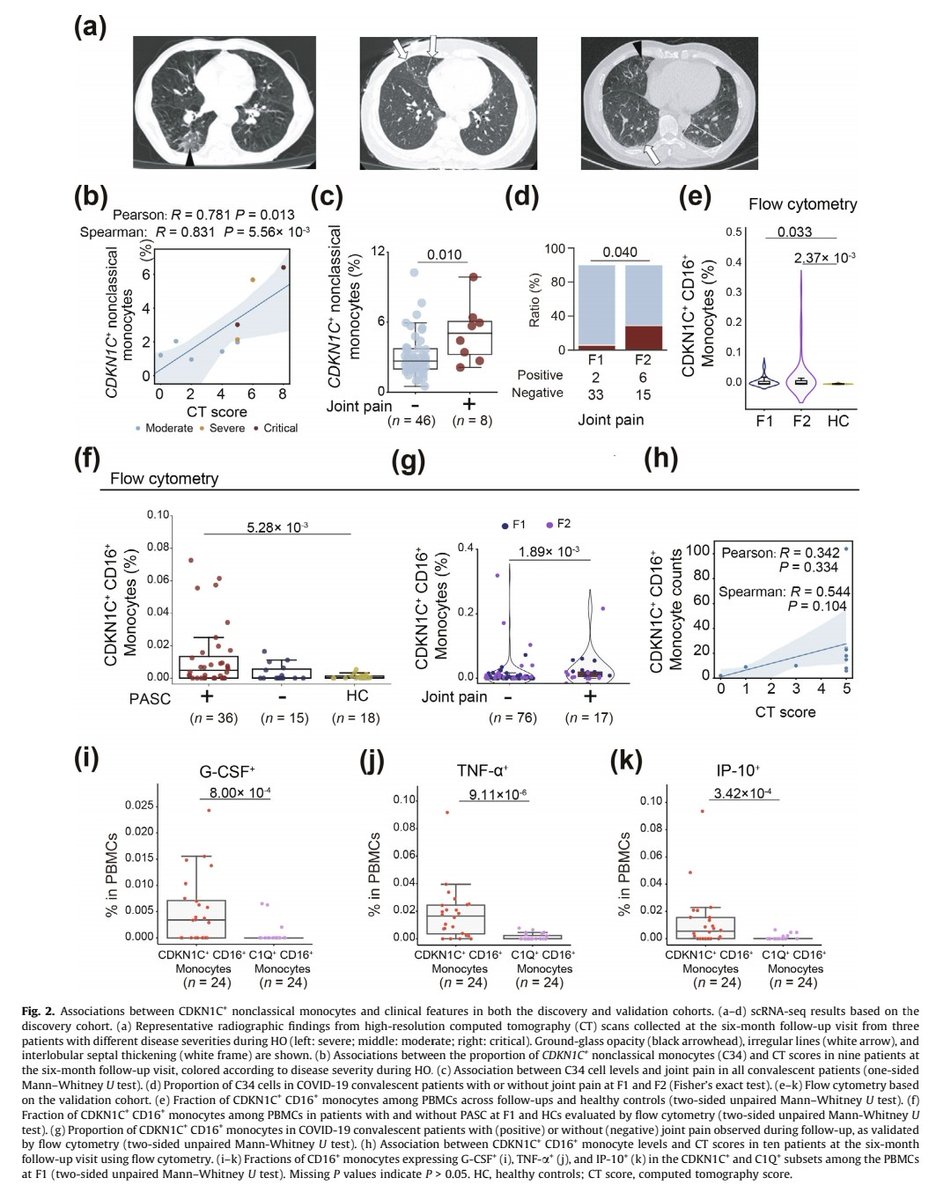
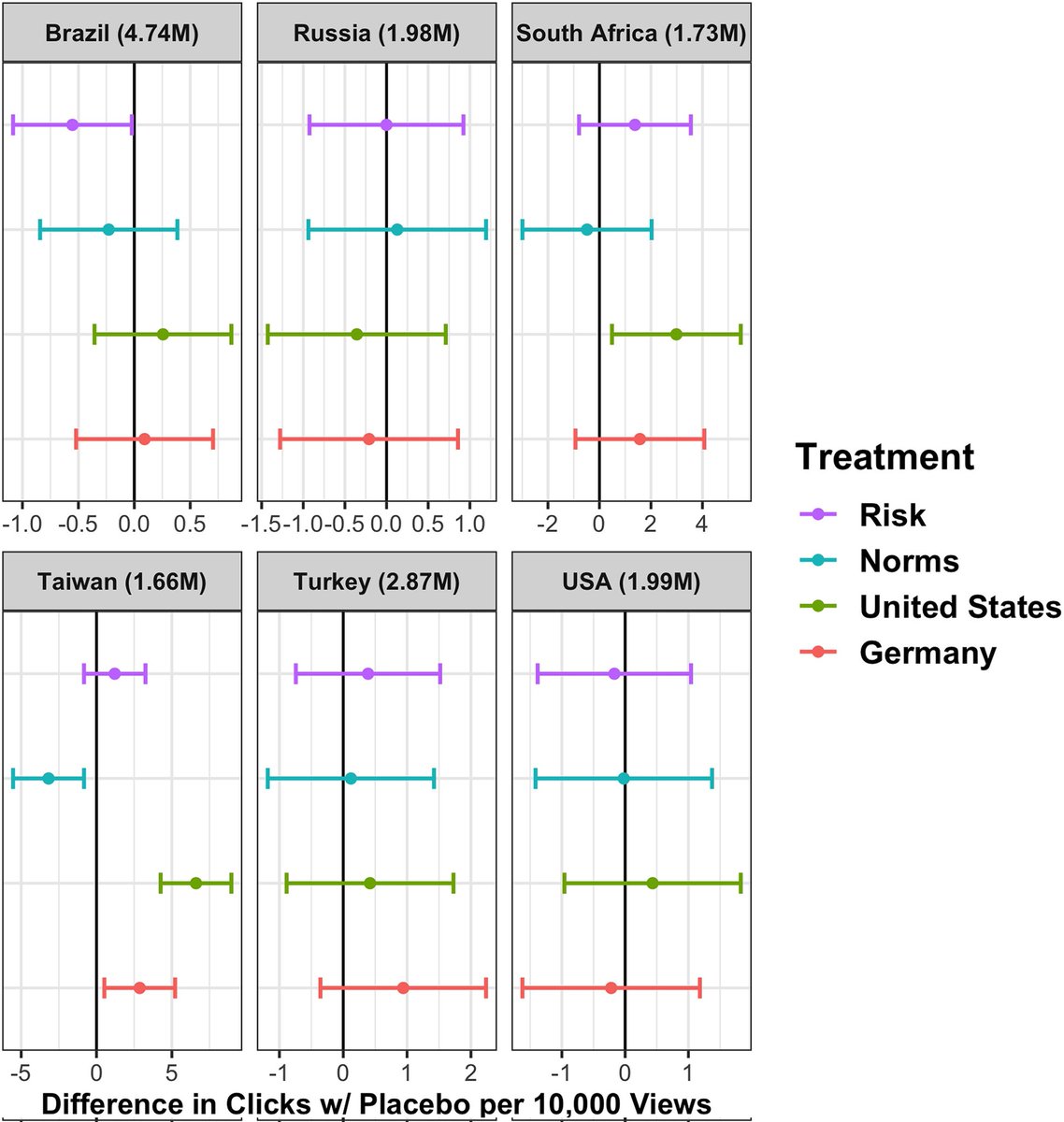
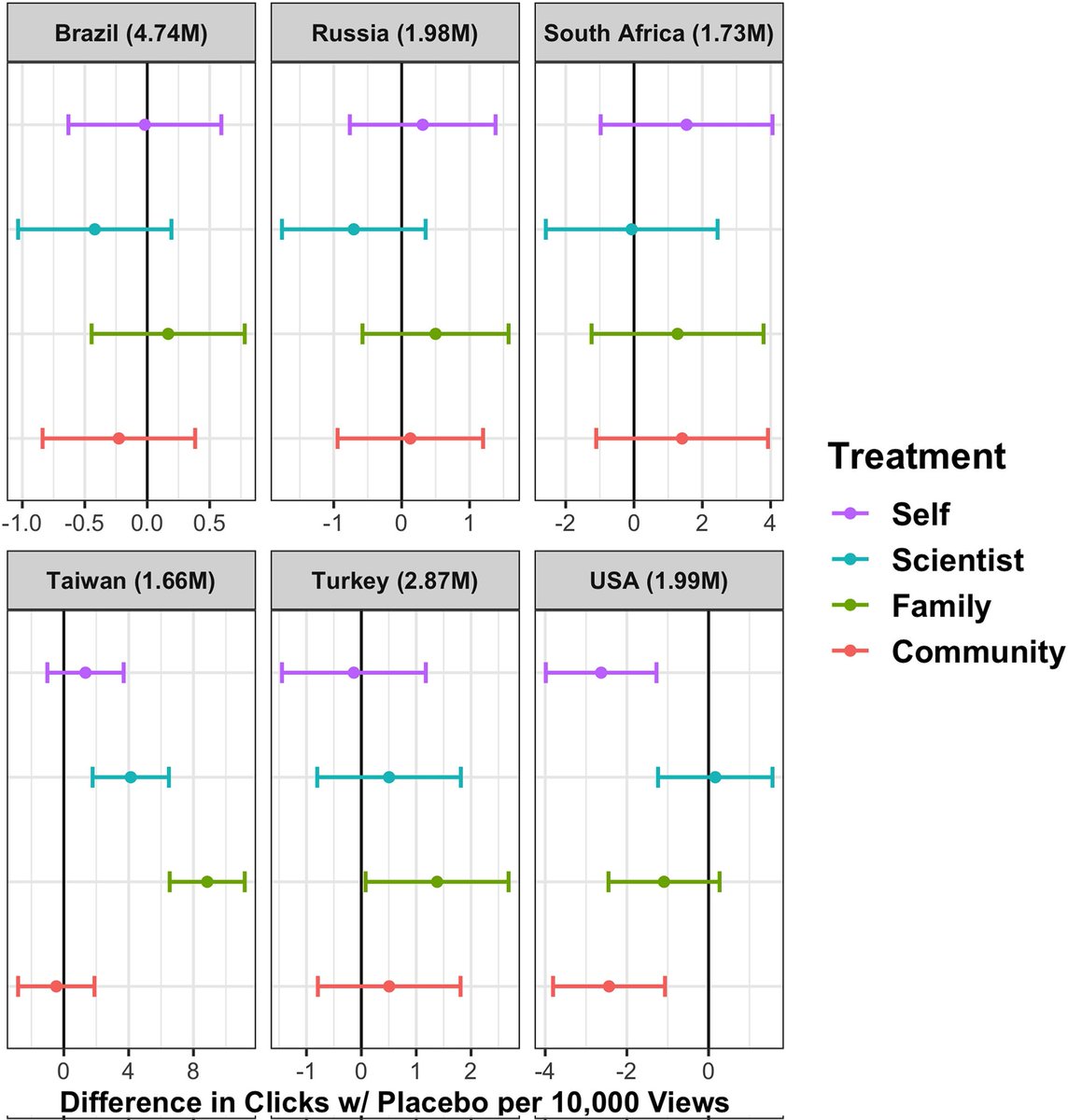
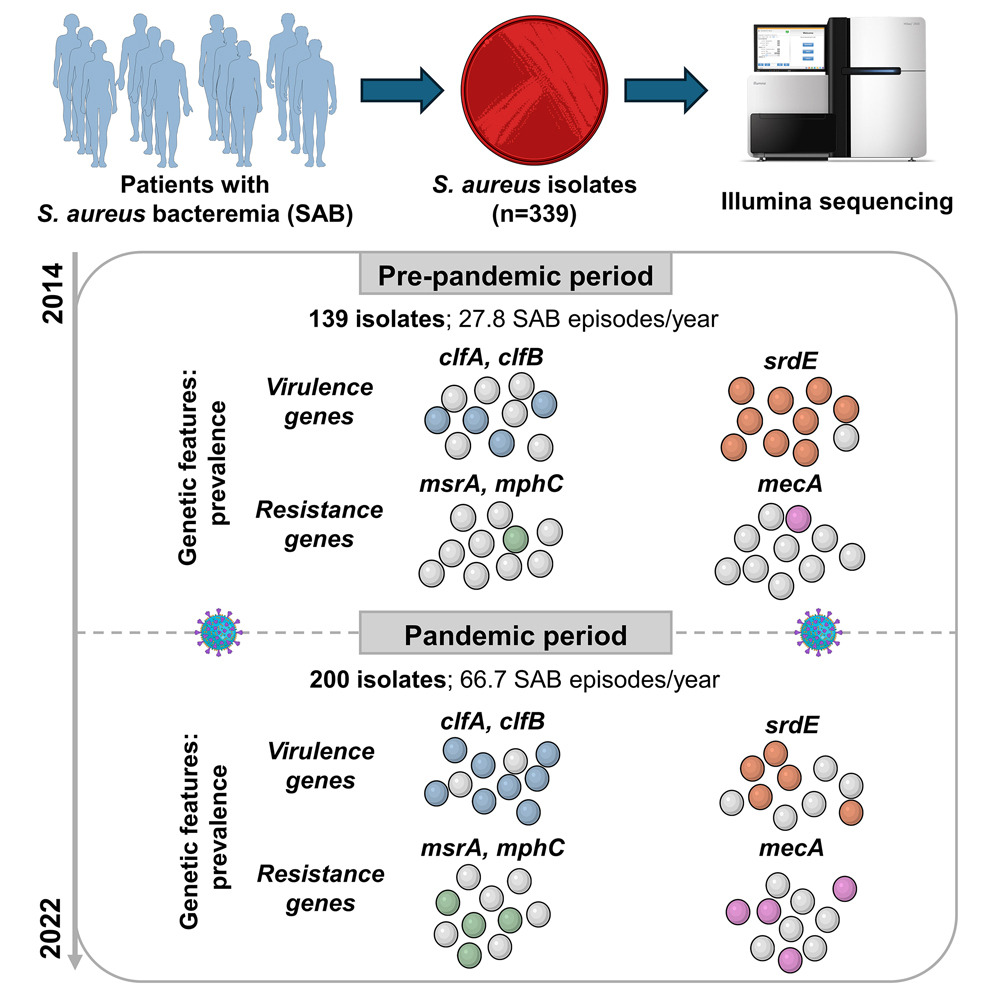
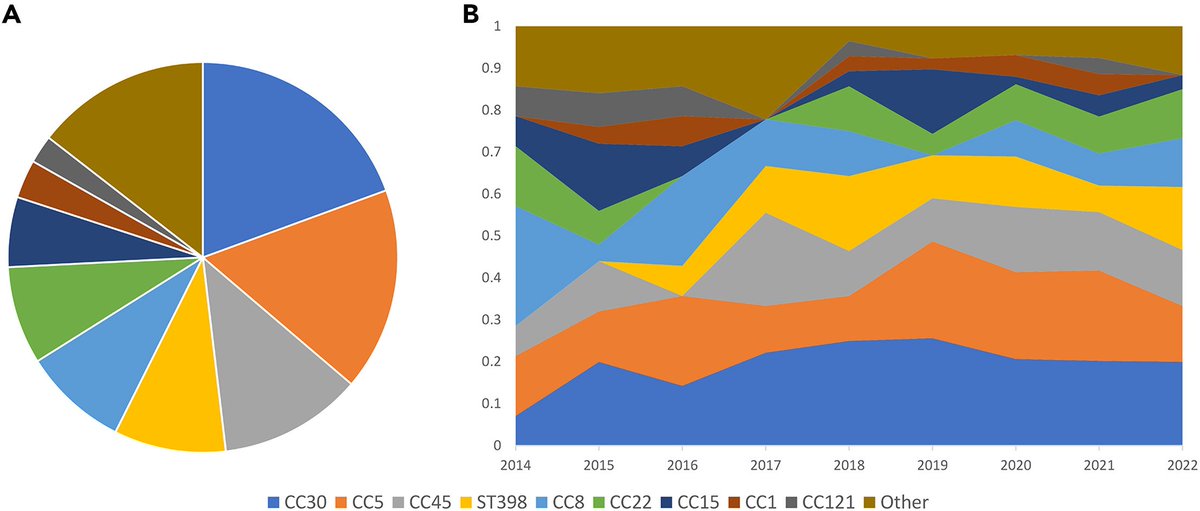
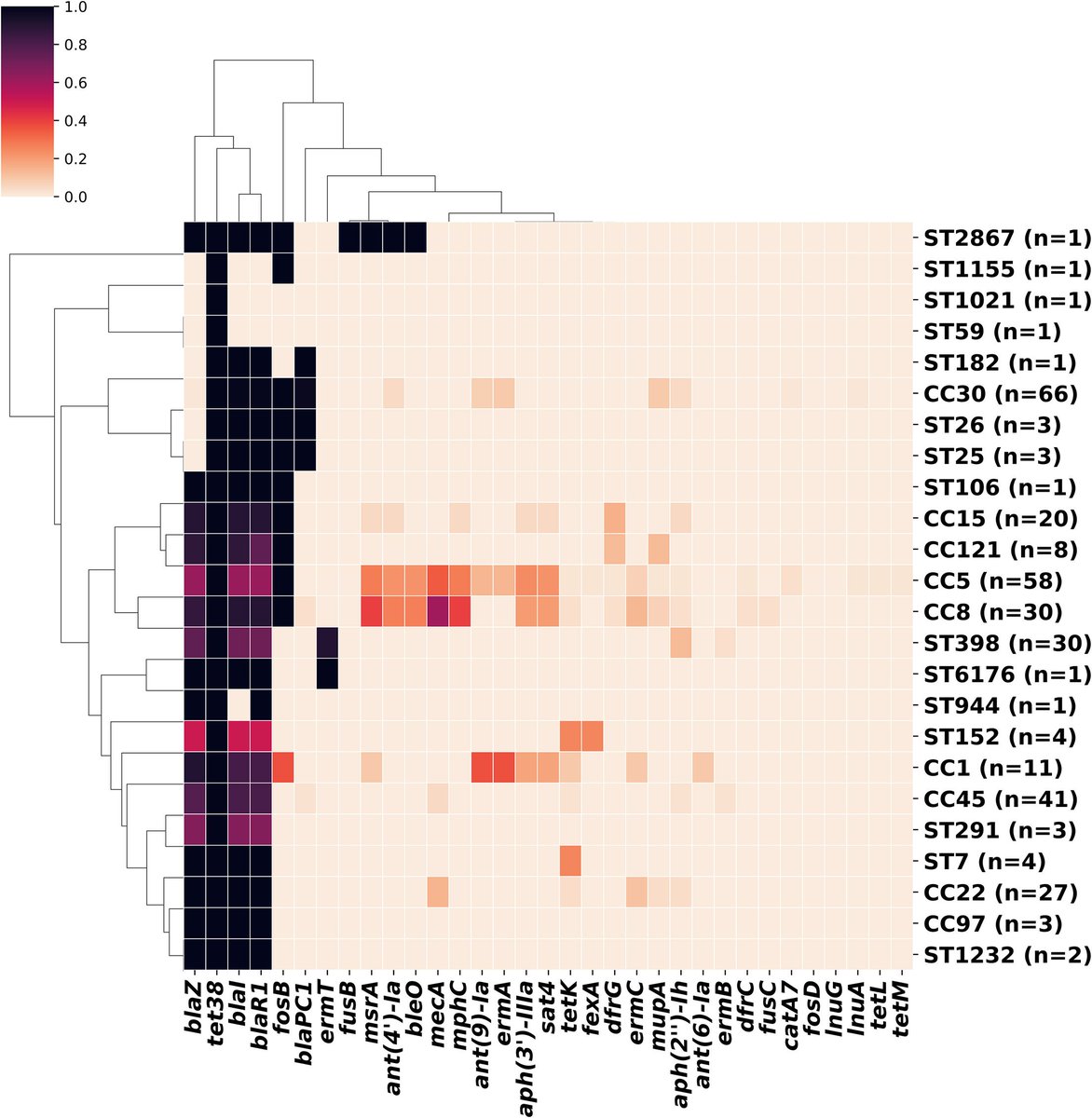
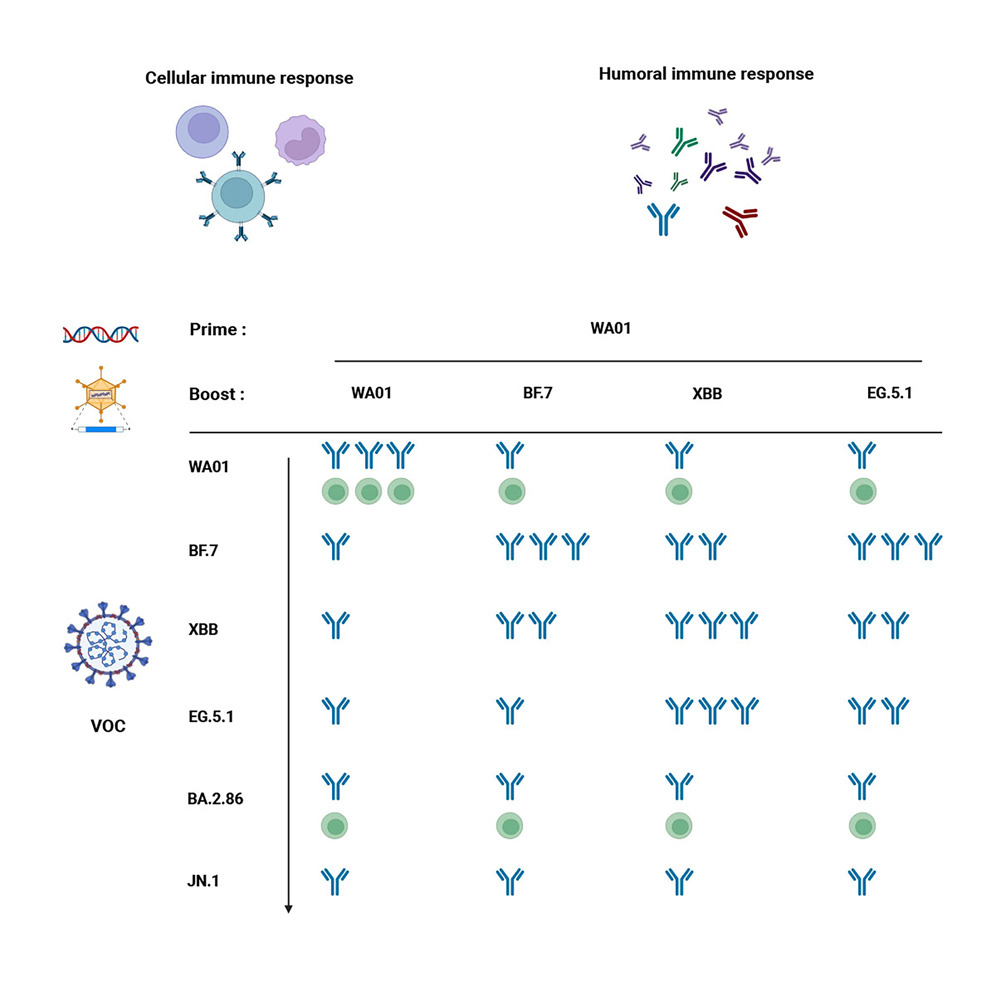
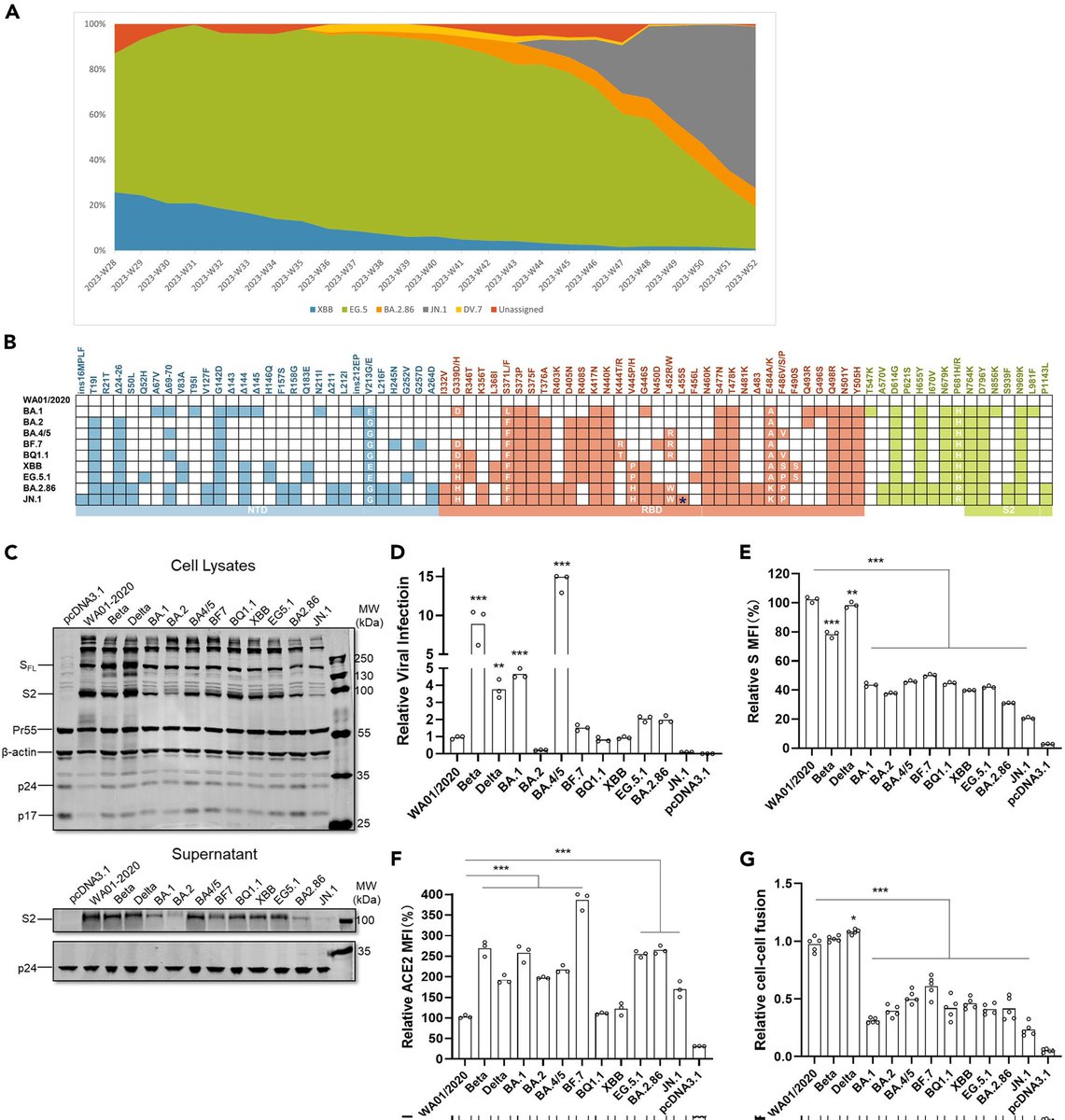
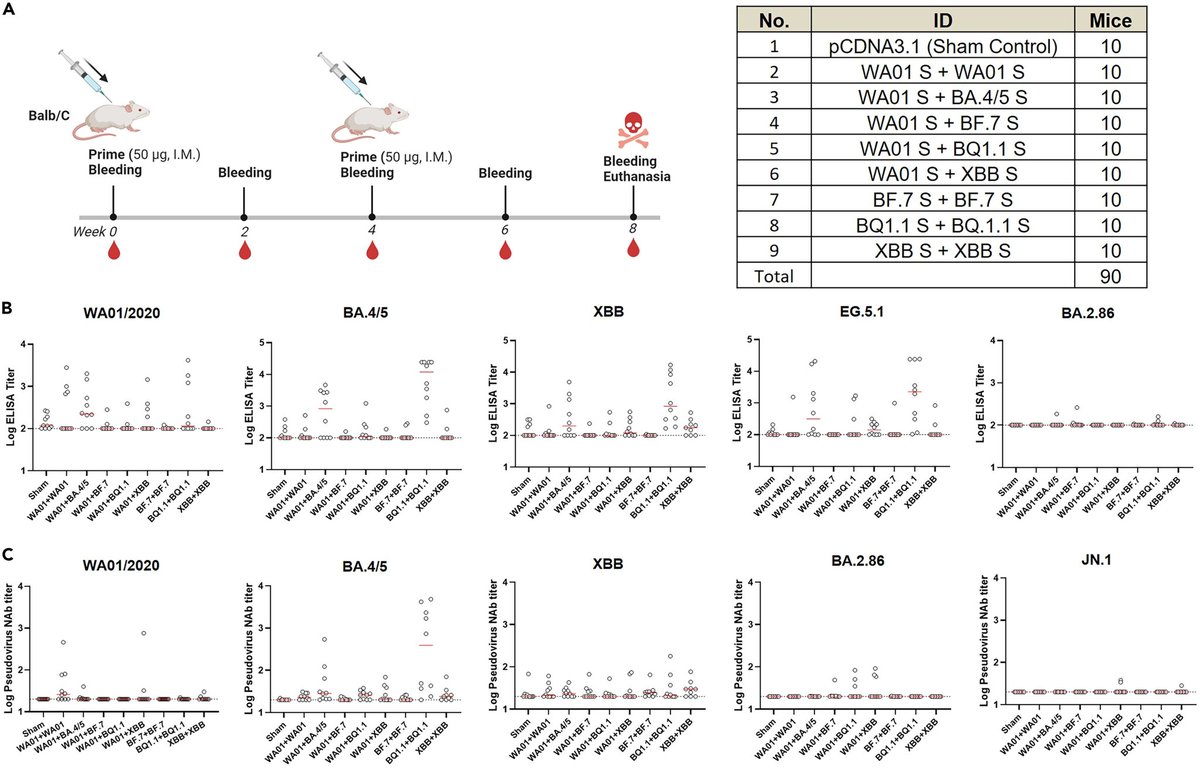
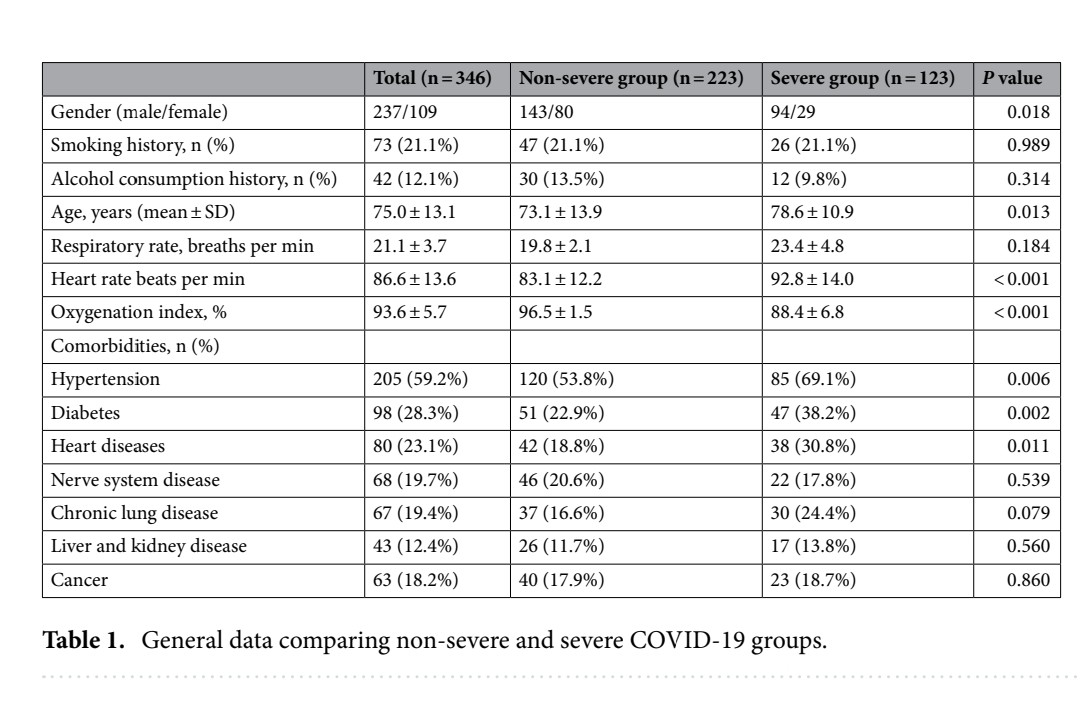
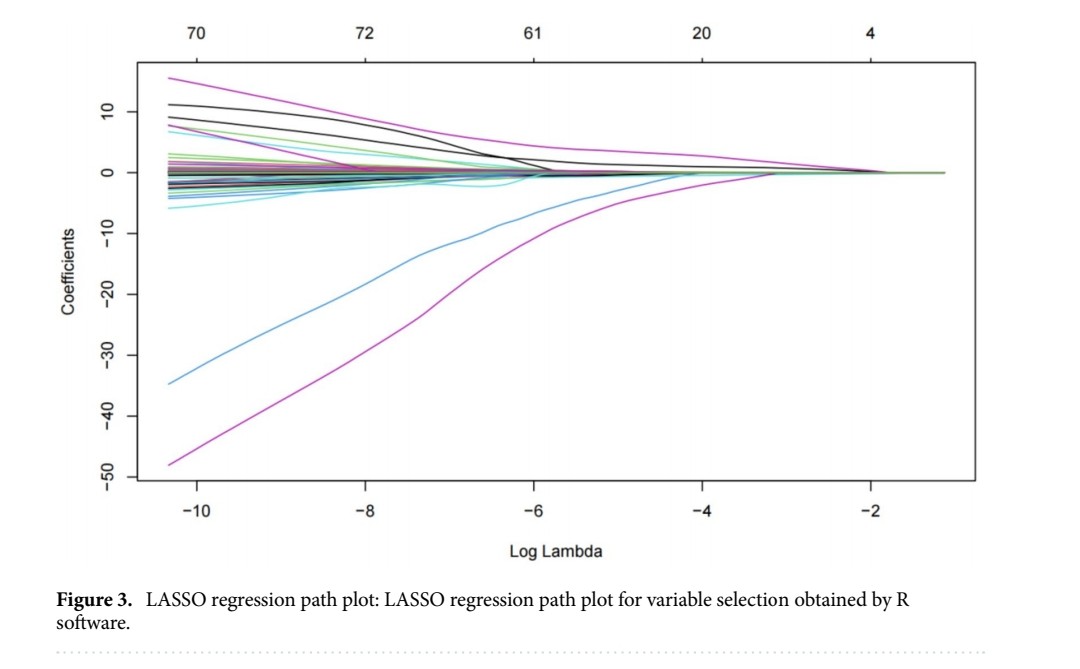
IMPACT of WANING IMMUNITY against SARS-CoV-2 SEVERITY EXACERBATED by VACCINE HESITANCY
journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/a…

journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/a…
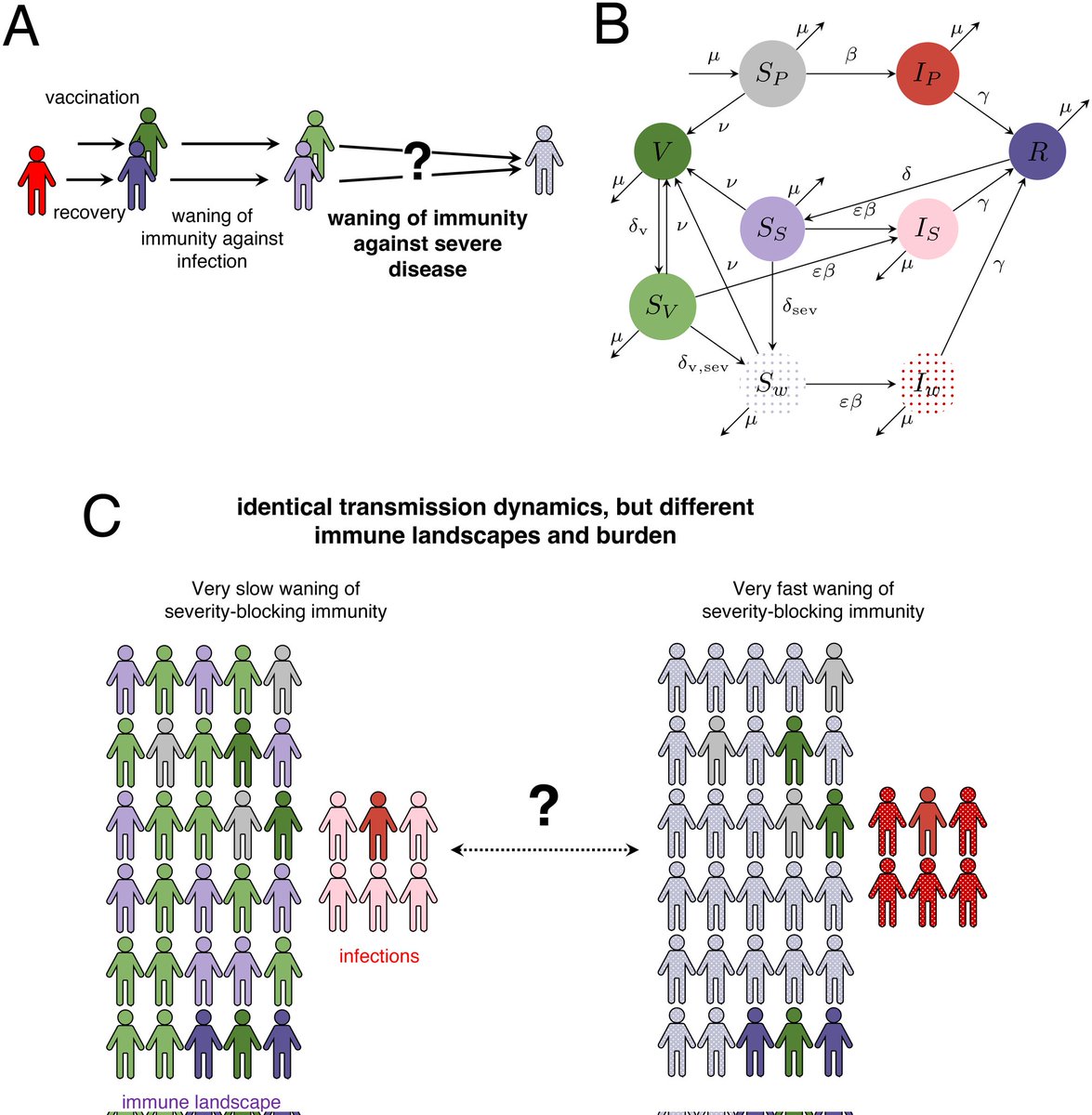
2) This study examines how uncertainty around the duration of immunity against severe COVID-19 can impact future disease dynamics.
Key findings:
- Unclear severity immunity duration leads to a wide range of possible outcomes ...
Key findings:
- Unclear severity immunity duration leads to a wide range of possible outcomes ...
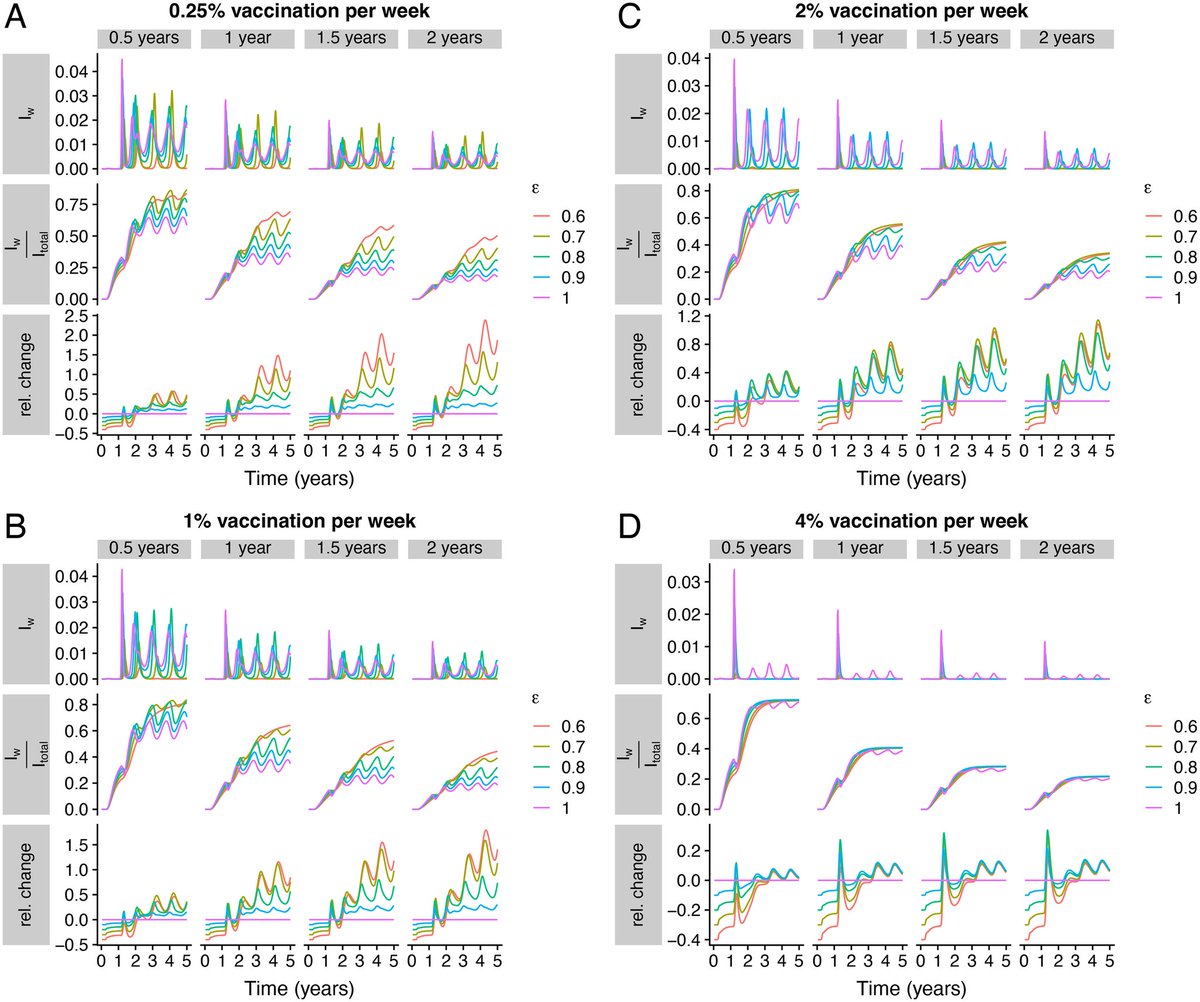
3) ...highlighting the need for better data on immune responses.
- Vaccines that provide long-lasting protection against infection and severe disease can help reduce these uncertainties and lower disease burden
- Vaccines that provide long-lasting protection against infection and severe disease can help reduce these uncertainties and lower disease burden
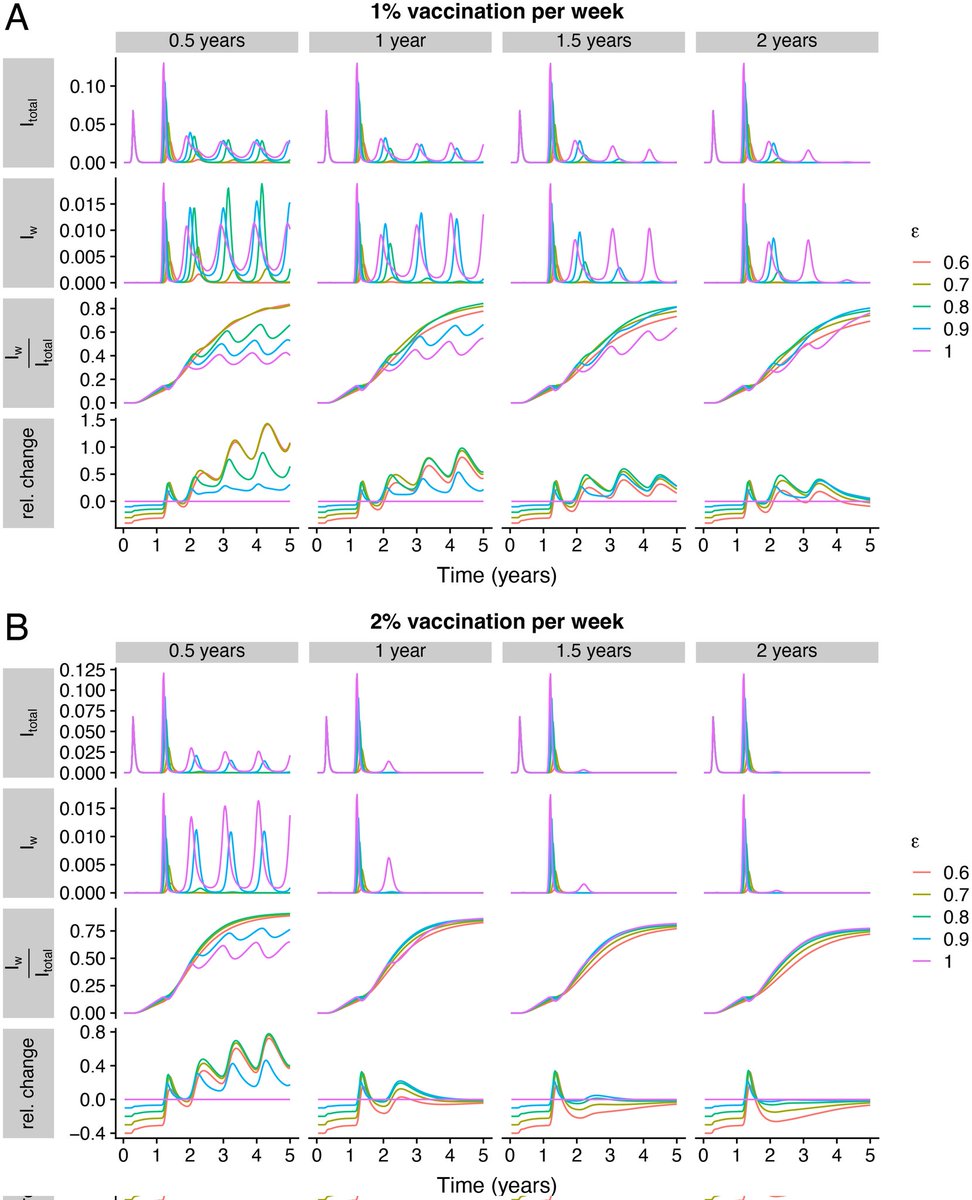
4) - However, vaccine hesitancy and uneven vaccine uptake can undermine the benefits of improved vaccines. Even with high overall vaccination, pockets of unvaccinated individuals can sustain outbreaks. 
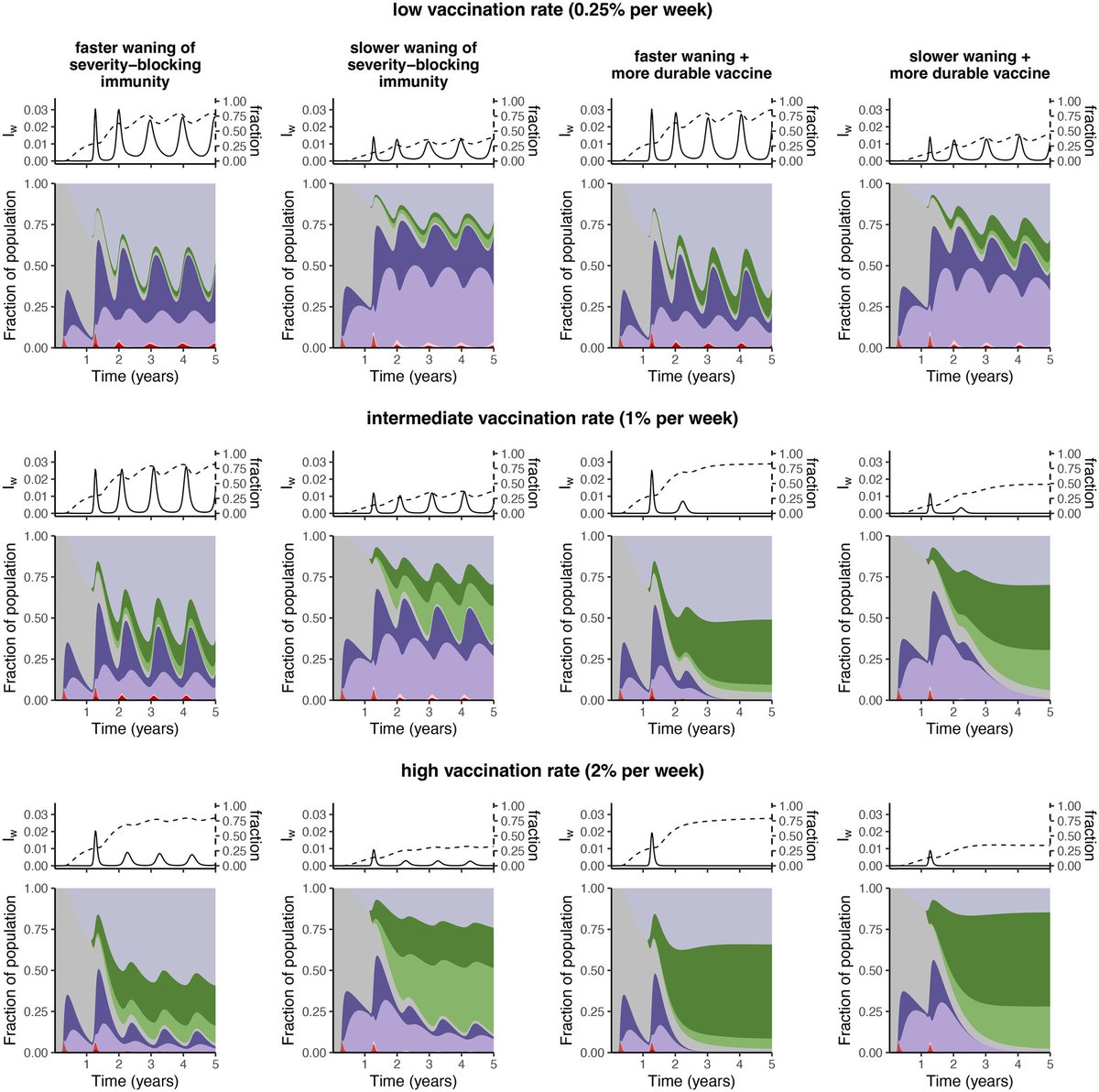
5) - To address waning immunity, the study emphasizes the importance of developing broadly protective vaccines and ensuring equitable global vaccine access and distribution. 
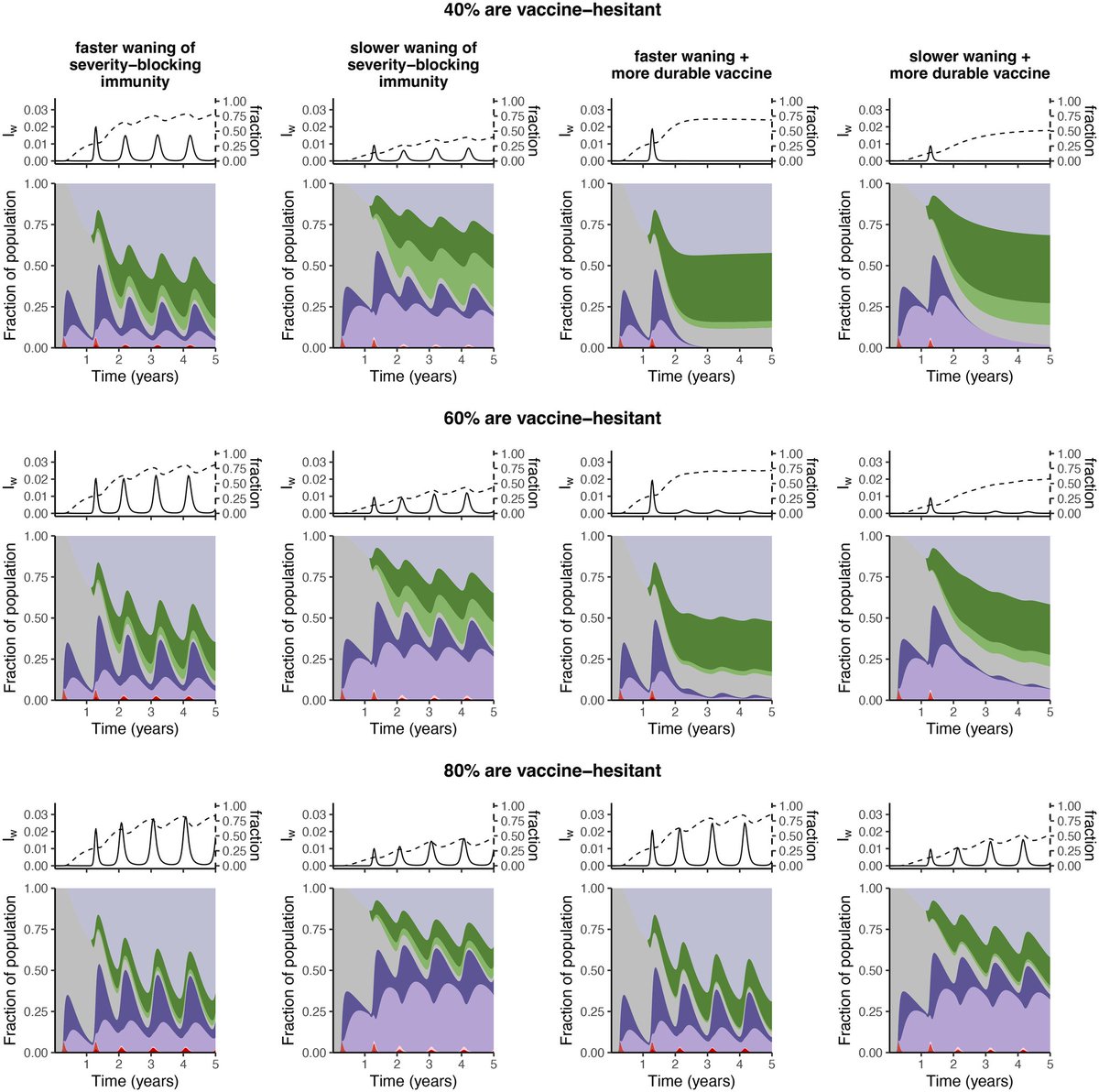
6) In summary, the duration of immunity against severe disease and vaccine coverage disparities are critical factors shaping future COVID-19 dynamics. Comprehensive monitoring and universal vaccine deployment are needed to manage the impacts of waning immunity.
Thanks 🙏
Thanks 🙏

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh