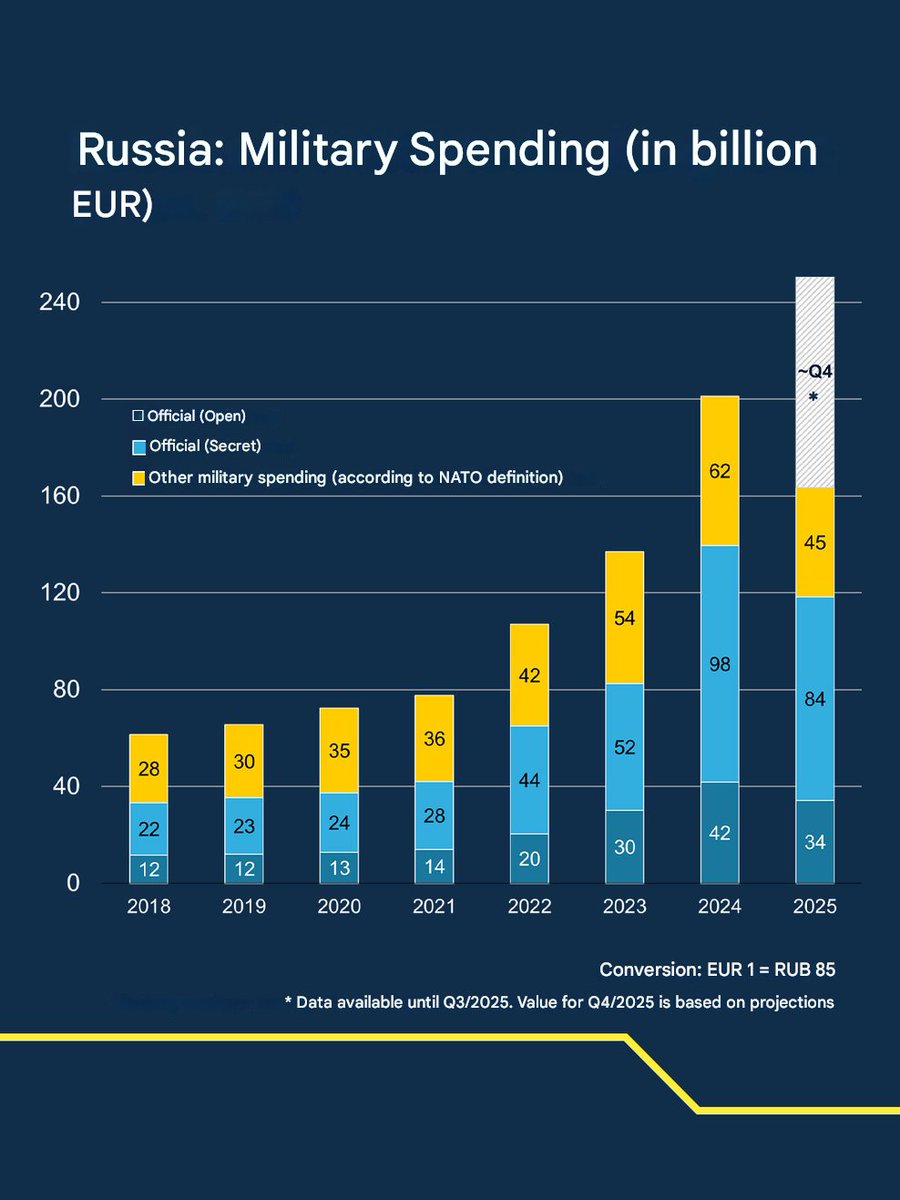
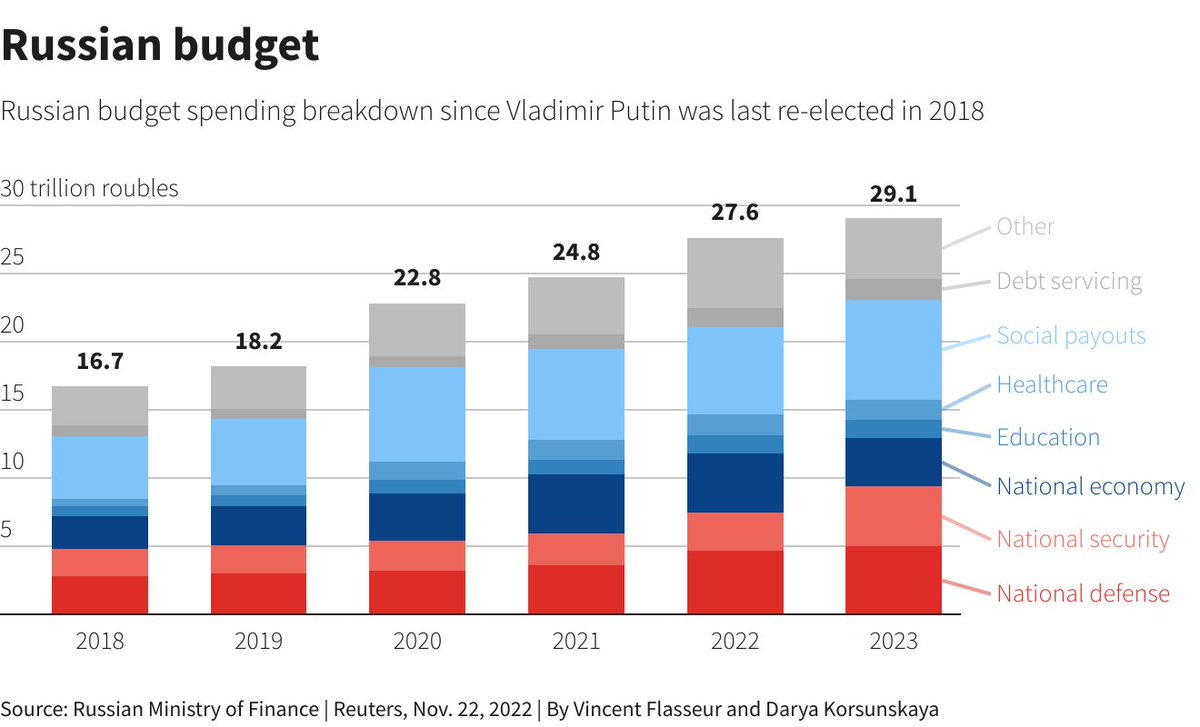
Vladimir Putin is unlikely to announce mobilization, but will continue to use conscripts to replenish the army. A survey in Russia showed that the level of public anxiety after Ukraine's entry into Kursk increased less than it was when mobilization was announced.
1/15
1/15

Putin considers mobilization even more dangerous for the government than the loss of the Kursk region, even in its entirety. The problems of the Kursk region in the eyes of Russians remain regional problems, and they will even survive the loss of the region as a whole.
2/15
2/15

Mobilization will come to almost every home. There are still enough regions in Russia, but mobilization violates the unspoken agreement that was formed under Putin - the people turn a blind eye to the theft of the government, and in exchange, the government does not touch
3/15
3/15

the citizens. Putin avoids mobilization, especially since there will be another call-up in October. Most likely, he will wait for it. Conscripts are another system of slavery in Russia. They have almost no rights, they obey the will of those above them. If they do not obey,
4/1
4/1

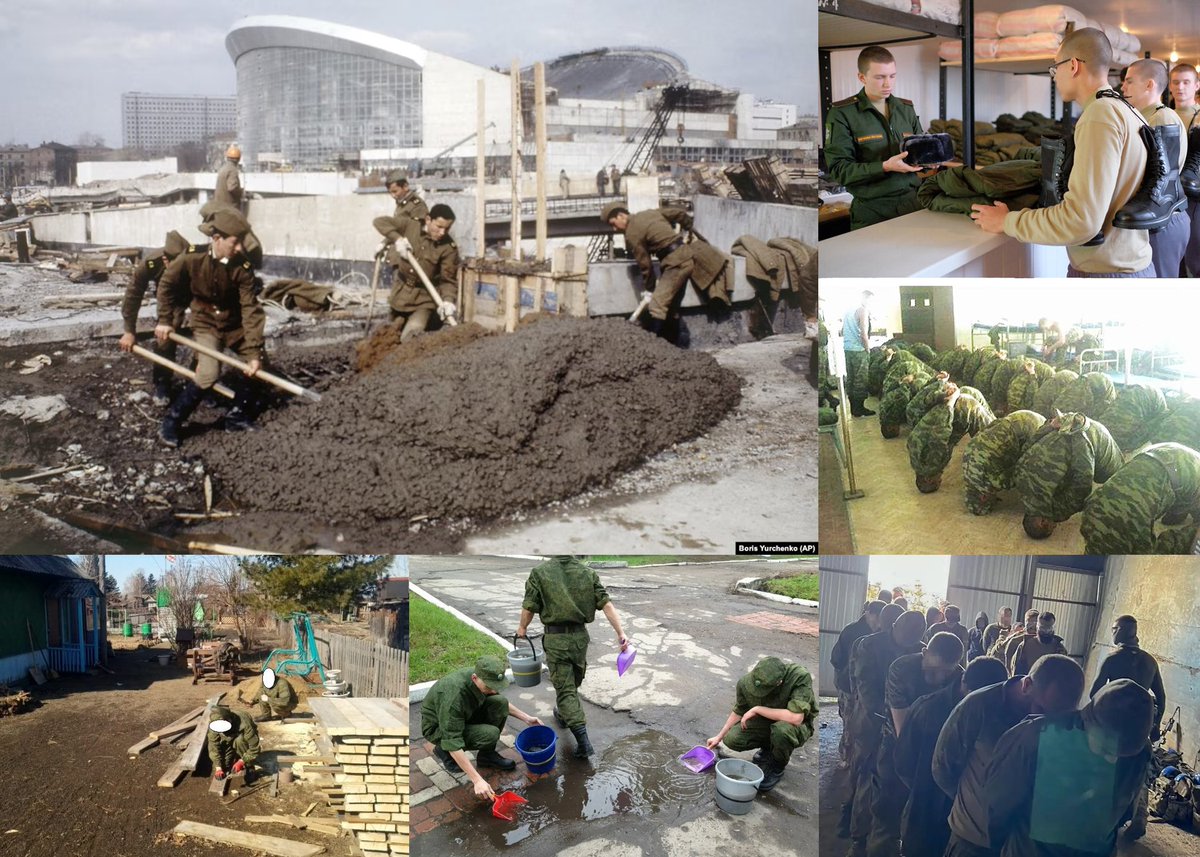
they are given such a life in the barracks that they change their minds. They are beaten, morally abused. They completely belong to the system. They were sent to Chernobyl to eliminate the consequences of the reactor explosion without proper protection and equipment, to
5/15
5/15

eliminate the consequences of other disasters. Along with prisoners from prisons, conscripts were used as free labor. Most often, they were sent to construction sites and field work. So, most of the facilities in Tallinn for the 1980 Olympics in the USSR were also built
6/15
6/15

using conscripts. The quality of such construction is, of course, very low. By the way, the City Hall building, which was the location of the Kiev Opera in Christopher Nolan's film "Tenet", was also built, including conscripts for the Olympics. Then it was called the "Palace
7/15
7/15

of Culture and Sports named after V. I. Lenin". Now it has completely fallen into disrepair and it is unprofitable to renovate it. There are discussions about its fate. Little has changed since the USSR. Only the service life has been reduced from 2 to 1 year. Instead of
8/15
8/15

training, recruits are most often busy with construction, cleaning, loading and unloading, and other chores for unit commanders. They are a kind of enslaved peasants, and he is the master. Structure of Russian army is a huge topic and needs to be analyzed separately. It is
9/15
9/15

a vertical hierarchy, closely connected with the government, state construction projects, the military industry, and everything is built in such a way as to steal as much as possible from the state budget, and in return provide models and Potemkin villages. If a big guest
10/15
10/15

comes to town, along with municipal services, these will be conscripts who will be forced to paint the grass green and hide garbage. In general, inventing useless tasks for soldiers is a long-standing tradition in the Russian army. Rolling a square, plucking grass with
11/15
11/15

bare hands, sweeping with crowbars. This is how commanders "instill discipline" and it is believed that if a soldier is not busy with anything, it is imperative to come up with a task for him. Therefore, the Russian army was never conceived as a normal army in function.
12/15
12/15

Its main strength has always been simply the number of "peasants" that it could afford to throw at embrasures with machine guns, regardless of losses. But Russia is not the USSR. Its resources are much more modest, mostly left over from the times of the USSR. Deliberately
13/15
13/15

keeping the population in poverty the Russian government found those who were ready to sign a contract, but now even payments of 2 million are not attractive. In addition, there was no Internet or communications in the USSR. Now people know a little more about what is
14/15
14/15

happening. This is why people are not very eager to join the army. Conscripts also do not have to be paid. Before the Kursk, conscripts were pressured to sign a contract and so that is how they ended up at the war. In Kursk region they are now simply sent to the front.
15/15
15/15

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh