💥 Even if the basic REPRODUCTION NUMBER for COVID-19 alone, is LESS THAN 1, COVID-19 WILL PERSIST in the population, in case of CO-INFECTION with other DISEASES 💥
Let me explain that point in simpler terms. medrxiv.org/content/10.110…

Let me explain that point in simpler terms. medrxiv.org/content/10.110…

2) Normally, if COVID-19 was the only disease present, and its basic reproduction number (R0C) was less than 1, then over time the COVID-19 outbreak would decline and the disease would die out completely.
But the presence of co-infection with another disease can allow COVID-19 ..
But the presence of co-infection with another disease can allow COVID-19 ..
3) ...to "hold on" and continue circulating.
Here's how that works.
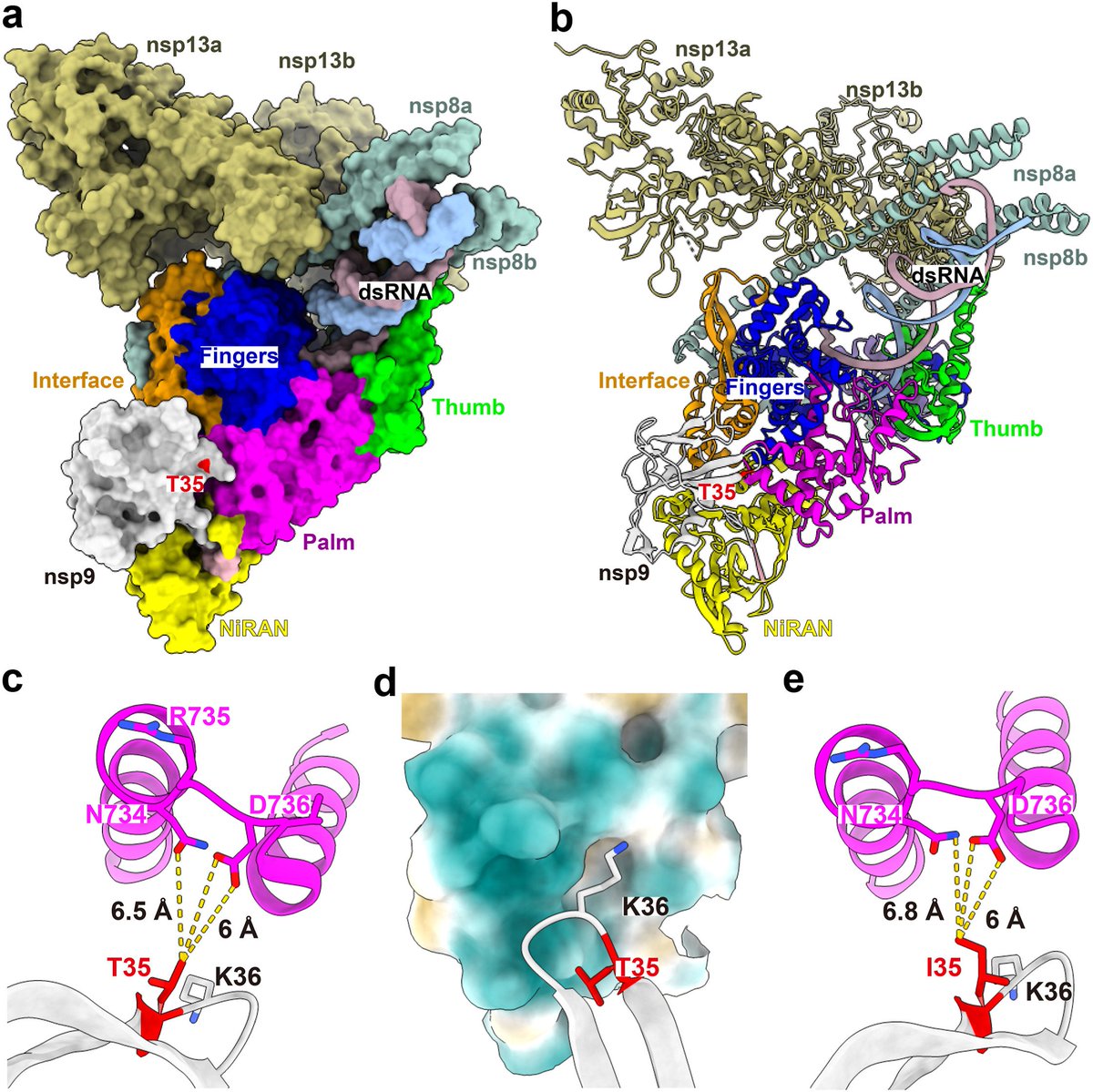
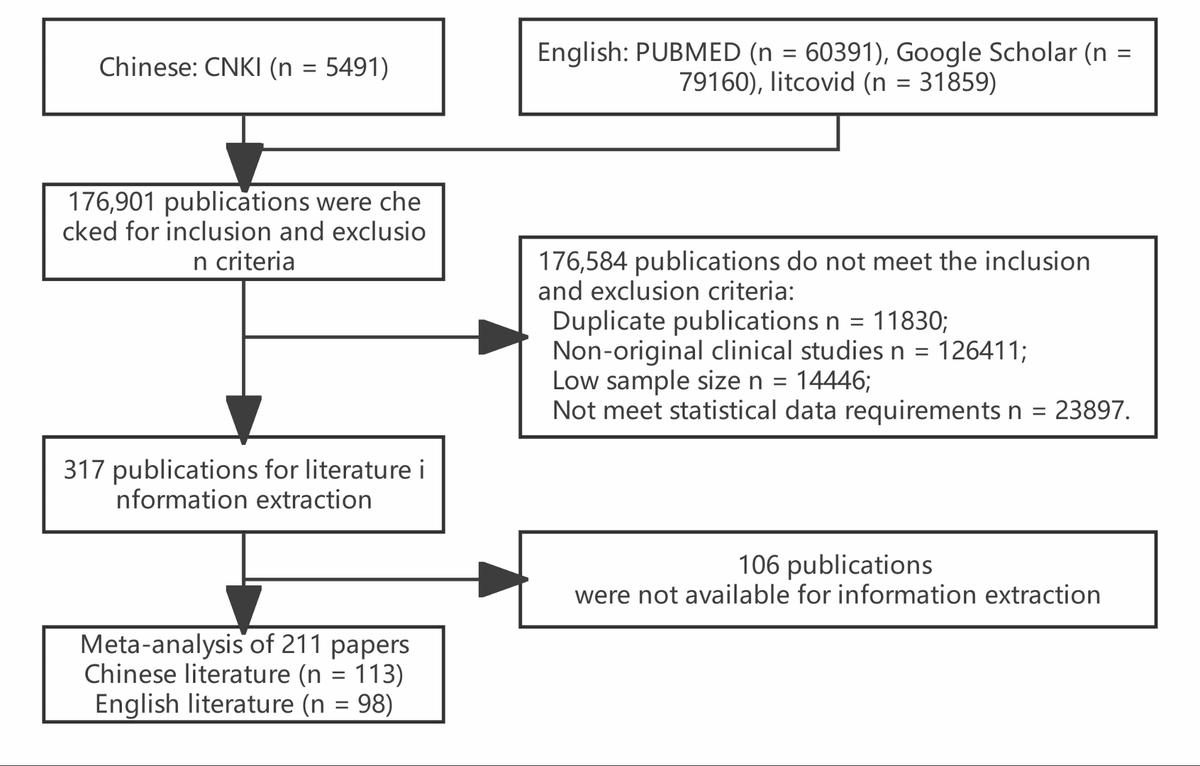
In this study scientists develops a mathematical model to study how COVID-19 and Hepatitis B diseases interact and spread when they infect the same population.
Here's how that works.
In this study scientists develops a mathematical model to study how COVID-19 and Hepatitis B diseases interact and spread when they infect the same population.

4) The model includes random factors, like small fluctuations and large unexpected events, to make it more realist.
They show that if there is co-infection with Hepatitis B, the overall co-infection reproduction number (R0HC) could still be greater than 1.
They show that if there is co-infection with Hepatitis B, the overall co-infection reproduction number (R0HC) could still be greater than 1.

5) This means the combined dynamics of COVID-19 and Hepatitis B co-infection create a situation where COVID-19 is able to maintain a "foothold" or presence in the population. It can continue circulating, even though on its own it would have died out. 

6) The co-infection essentially provides an "avenue" for COVID-19 to persist, when it otherwise would have been eliminated. The interactions between the two diseases allow COVID-19 to keep spreading and not fully disappear from the population.
7) So in summary, the co-infection dynamics act as a "lifeline" for COVID-19, enabling it to hang on and continue circulating, even in situations where COVID-19 alone would have been eradicated.
Thanks for reading 🙏
Thanks for reading 🙏

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh