This preprint (from April 5) is FASCINATING. Someone requested I have a look at it, and I'm glad they did, because it made SO MANY separate things suddenly make sense.
Here's a look at how a specific type of MICROCLOTS may be associated with LONG COVID pathology...
1/many
Here's a look at how a specific type of MICROCLOTS may be associated with LONG COVID pathology...
1/many

This thread will have three things:
- Takeaways of this study
- Breakdown of the method they developed
- How these findings connect with other known patterns
This is a study that looks at some rugged little blood clots that come courtesy of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
2/
- Takeaways of this study
- Breakdown of the method they developed
- How these findings connect with other known patterns
This is a study that looks at some rugged little blood clots that come courtesy of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
2/

Some important background info:
- FIBRINOGEN is a protein that just kinda hangs out in the blood, waiting.
- FIBRIN is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh to hold platelets together to form a blood clot.
- THROMBIN is the enzyme that converts FIBRINOGEN into FIBRIN.
3/
- FIBRINOGEN is a protein that just kinda hangs out in the blood, waiting.
- FIBRIN is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh to hold platelets together to form a blood clot.
- THROMBIN is the enzyme that converts FIBRINOGEN into FIBRIN.
3/
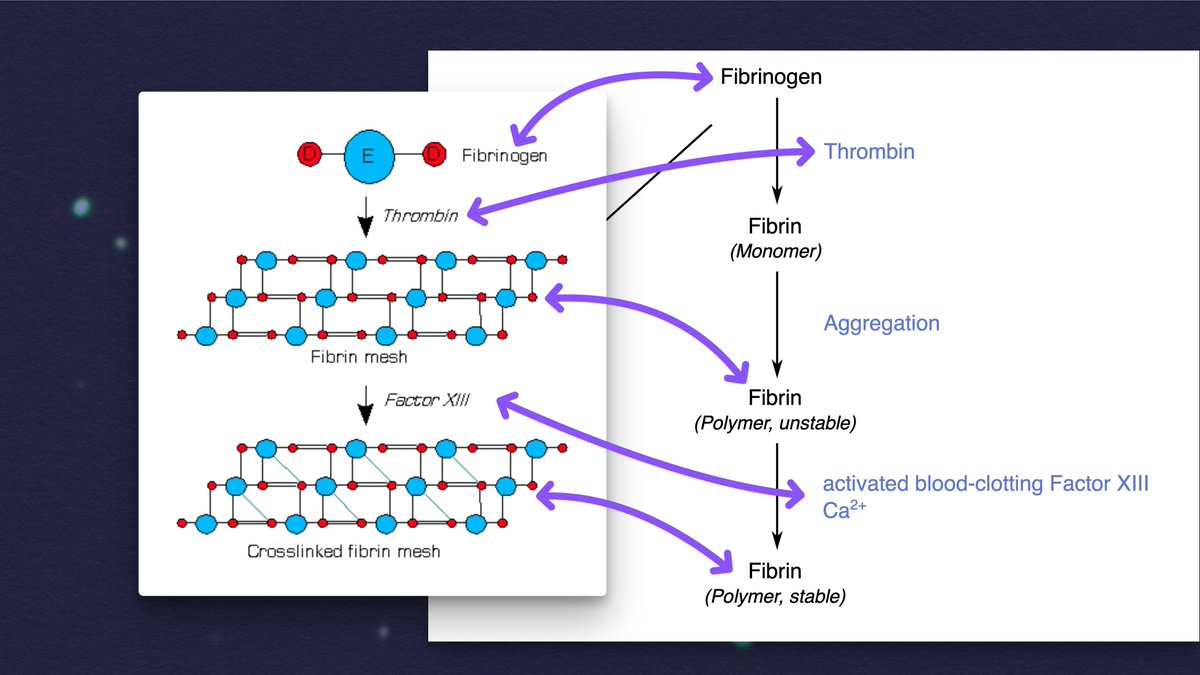
If you add thrombin to blood plasma "from people with various chronic inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases," anomalous microclots can form that are "more resistant to breakdown than normal clots."
These can also be induced JUST by adding the spike protein to plasma.
4/
These can also be induced JUST by adding the spike protein to plasma.
4/

These microclots may impair oxygen exchange in various ways, which would lead to a cascade of issues, and it's a plausible explanation for why PEM occurs. If the virus directly enters pulmonary vasculature through the mouth, these spike protein clots could be a huge problem.
5/
5/

In this study, they developed a new method to measure the microclot counts for individuals, then demonstrated "that as a cohort, samples from people with Long COVID have a higher mean microclot count compared to samples from control groups."
6/
6/

What are the takeaways?
- Microclot counts are raised in the LC cohort compared to controls
- SARS-CoV-2 infection raises microclot counts, which "take several months to return to control levels."
- Microclots may be a biomarker to screen, or even a treatment target.
7/
- Microclot counts are raised in the LC cohort compared to controls
- SARS-CoV-2 infection raises microclot counts, which "take several months to return to control levels."
- Microclots may be a biomarker to screen, or even a treatment target.
7/

What is the new method they devloped? It's a way to screen for microclots, and it specifically addresses a few potential issues with past studies.
In particular, the type of slidse typically used often have specks of reflective material about the size of the microclots!
8/
In particular, the type of slidse typically used often have specks of reflective material about the size of the microclots!
8/

Critically, they also found that leaving the blood tubes sitting around for an hour before separating out the components affected the microclot count, as did repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
So, they designed a method that was quick and had as little handling as possible.
9/
So, they designed a method that was quick and had as little handling as possible.
9/

In this method, they're able to keep the blood samples in little wells, rather than smearing them on a slide. An imaging module focuses at different depths to capture a multi-layered image, and the microclots are then automatically identified and counted.
10/
10/

Importantly, they did repeat data collection and found that they got consistent results up to six hours after initial data collection, which means it can be done with an autosampler.
This method seems robust both for research and, potentially, diagnostics.
11/
This method seems robust both for research and, potentially, diagnostics.
11/

What was found, specifically?
LC group has significantly higher clot counts compared to both uninfected controls and infected-but-no-LC controls.
Interestingly, there was ALSO significant difference in clot counts between the "recent COVID" group and other control groups.
12/
LC group has significantly higher clot counts compared to both uninfected controls and infected-but-no-LC controls.
Interestingly, there was ALSO significant difference in clot counts between the "recent COVID" group and other control groups.
12/

It's very notable that "only one [control] had a microclot count >50 while approximately half the LC group had counts above this level."
Also very interesting: there was a statistically significant difference in LC vs. control for microclot counts for women, but not men.
13/
Also very interesting: there was a statistically significant difference in LC vs. control for microclot counts for women, but not men.
13/

The difference in immune response seen between men and women may pattern with what has been observed elsewhere (including a stronger innate immune response in men, but a more robust adaptive response in women).
14/
14/

Very notably, the "Recent COVID samples have microclot counts comparable to" around the *top 25% of the LC group!*
"Together, these data indicate that exposure to SARS-CoV-2 initially increases the microclot count..., but these microclots are cleared over time."
15/
"Together, these data indicate that exposure to SARS-CoV-2 initially increases the microclot count..., but these microclots are cleared over time."
15/

IMO, this finding is a really strong explanation as to why there seems to be an increased risk of cardiac incidents in the 3-6 months following a SARS-CoV-2 infection: The presence of the spike protein may be creating microclots throughout the cardiovascular system!
16/


16/


How did the microclots relate to symptoms? Their questionnaire was basic, but they generally found the symptoms you'd expect being prominent in the LC group: fatigue, post-exertional malaise, difficulties concentrating, etc.
However, high microclots didn't GUARANTEE LC!
17/


However, high microclots didn't GUARANTEE LC!
17/


So, do microclots cause LC? I mean, they probably don't *help*.
One possible explanation is that LC may reflect a persistent dysregulated state (e.g. a "pro-coagulable state"), and external intervention would be required to shift things back to normal.
18/
One possible explanation is that LC may reflect a persistent dysregulated state (e.g. a "pro-coagulable state"), and external intervention would be required to shift things back to normal.
18/

I think the "potential role of the spike protein in inducing amyloid formation and seeding microclots" is a FASCINATING possibility—especially given that there seems to be the possibility of a runaway process of consistent clotting.
(It may also explain vCJD!)
19/
(It may also explain vCJD!)
19/

The authors also note that, since this is a new line of research, we have no idea what role microclots may play in other conditions—but they're beginning by investigating whether pwME have similar microclot profiles to pwLC!
I'm also very curious how EBV impacts clotting!
20/
I'm also very curious how EBV impacts clotting!
20/

Of course, this isn't the only way that the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein has been shown to cause cardiac damage: It may also lead to fusion of uninfected cells!
21/
21/
https://x.com/NickAnderegg/status/1820670548814299264
Overall, the implications are significant. At the very least, I think this is a plausible explanation for why there are often cardiac issues *in the time period shortly after infection,* even if it doesn't explain LC!
Source: (h/t @JPeaceJPeace)
22/22medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
Source: (h/t @JPeaceJPeace)
22/22medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh



!["Data on BW consumption were obtained from the “Aspects of Daily Life” survey on households, conducted by the Italian National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT) [19]. ... The aim of the survey is to identify a variety of behavioral dimensions and aspects of daily life. ... We analyzed data from the 2021 edition of the survey, which included 45,597 individuals and 20,000 families, focusing on those who were 18 years or older at the time of the survey. ... a distinct stratum of municipalities with larger populations, labeled as self-representative (SR), and other municipalities, designated...](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/GVDBF48W4AAKDgi.jpg)









![Published August 5, 2024 in PLOS Pathogens: "SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia are senescent and contribute to exacerbated heart failure" "Author Summary In this paper, we directly linked SARS-2-S-triggered syncytium [fused cells] formation in the absence of infection with the ensuing induction of cellular senescence and its pathophysiological contribution to heart failure. We propose that both SARS-2-S expression and SARS-2-S protein internalization were sufficient to induce senescence in nonsenescent ACE2expressing cells. This is important because of the persistent existe...](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/GURP49TW0AAb71d.jpg)


!["Introduction ...Although symptoms resulting from infection typically resolve within weeks, some individuals experience persistent symptoms following the acute phase of COVID-19, the so-called post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) or long COVID [2–4]. SARS-CoV-2 infection predominantly offends the respiratory system. Currently, evidence has suggested cardiac complications as one of the important pathogenic features of COVID-19 [5,6]. More importantly, compared with patients without heart failure, those with diagnosed heart failure experienced a longer length of hospital stay, increas...](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/GURP9_CWQAA3NX-.jpg)










