There's a popular saying that if you're not a liberal at 20, you have no heart, but if you're not a conservative by 40, you have no brain.
It might be more accurate to imagine that people's formative years have large, persistent impacts on their beliefs. A study by Andy Gelman showed how.
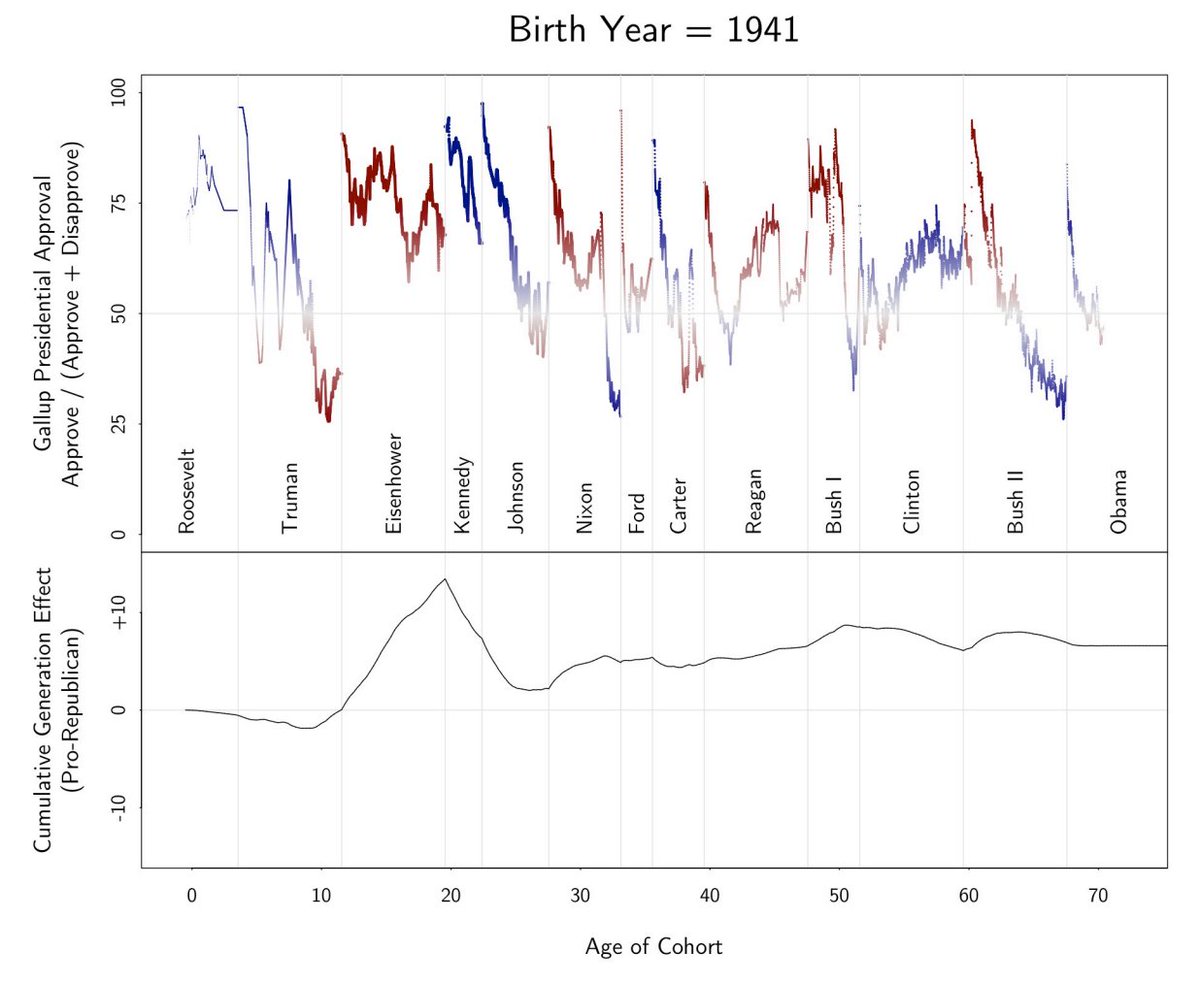
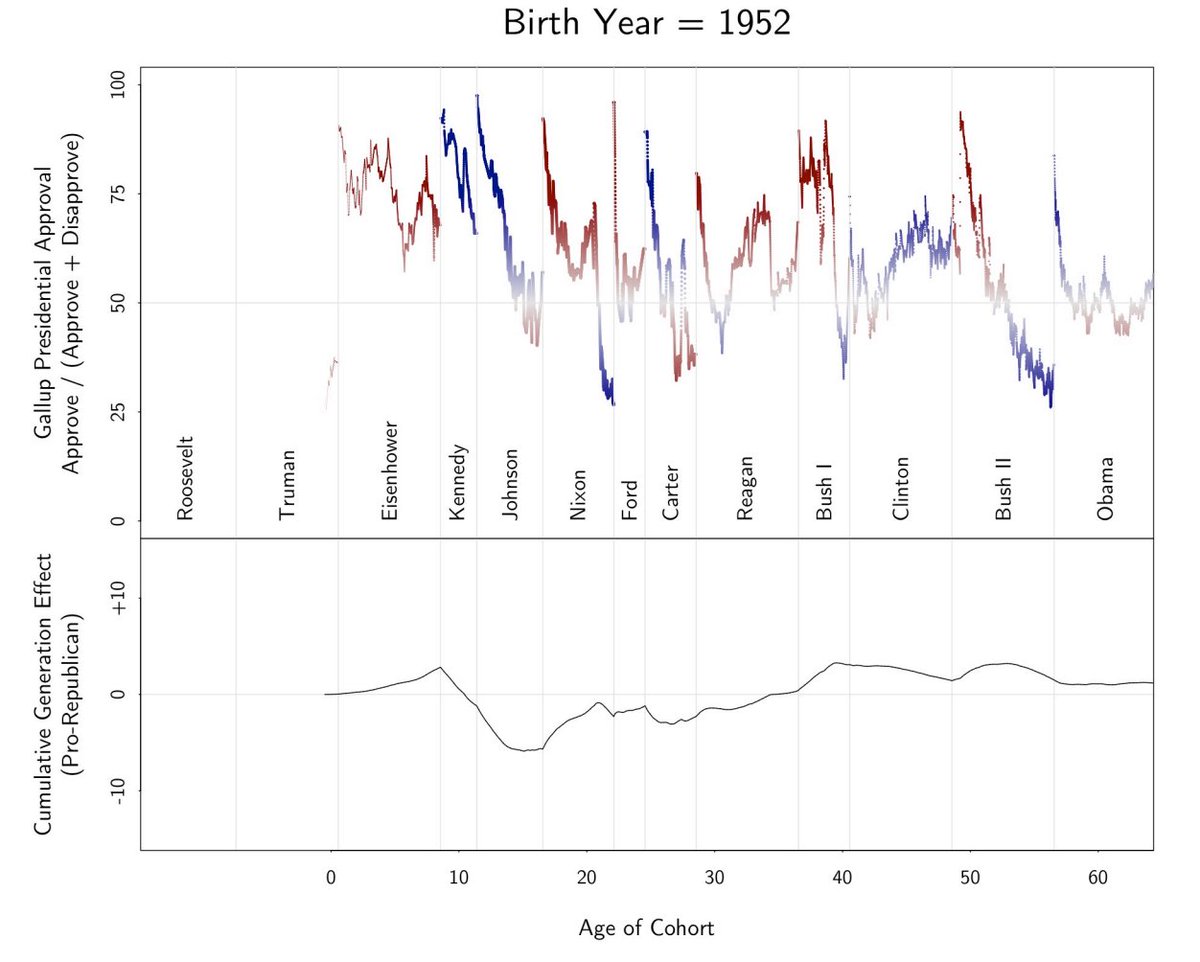
In the Gelman model, high presidential approval during a (White) birth cohort's teen years leads them to favor that president's party for the rest of their lives. Whatever the reason, it's as if they're acting to bring back the 'good old days' of their cognizant childhood. To get an idea of how this looks, look at Eisenhower Republicans:
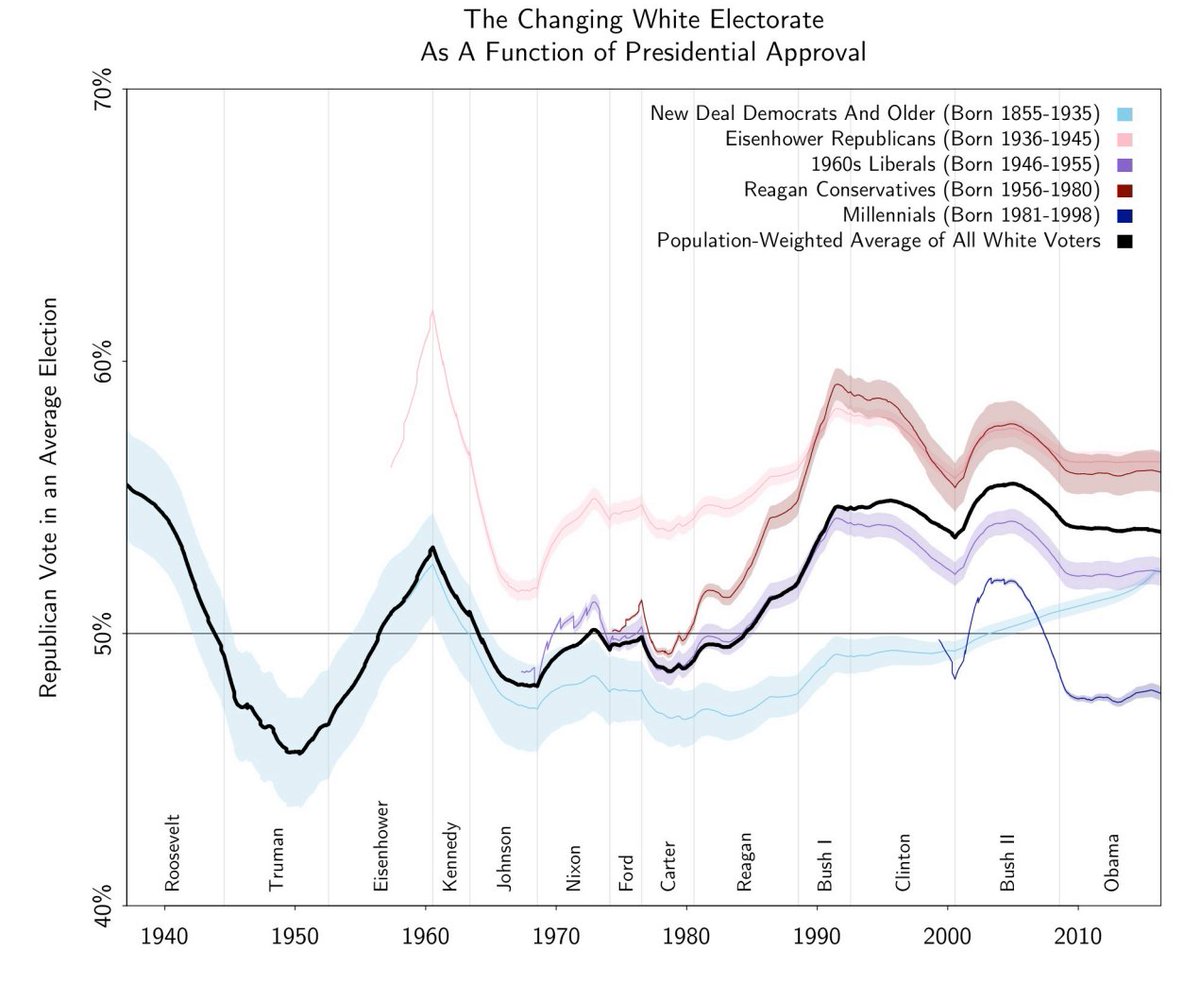
The Eisenhower Republicans were those who missed most of the FDR years and were socialized in ten straight years of Republicans, of which the Eisenhower years had positive spin. As a result, that cohort became very pro-Republican, but then the very pro-Democrat Kennedy and Johnson years moderated them back to being a bit less pro-Republican.
The 1960s Liberals were born a bit later than the Eisenhower Republicans and they got to experience the pro-Kennedy and Johnson years in their formative years, but the next 25 years of strongly pro-Republican sentiment brought them to near-neutrality.
One of the most well-known political generations is the Reagan Conservatives. This generation got to experience strong pro-Republican sentiment and they ushered in the real Reagan Revolution: a cohort with strong pro-Republican leanings and little moderation due to the balance of sentiment between Clinton and Bush II, and Obama's nearly neutral sentiment.
Other cohorts like the New Deal Democrats and Millennials have their own biases that follow from the same dynamics, and if you plot them all together, you get a clear picture of the sentiment of the White electorate:
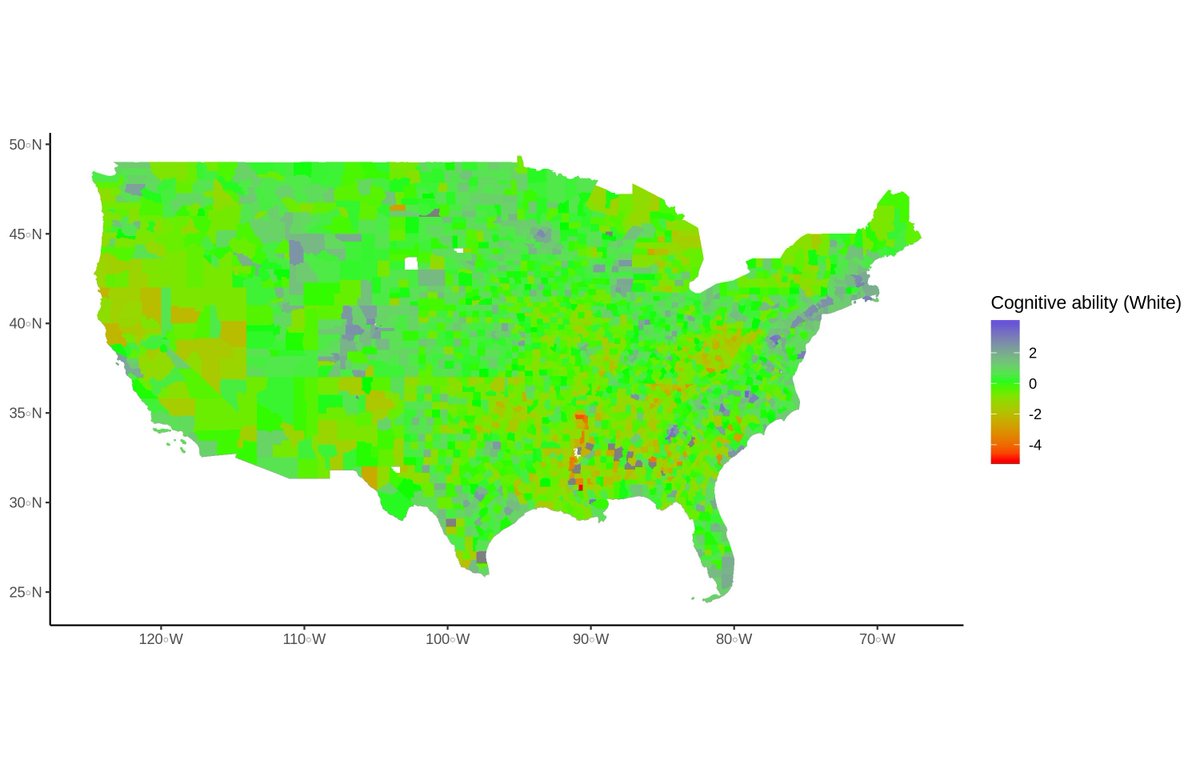
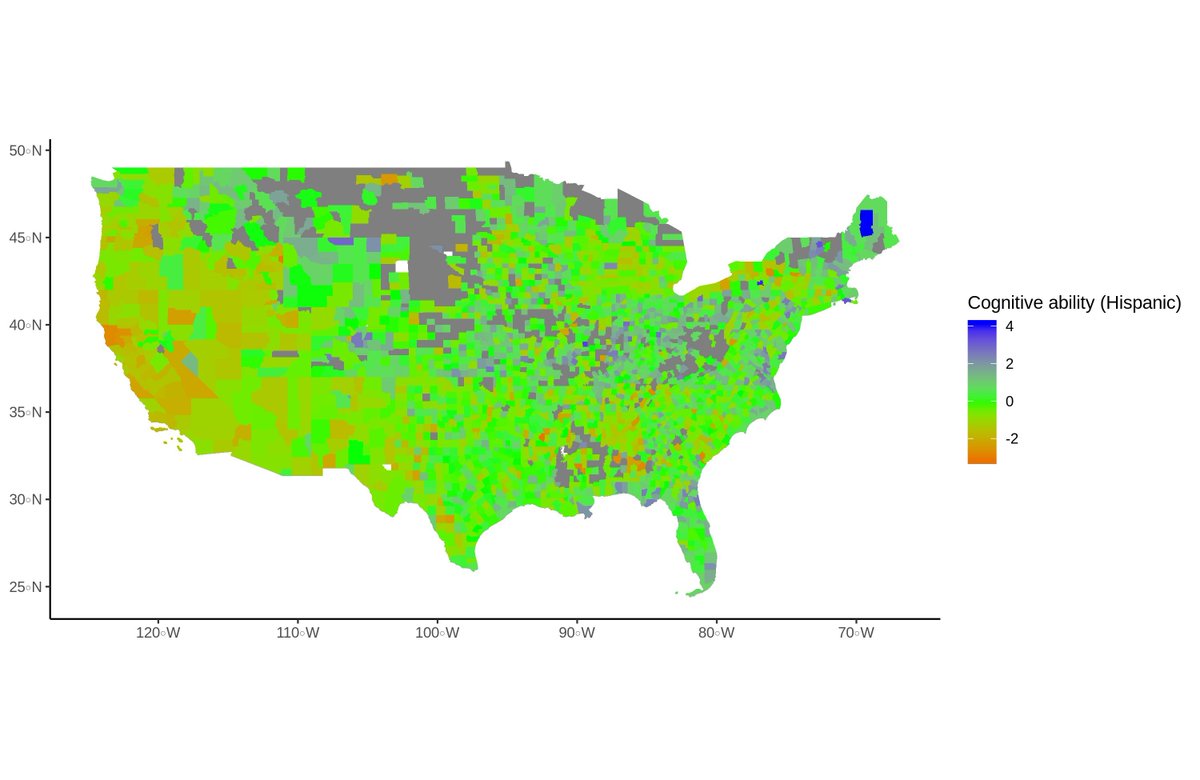
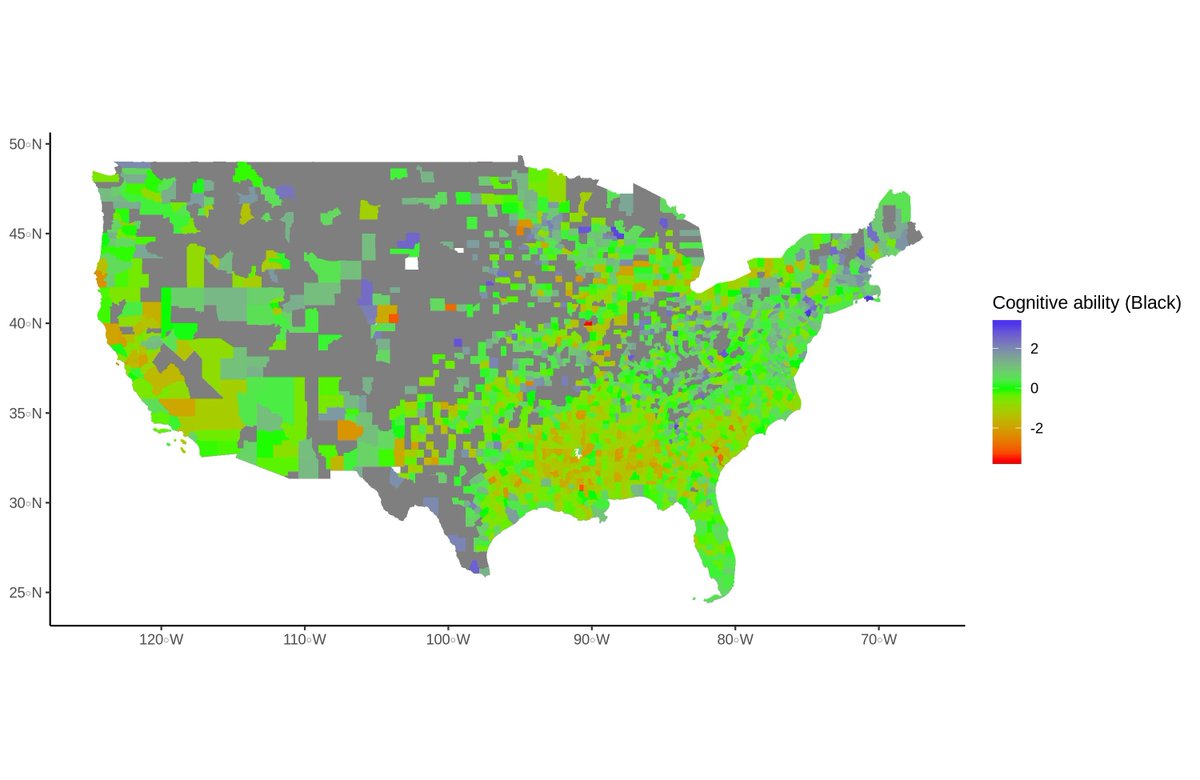
Now do note, I said Whites. This model works slightly better for non-Southern than for Southern Whites, and compared to those two groups, it works less than half as well for non-White minorities.
In any case, this model based on formative year impacts can explain roughly 90% of the variance in vote choices in the electorate. If you want to get people's votes, get them early in life, and you might be able to hold them through waves of less popular candidates from your own party.
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.111…



It might be more accurate to imagine that people's formative years have large, persistent impacts on their beliefs. A study by Andy Gelman showed how.
In the Gelman model, high presidential approval during a (White) birth cohort's teen years leads them to favor that president's party for the rest of their lives. Whatever the reason, it's as if they're acting to bring back the 'good old days' of their cognizant childhood. To get an idea of how this looks, look at Eisenhower Republicans:
The Eisenhower Republicans were those who missed most of the FDR years and were socialized in ten straight years of Republicans, of which the Eisenhower years had positive spin. As a result, that cohort became very pro-Republican, but then the very pro-Democrat Kennedy and Johnson years moderated them back to being a bit less pro-Republican.
The 1960s Liberals were born a bit later than the Eisenhower Republicans and they got to experience the pro-Kennedy and Johnson years in their formative years, but the next 25 years of strongly pro-Republican sentiment brought them to near-neutrality.
One of the most well-known political generations is the Reagan Conservatives. This generation got to experience strong pro-Republican sentiment and they ushered in the real Reagan Revolution: a cohort with strong pro-Republican leanings and little moderation due to the balance of sentiment between Clinton and Bush II, and Obama's nearly neutral sentiment.
Other cohorts like the New Deal Democrats and Millennials have their own biases that follow from the same dynamics, and if you plot them all together, you get a clear picture of the sentiment of the White electorate:
Now do note, I said Whites. This model works slightly better for non-Southern than for Southern Whites, and compared to those two groups, it works less than half as well for non-White minorities.
In any case, this model based on formative year impacts can explain roughly 90% of the variance in vote choices in the electorate. If you want to get people's votes, get them early in life, and you might be able to hold them through waves of less popular candidates from your own party.
Source: onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.111…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh