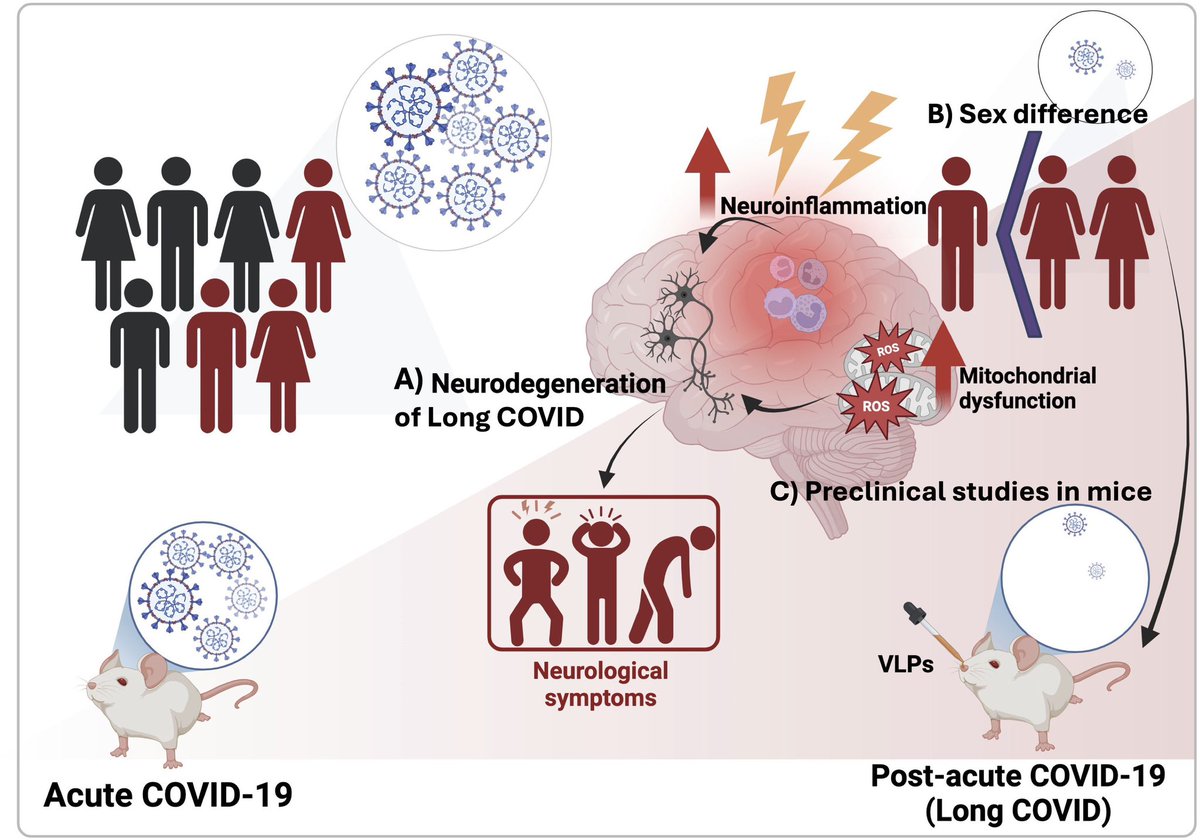
A recent discovery could transform our understanding of how cancers develop.
The classical theory that attempts to explain why normal cells become cancer cells, posits that DNA mutations are the primary cause of cancers. 1/
The classical theory that attempts to explain why normal cells become cancer cells, posits that DNA mutations are the primary cause of cancers. 1/
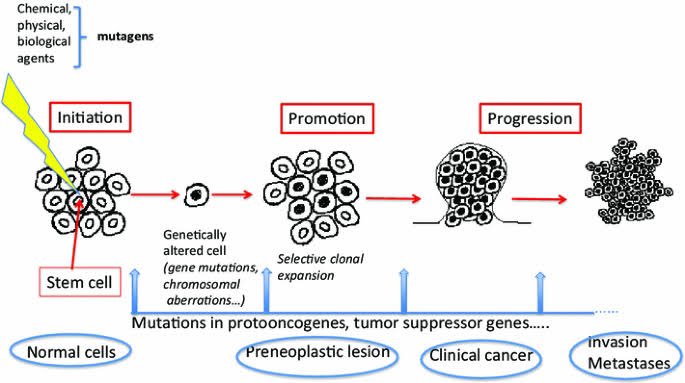
It's well known that aging, as well as some lifestyle and environmental factors (such as smoking and UV radiation) cause random DNA mutations (also known as genetic alterations) in our cells. 2/ 
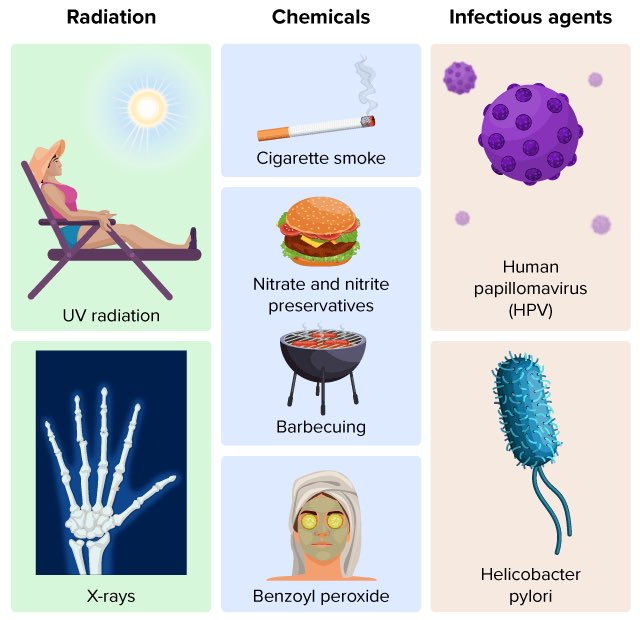
Most genetic alterations trigger cell death or have no consequence. But a few mutations favor cell survival. If sufficient number of "life extending" mutations occur in a cell, this cell will become virtually immortal—starting uncontrolled duplications that results in cancer 3/ 

However, this theory places a lot of importance on DNA mutations, which are irreversible and often difficult to target with drugs. So, if cancer is caused by genetic mutations only, our ability to kill cancer cells may be limited. 4/ 
Interestingly, there are other theories on how cancer starts. If these theories are also valid, we could develop better ways of preventing and treating cancers. 5/ 
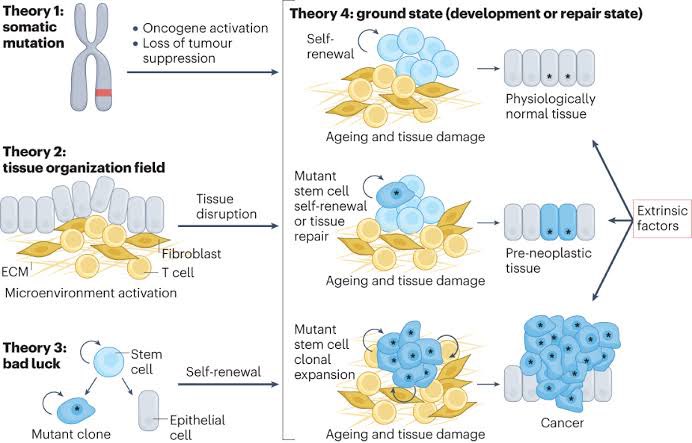
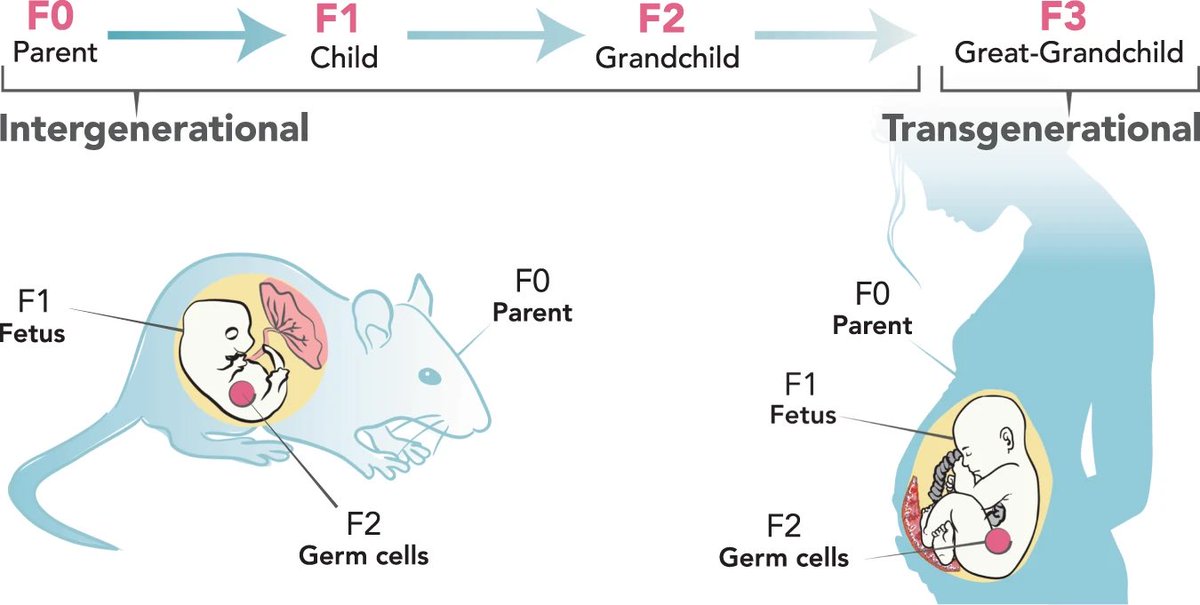
One of these new theories has been tested by researchers in a recent study. This study was conducted in fruit flies (which share 75% of the genes associated with human diseases). 6/ 

The researchers used the flies to investigate whether cancers could be caused by epigenetic changes—reversible "marks" that are added to the genome to turn genes on and off. 7/ 
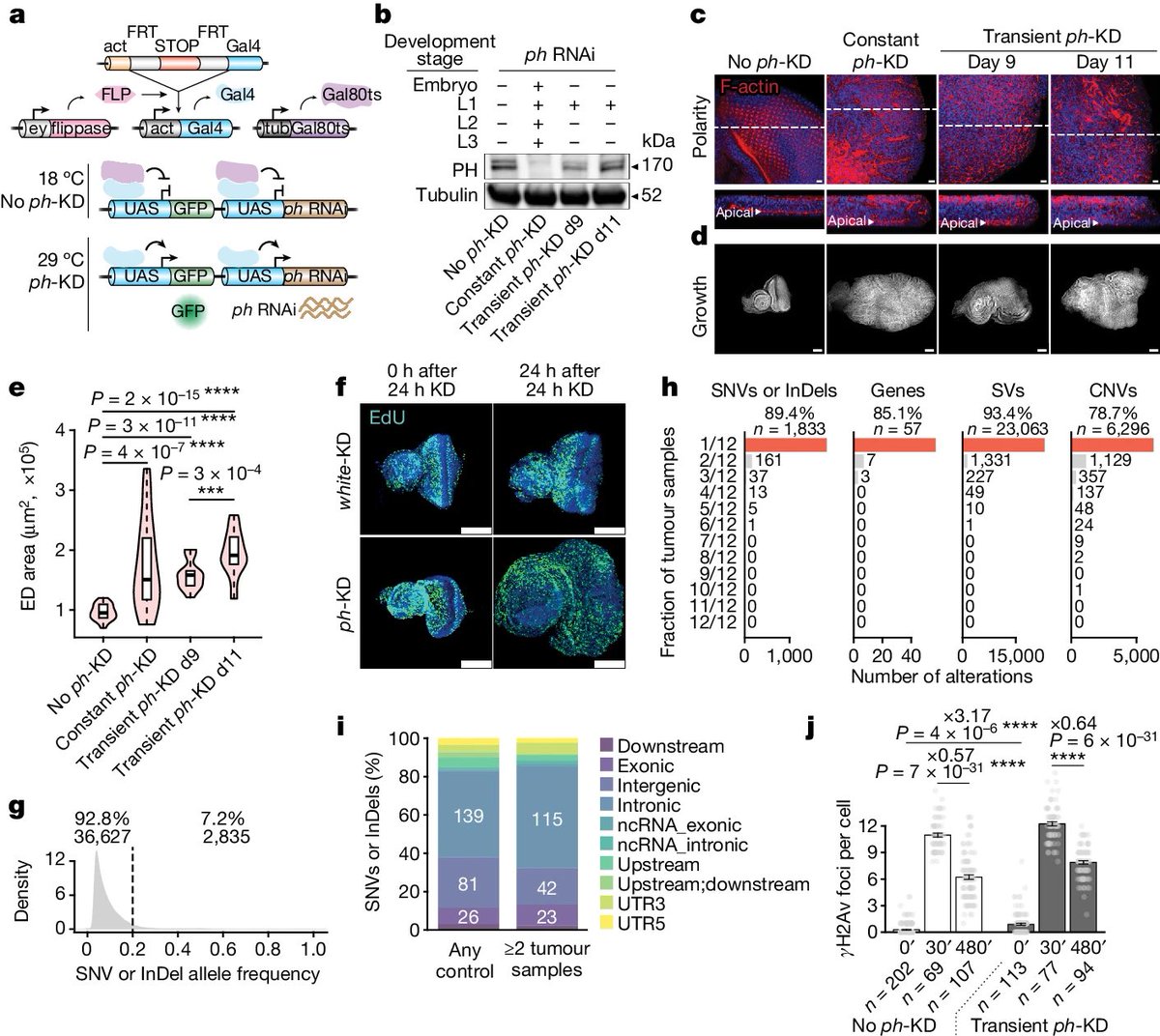
"Genetics" and "epigenetics" may sound similar, but they denote two very different processes. To understand the difference between genetic mutations and epigenetic alterations, think of your DNA as a book that contains some of the information needed to make yourself. 8/ 
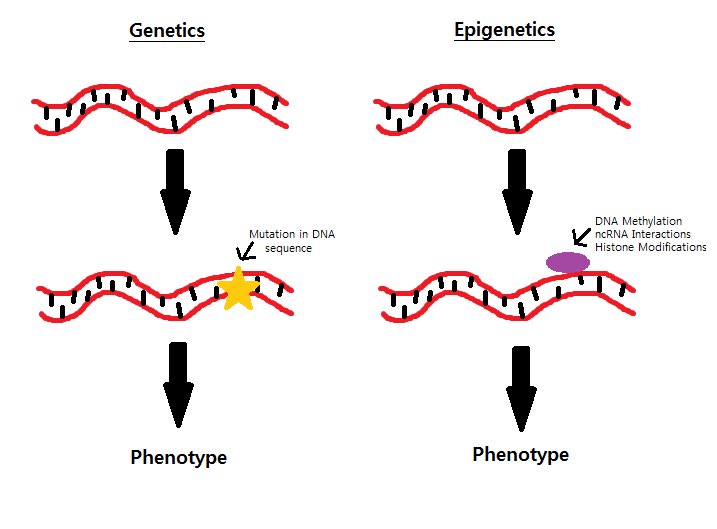
According to this metaphor, each gene would be the equivalent of a sentence in this book. A genetic mutation would correspond to using a pen to scratch out or modify a sentence. Once done, you cannot undo it. 9/
Epigenetic marks are more subtle changes—like underlining a sentence with a pencil or using a bookmark to quickly retrieve a certain page. These changes are achieved by adding or removing small molecules to the DNA itself, or to proteins that are closely associated to DNA. 10/ 
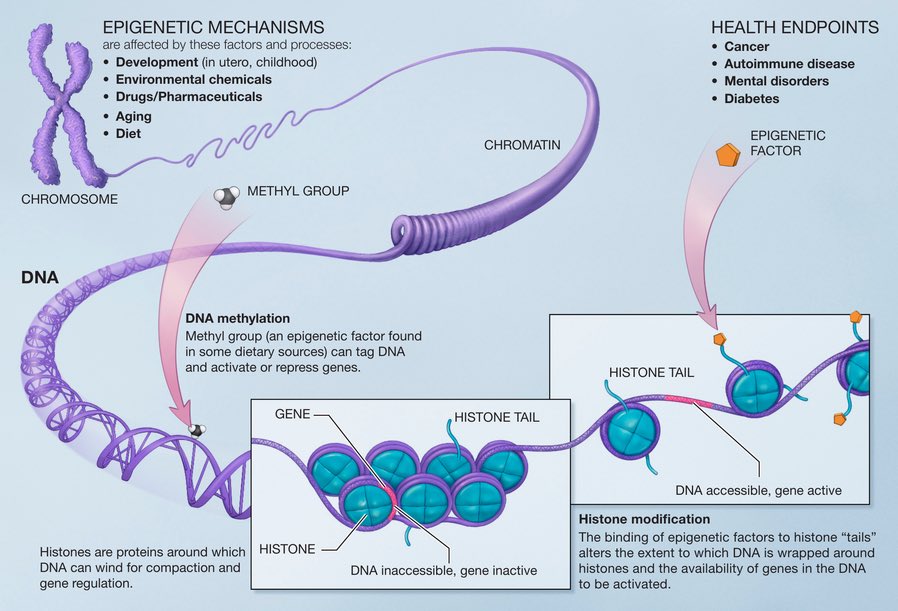
As such, epigenetic changes are reversible—but they can have a profound impact on the way your cells "read" the DNA. 11/ 
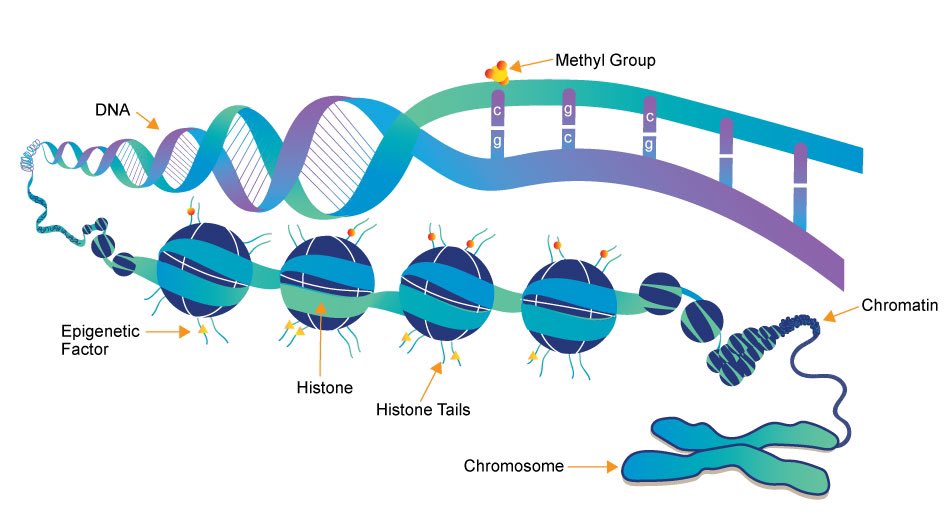
Epigenetic marks are essential for turning genes on & off during development (such as helping us form our eyes in the womb). They also create a bridge between external environment & genes. For ex, epigenetic regulation of genes allows animals to adapt to changing seasons. 12/ 
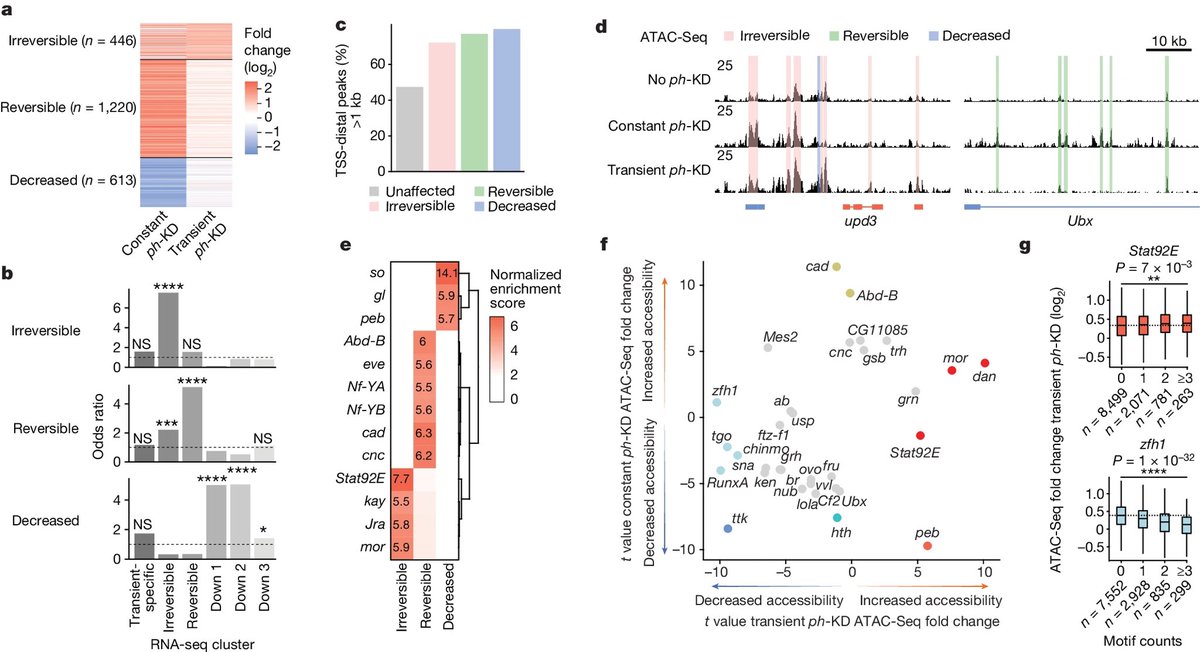
For a long time, epigenetic marks were considered too fleeting to actually cause cancer. But studies have shown that cancer cells accumulate several epigenetic alterations—and these alterations can promote cancer cell survival as effectively as DNA mutations do. 13/
This would suggest that cancer develops through the accumulation of both genetic and epigenetic alterations. 14/
Previous studies hadn't had sufficient evidence to show epigenetic alterations could cause cancer in the absence of DNA mutations. This study has shown for the first time that a temporary change in epigenetic marks—even w/out a DNA mutation—is sufficient to cause cancer. 15/ 
This is not only a scientifically fascinating result, but evidence that could change the way we treat some cancers—especially if these results are confirmed in future studies. 16/
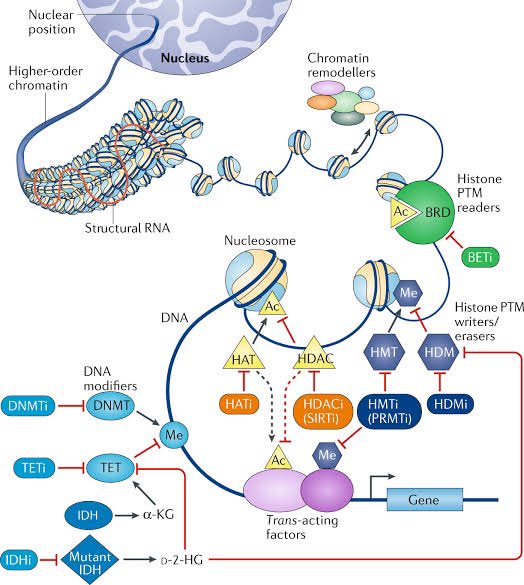
If epigenetic alterations contribute to cancer then researchers could develop epigenetic therapies for this deadly disease. Many scientists and pharmaceutical companies have been working on this for the last few decades. 17/
These therapies would reprogram cancer cells by changing the distribution of reversible epigenetic marks. This would allow cells to revert to their normal behavior, thereby stopping uncontrolled reproduction. 18/ 
Some of these new epigenetic drugs are now approved in some countries for the treatment of blood cancers and sarcomas. Other epigenetic drugs are in clinical trials for the most common cancer types—including breast and prostate cancer. 19/
The epigenetic cancer theory also has implications for cancer detection. Traces of abnormal epigenetic marks are released by cancer cells and can be found in the blood of cancer patients. 20/
A blood test can detect epigenetic marks from tiny amounts of blood. Since DNA mutations can also be found in the blood of cancer patients, combining genetic and epigenetic tests could make cancer detection even more accurate. 21/
Epigenetic therapies can also be combined with traditional cancer therapies—such as surgery or radiotherapy, which are very effective in many cases. 22/ 
While the epigenetic theory of cancer explains important aspects of how the disease progresses, this doesn't mean the classical theory is wrong.
This new theory enriches our understanding of a complex phenomenon, reminding us there's still a lot to learn about cancer 23/
This new theory enriches our understanding of a complex phenomenon, reminding us there's still a lot to learn about cancer 23/
The next steps in this research are to test the epigenetic theory in other models—such as human cells—to further the development of precision treatments. 24/24
nature.com/articles/s4158…

nature.com/articles/s4158…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh