Sanctions and Reality: Western Tech's Enduring Role in Russian Arms.
Frontelligence Insight presents a special investigation into how Western components continue to power Russian missile navigation systems that guide Russian missiles to Ukrainian cities.
🧵Thread:
Frontelligence Insight presents a special investigation into how Western components continue to power Russian missile navigation systems that guide Russian missiles to Ukrainian cities.
🧵Thread:

2/ A batch of confidential documents, spanning hundreds of pages and supplied to our team by the @CyberResUa, directed our investigation to a military base in Shaykovka, Kaluga Oblast. This base is home to military unit #33310 or 52nd Guards Heavy Bomber Aviation Regiment 

3/ It gained notoriety for several incidents, including the launch of a Kh-22 missile that struck a civilian shopping center in Kremenchuk in 2022.
According to a confidential document, this unit has been using the "SN-99" as the satellite navigation system in Kh-32 missiles.
According to a confidential document, this unit has been using the "SN-99" as the satellite navigation system in Kh-32 missiles.

4/ The CN-99 (in English) is a navigation module for cruise missiles that is heavily composed of Western components. In September 2022, Conflict Armament Research (CAR) released a comprehensive report detailing its use in Russian cruise missiles
https://x.com/conflictarm/status/1566445254475120640
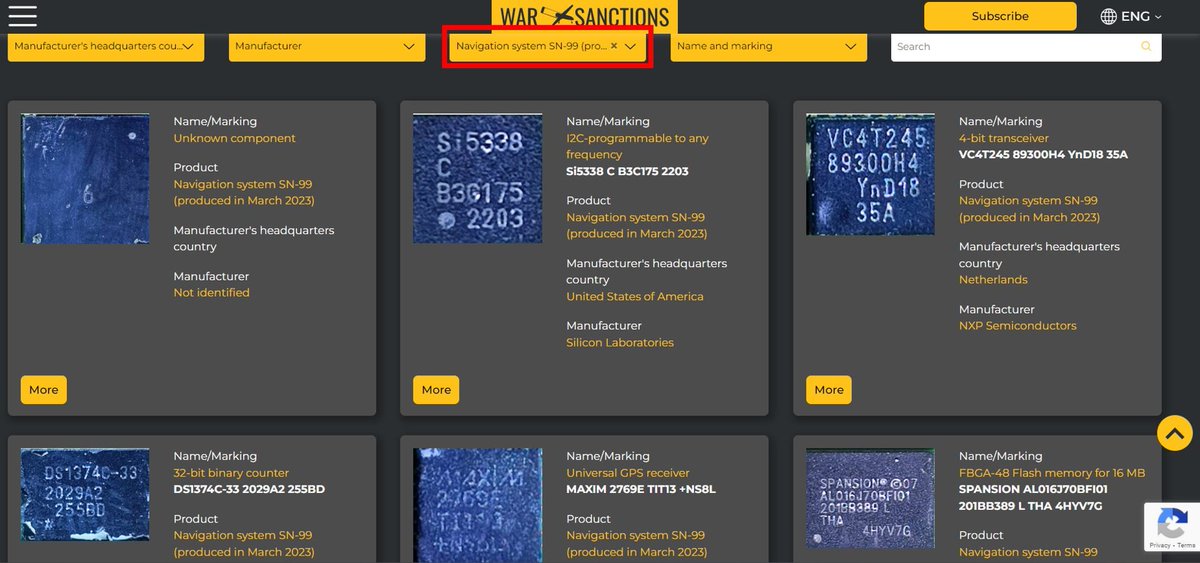
5/ According to the "War-Sanctions" database, which includes photos, the CN-99 module can be traced back to several Western manufacturers - Silicon Laboratories, NXP Semiconductors, Dallas Semiconductor, SPANSION, Maxim Integrated Products, and Integrated Silicon Solution. 
6/ The same documents reveal that the State Machine Building Design Bureau "Raduga," a Russian developer and manufacturer of missiles, has been tasked with retrofitting modernized SN-99 modules into Kh-32 missiles. 

7/ The modernization and repairs are carried out in collaboration between the Dubnensky Machine Building Plant and Design Bureau "Raduga," both of which are sanctioned by Western countries. Unfortunately, the documents do not specify the way Russia gets parts for the SN-99. 

8/ Sanctions are crucial not only to hinder Russia's missile production but also to disrupt their maintenance and repair efforts. According to a 2022 restoration report, at least 15 Kh-32 missiles, produced between 2007 and 2010, were identified as defective at the Shaykovka. 

9/ The presence of Western components in the SN-99 module used in Kh cruise missiles at Shaykovka is just one example out of thousands, and points to a much broader issue: sanctions are not that ineffective if not enforced properly.
10/ Without strict enforcement, sanctions will lose their effectiveness, as seen with the 2014 sanctions that faded with time. Consequently, Russia will continue to modernize its equipment using Western components, exploiting enforcement gaps to its advantage.
11/ We appreciate your support. Please consider retweeting and liking the first message in this thread to boost visibility. Raising public awareness is crucial to prevent the issue of sanctions from being swept under the rug and ignored.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh
















