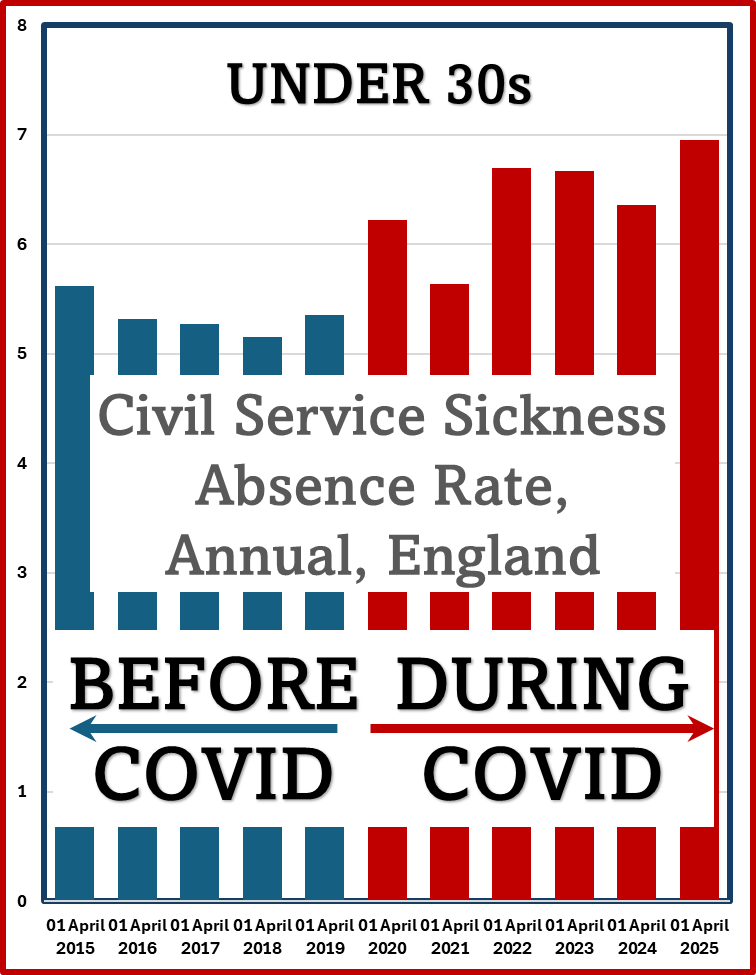
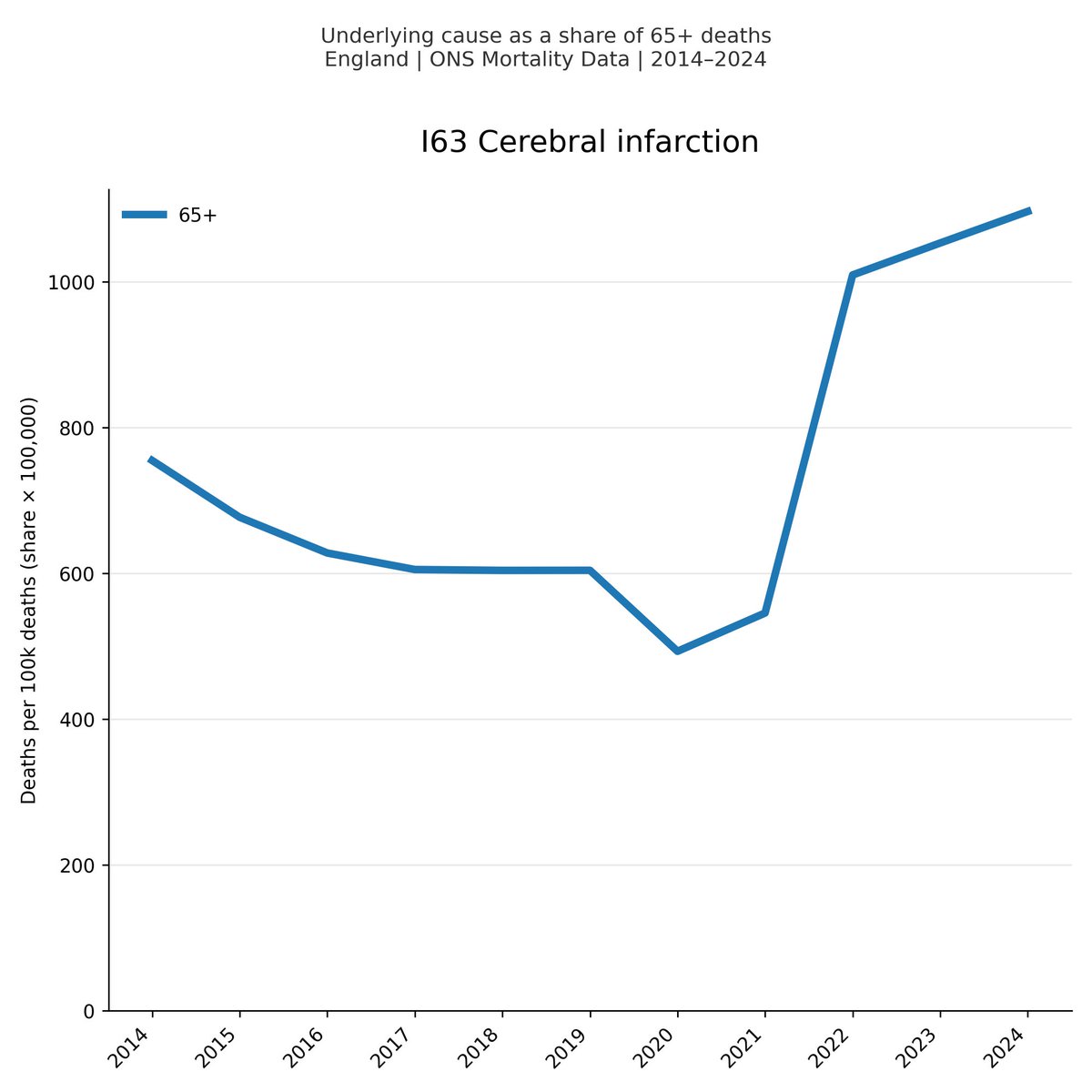
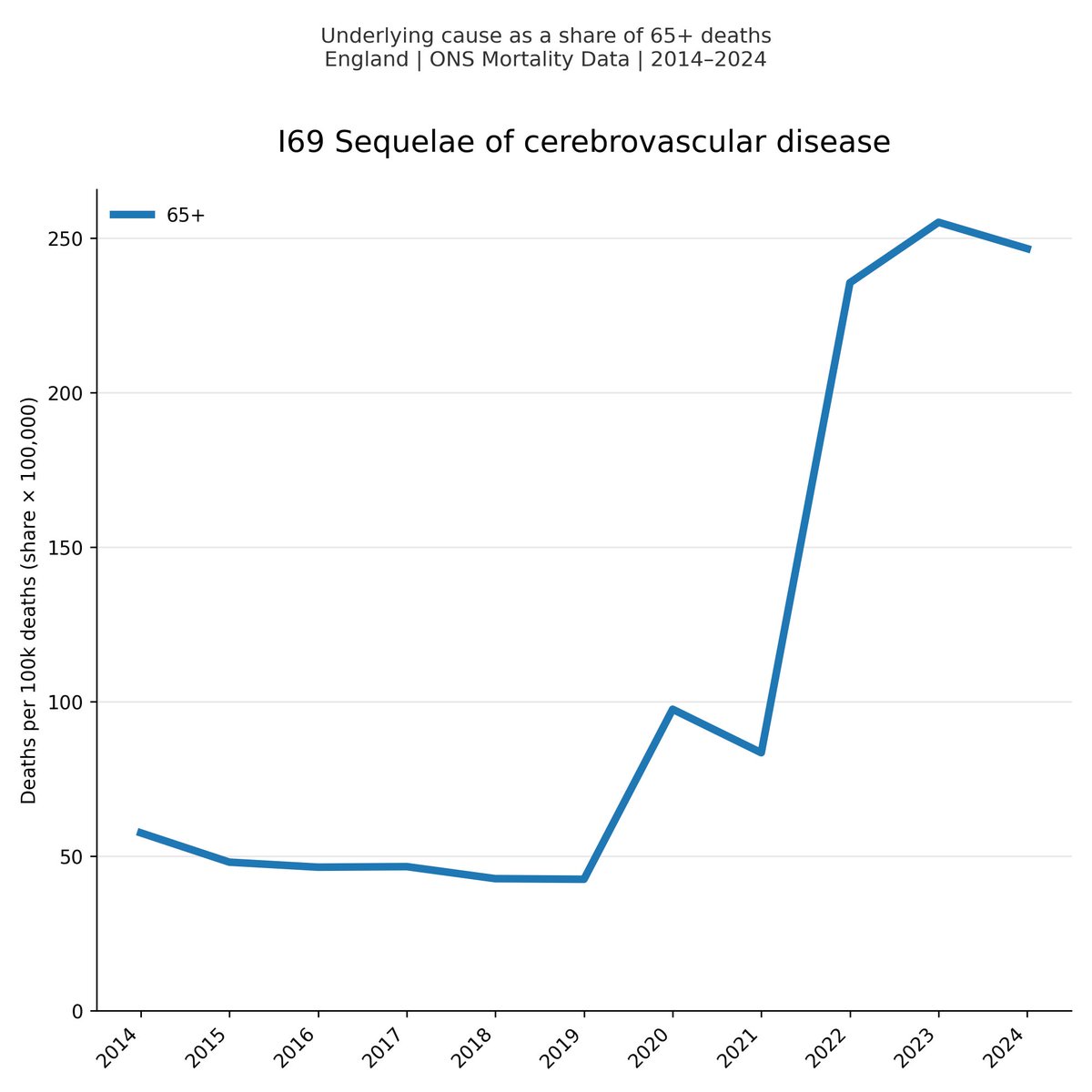
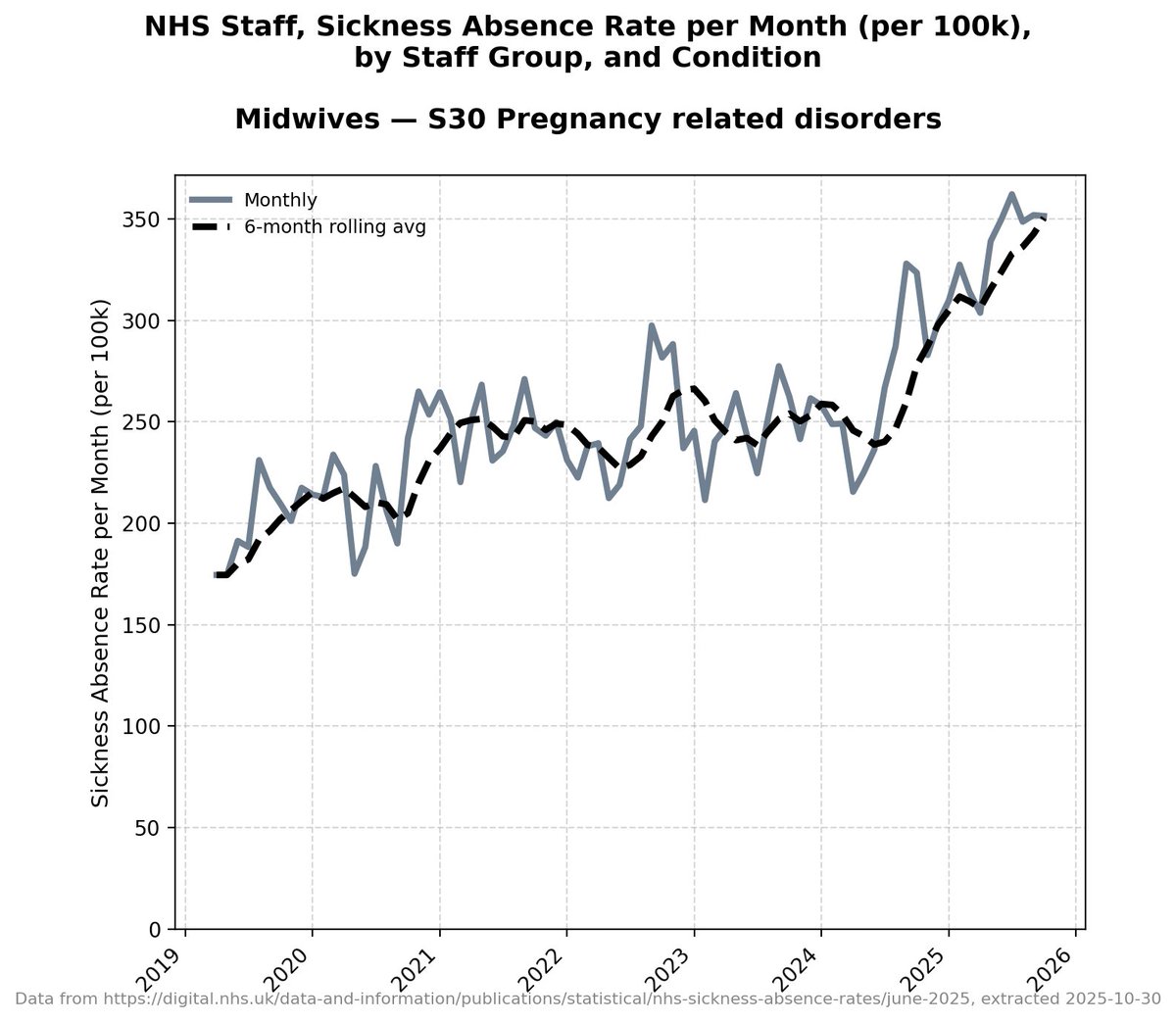
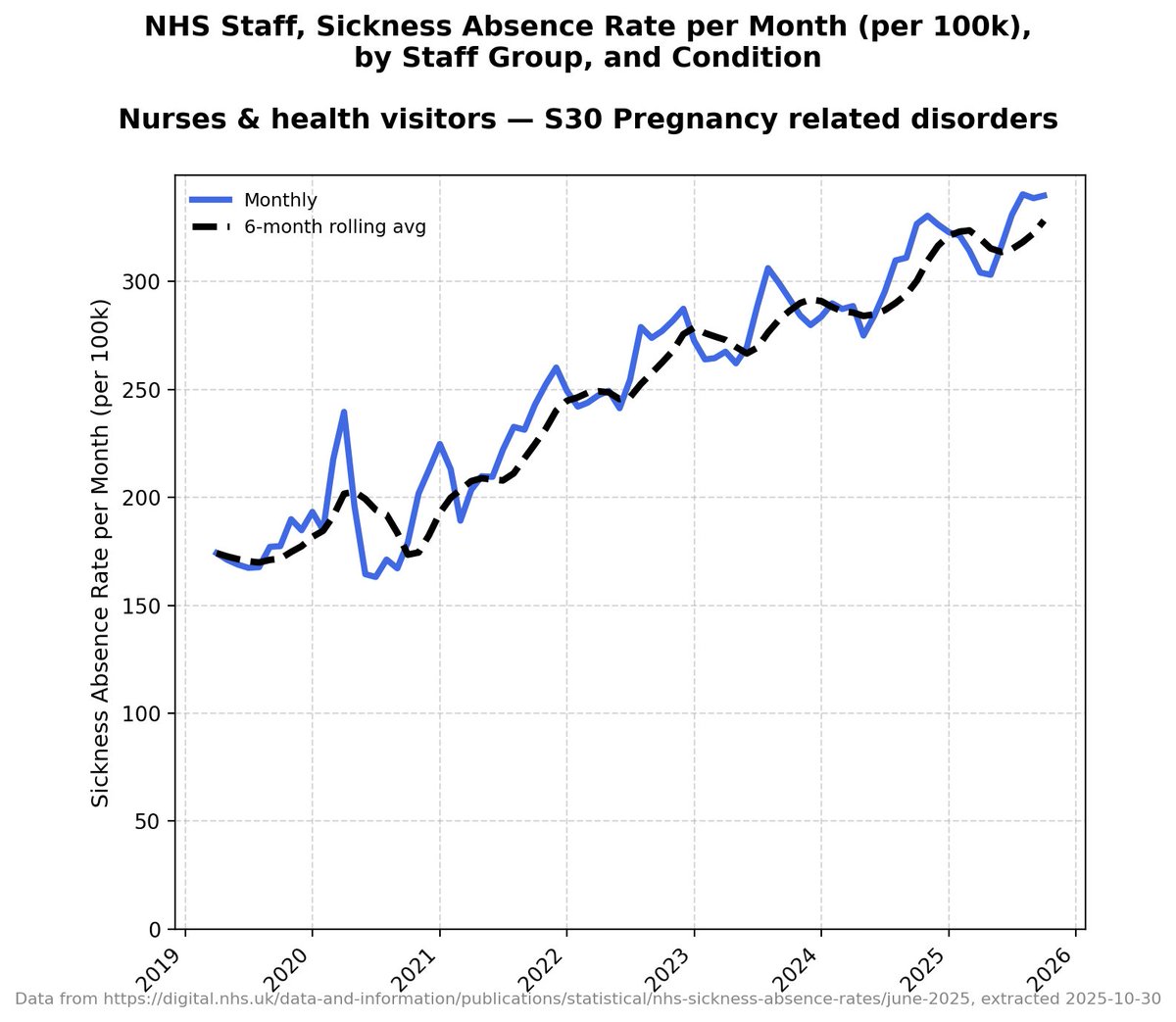
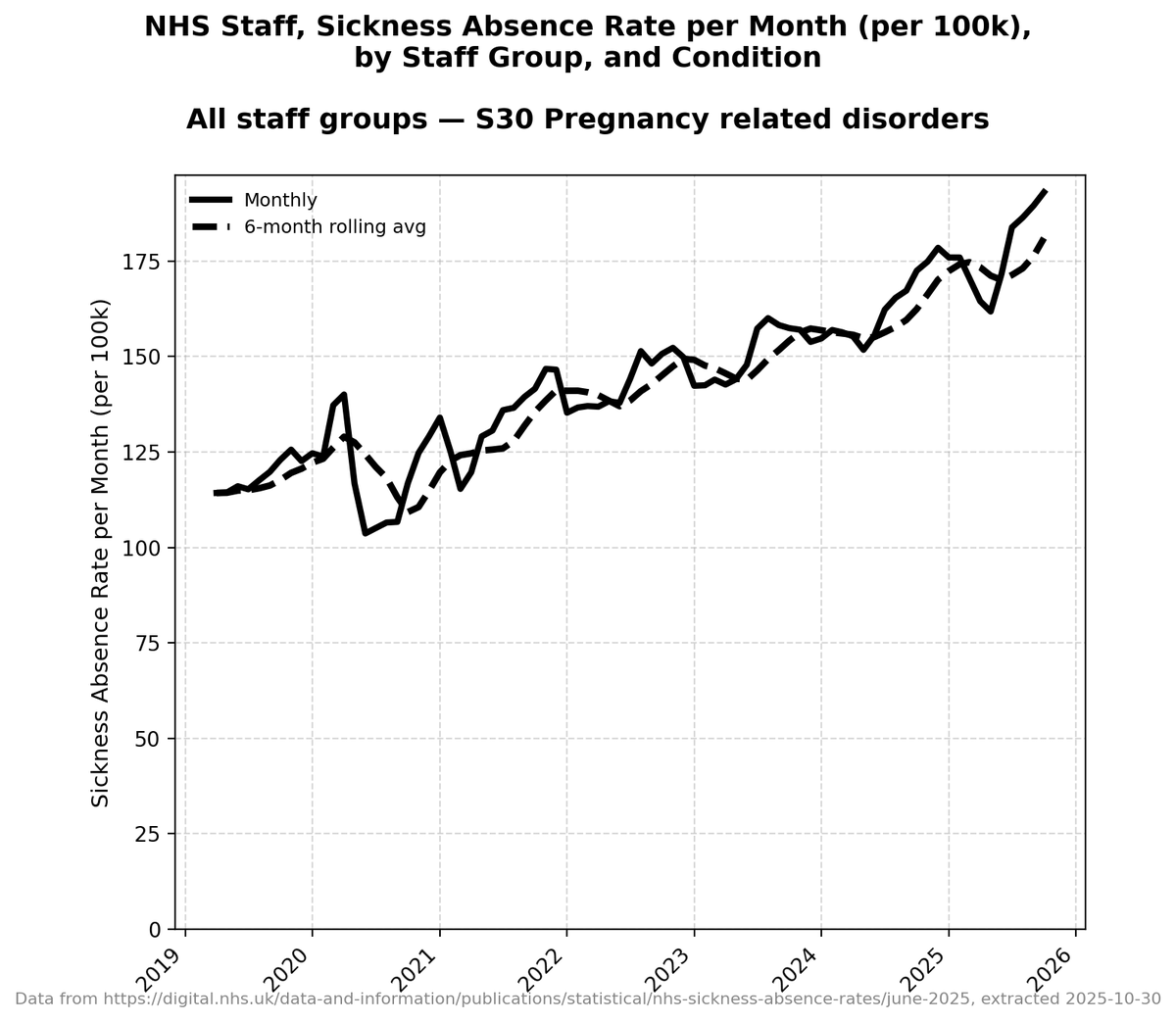
There have now been more cases in the first five months of this year than in ANY FIVE YEAR PERIOD IN THE LAST TEN YEARS.
So, before the arrival of Covid, you'd get a few years' cycle of Whooping Cough cases that would build in a series of peaks before a drop. 

And along with the roughly three year cycle, you'd also get a yearly cycle, with the main peaks happening around October. 

So build up to October, drop a little, build up higher to the following October, drop a little, build up even higher to the following October, drop a lot.
How high does that graph go if it continues rising to an October peak?
Too high.
Somewhere between 8,000 - 16,000 notifications a month, I reckon.
Just a reminder that the UKHSA expect Whooping Cough cases to follow the usual seasonal pattern, so expect another five months of growth, and another few months to get back to the normal level. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh