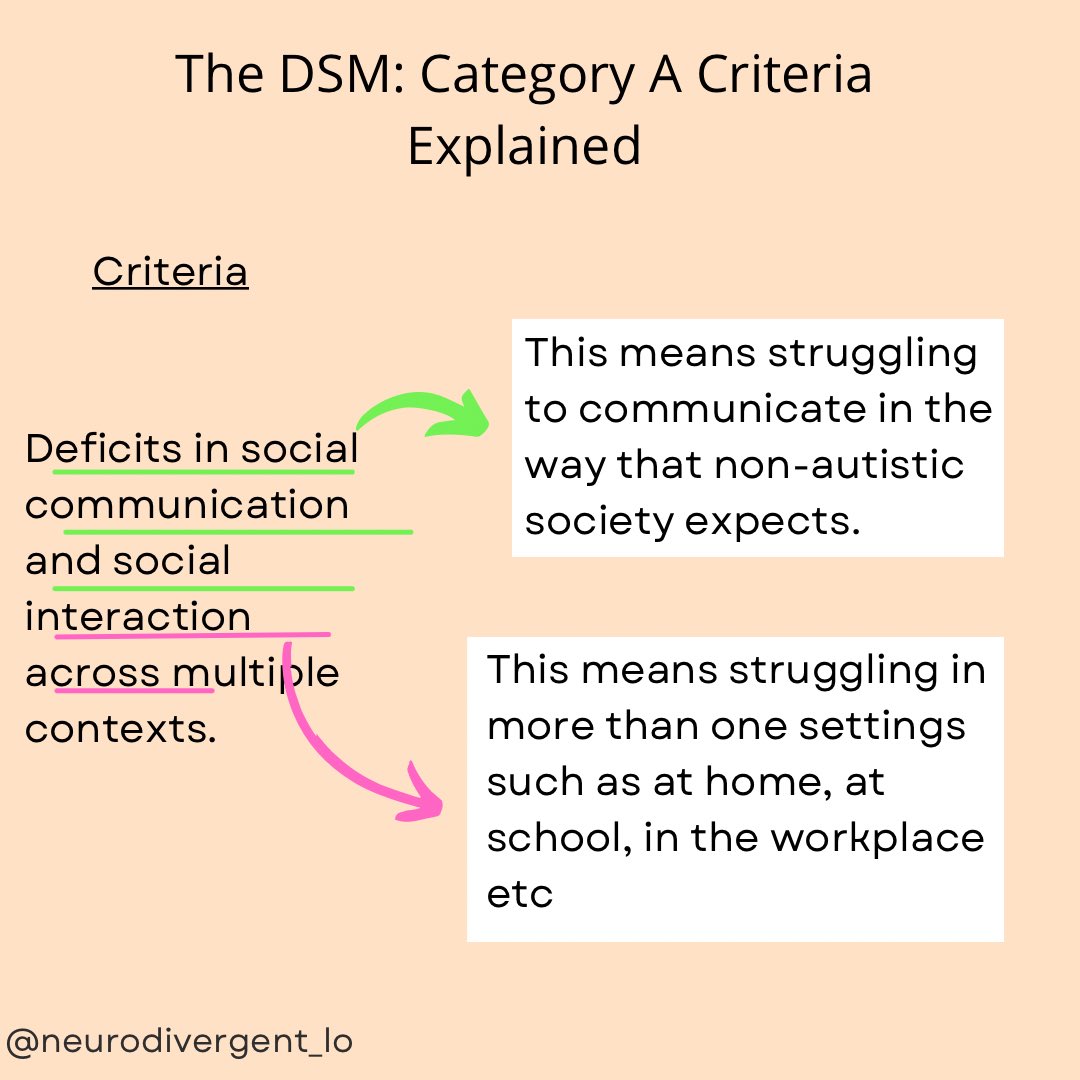
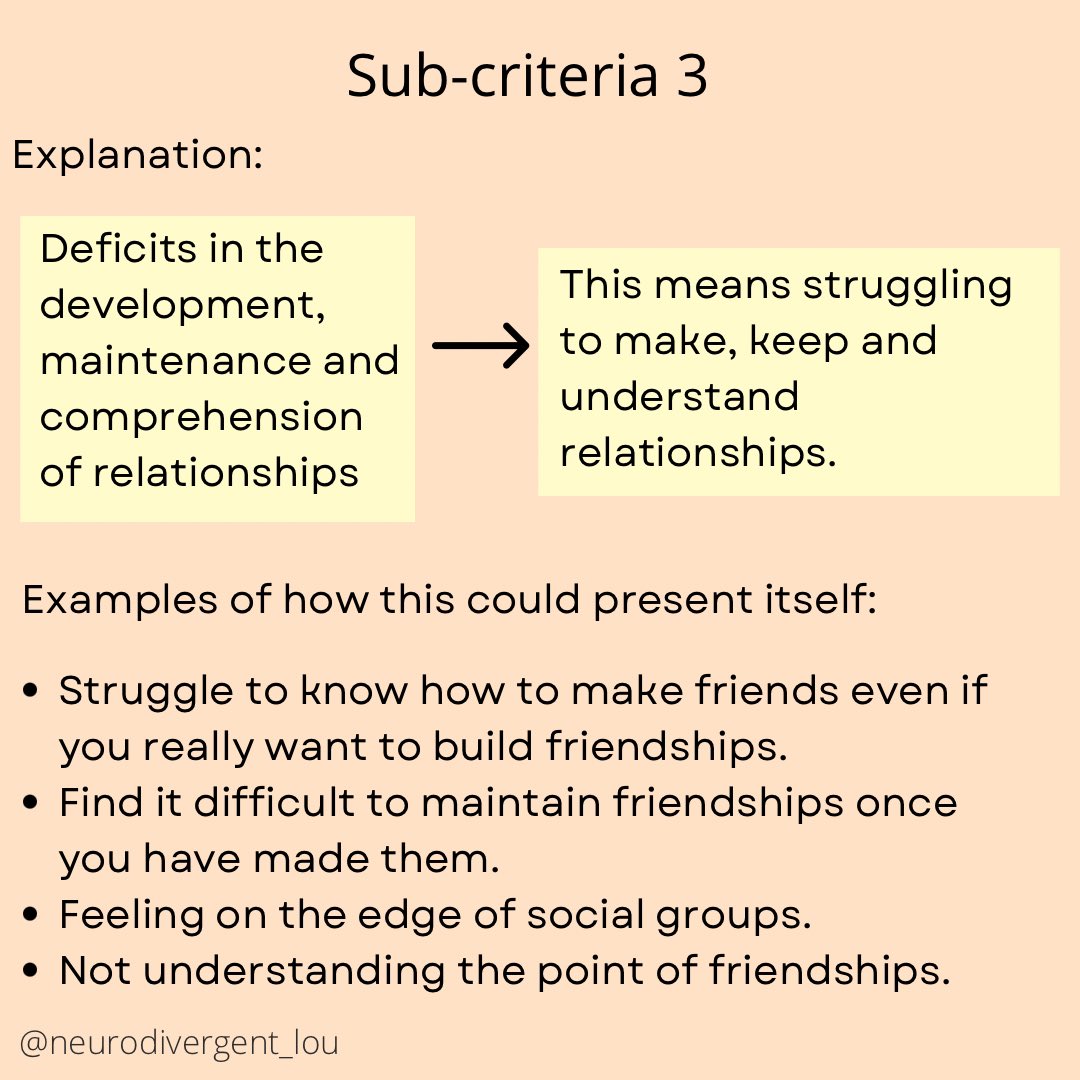
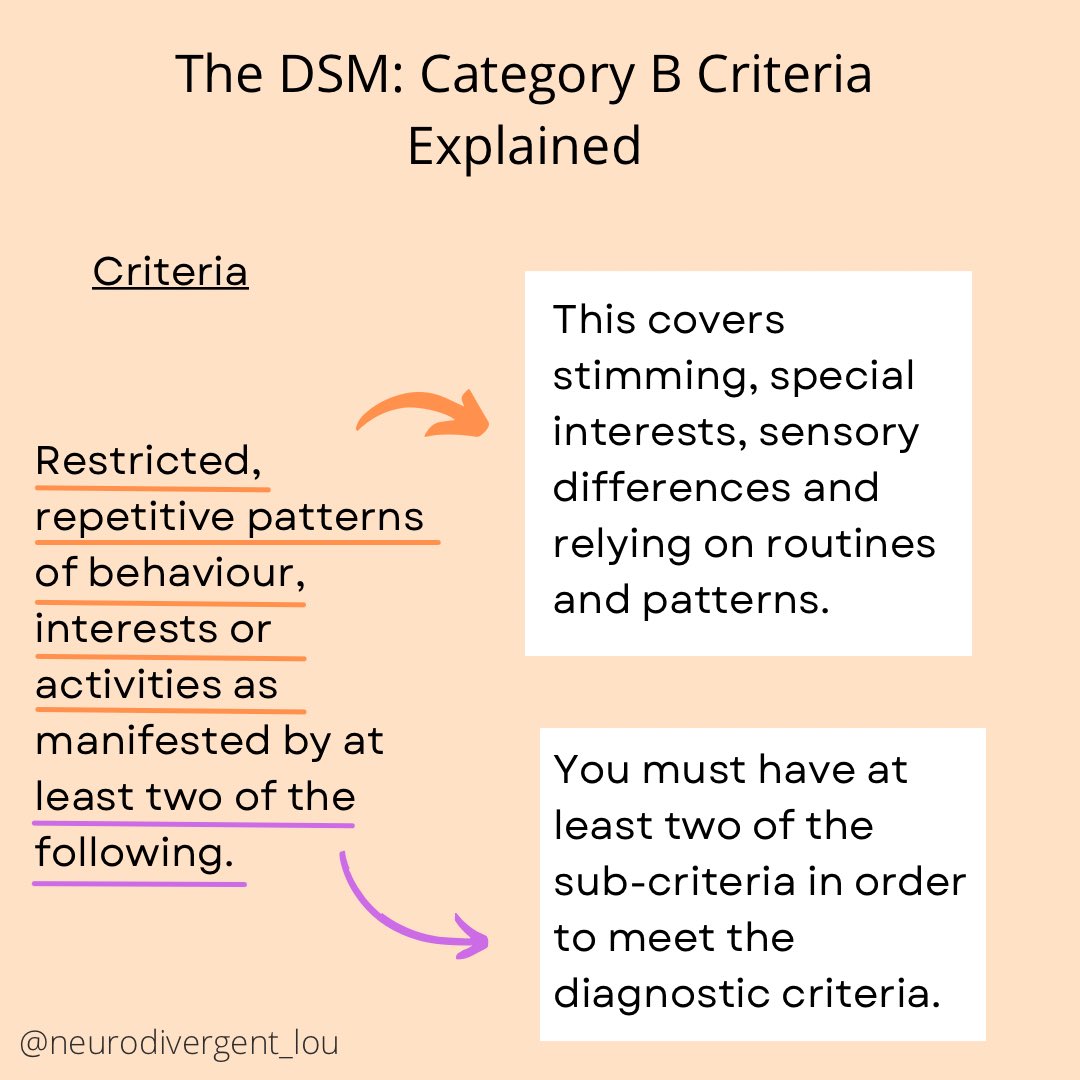
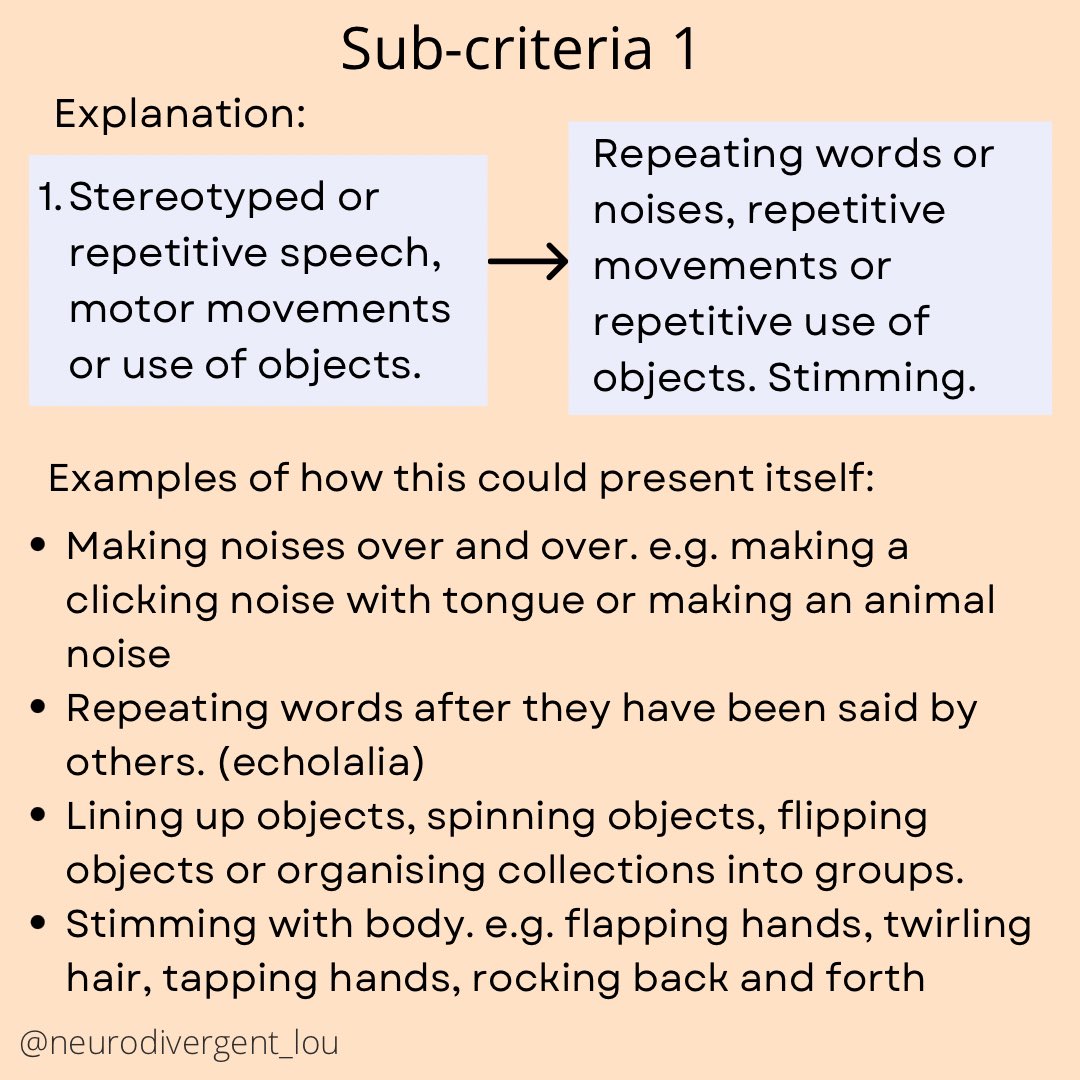
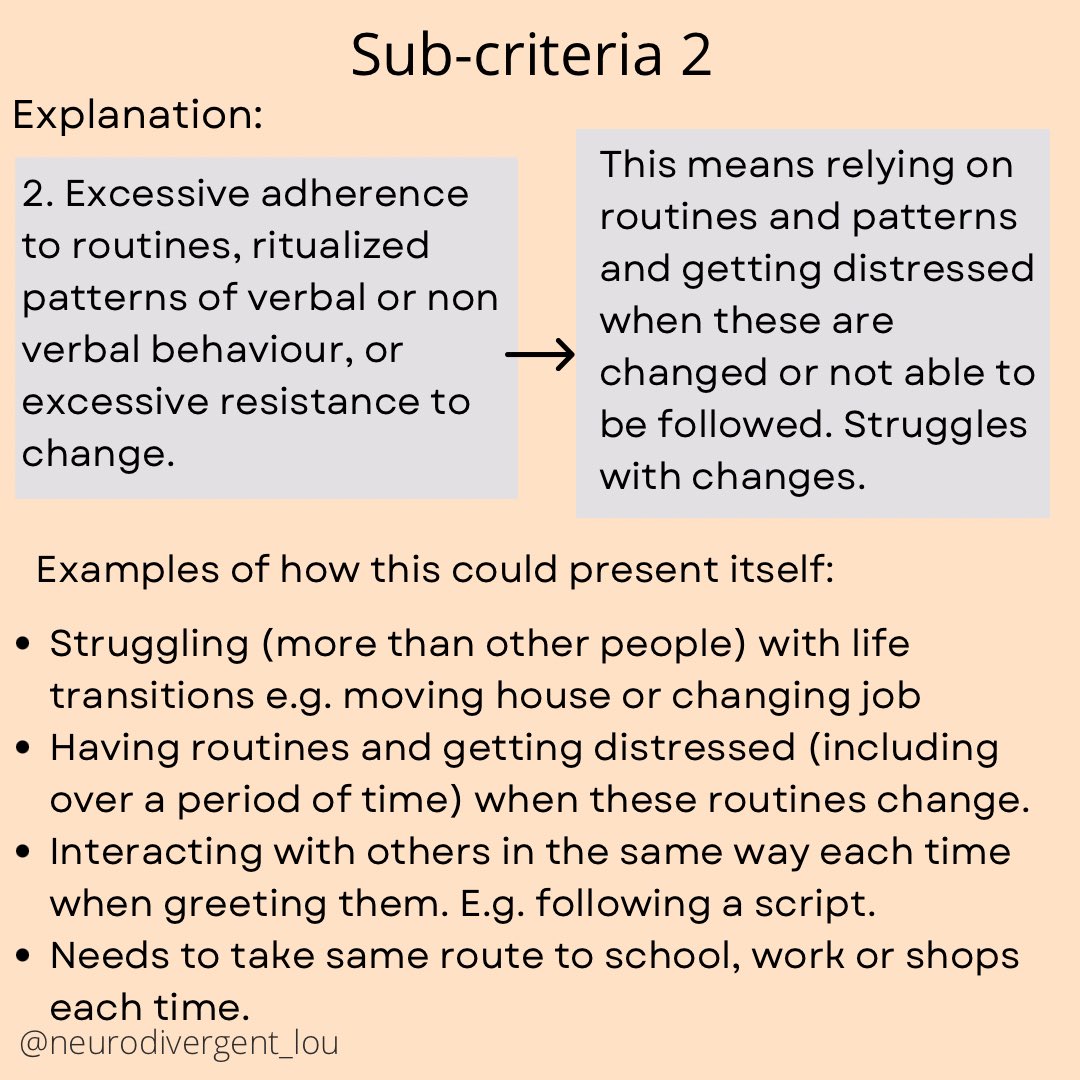
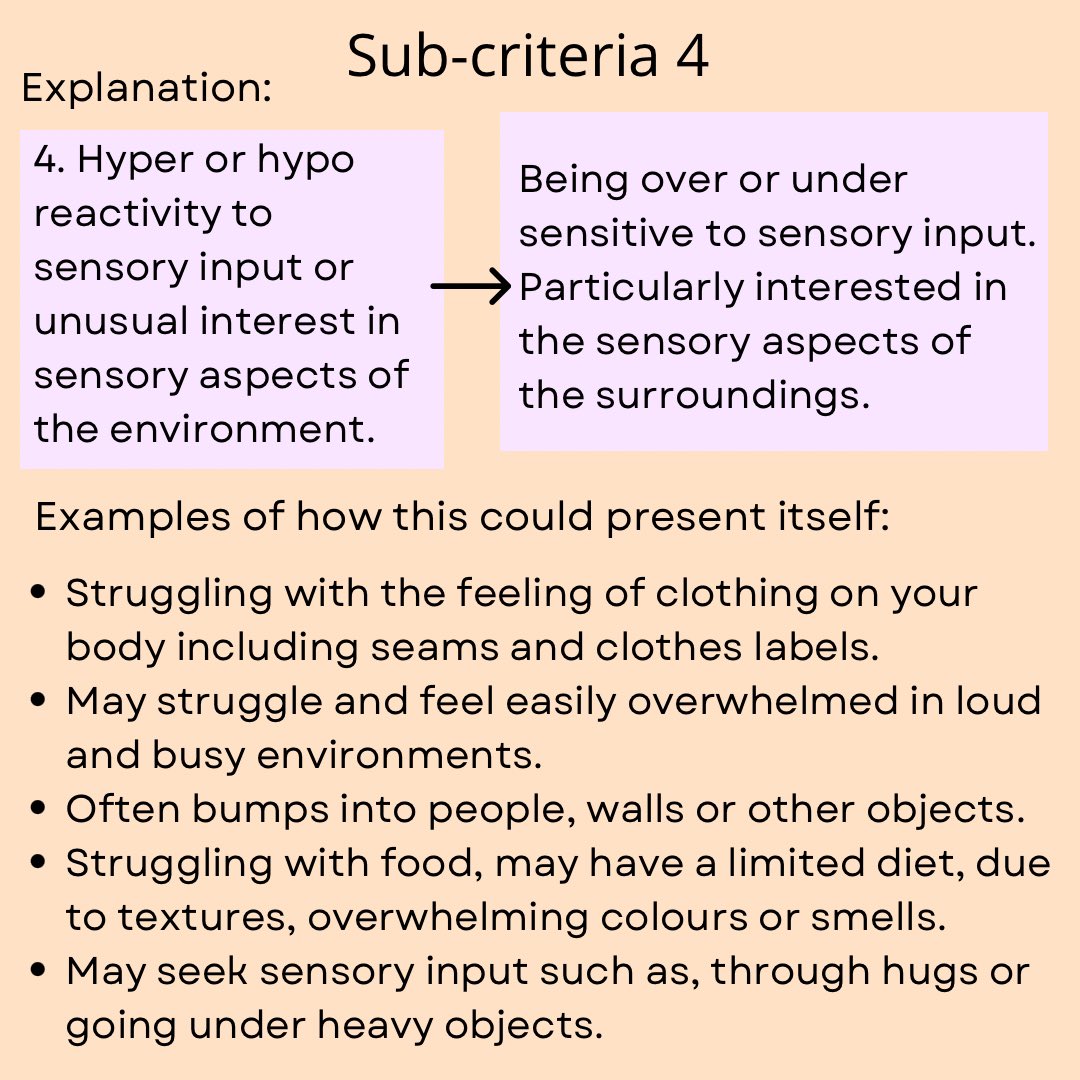
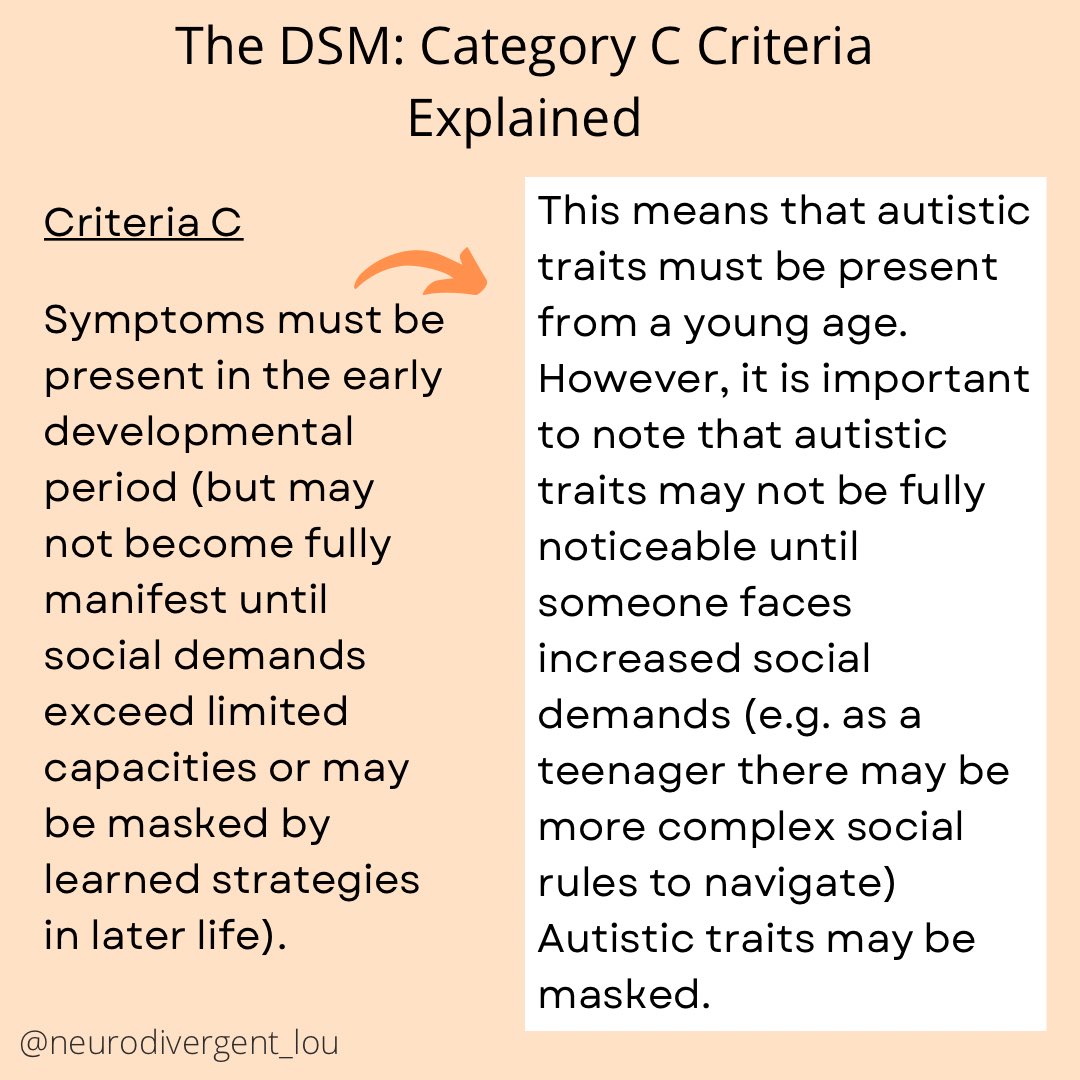
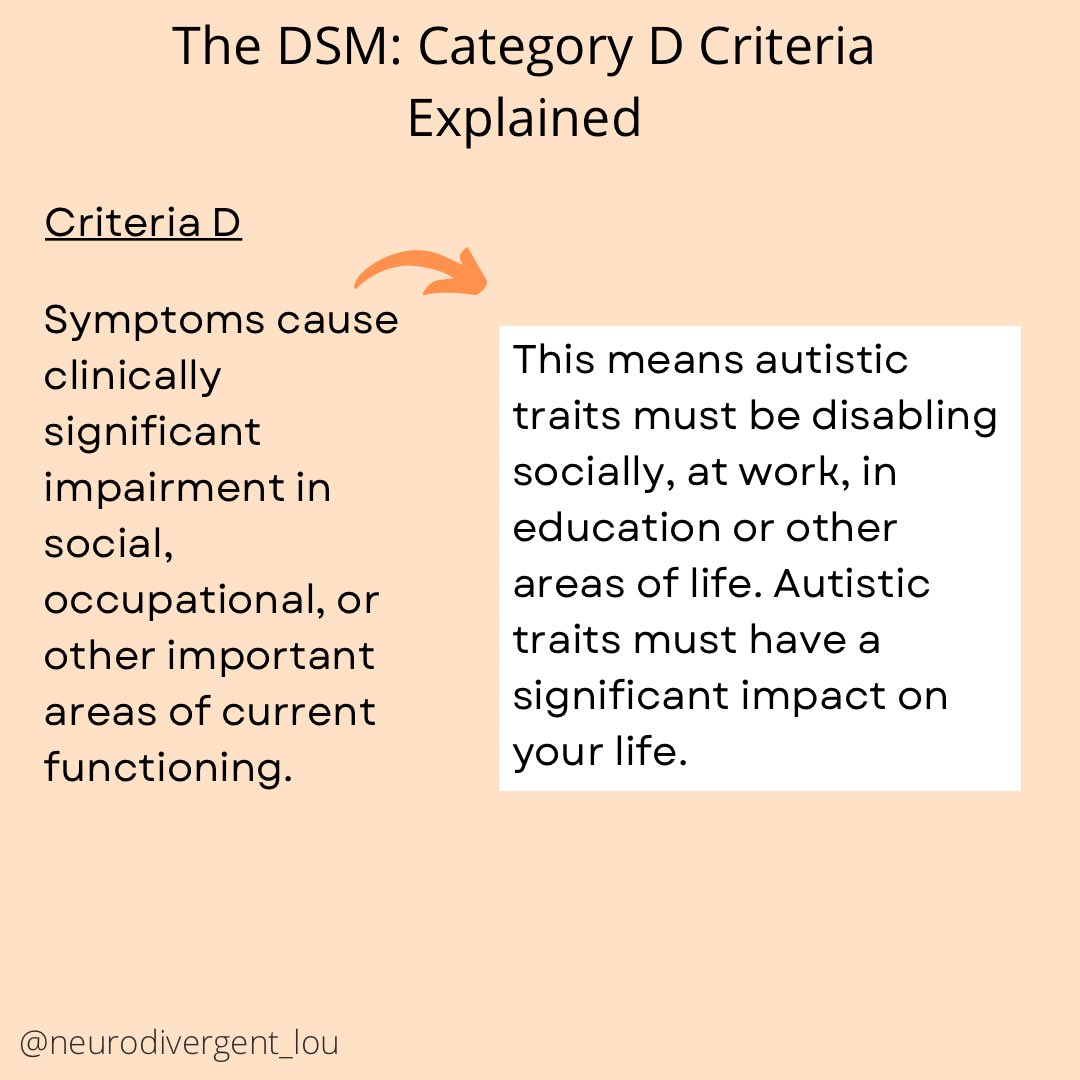
Autism Diagnosis Criteria Explained: The Full Criteria in Easy to Understand and Neurodiversity Affirming Language
#Autism #Neurodivergent #Disability #ActuallyAutistic
#Autism #Neurodivergent #Disability #ActuallyAutistic

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh