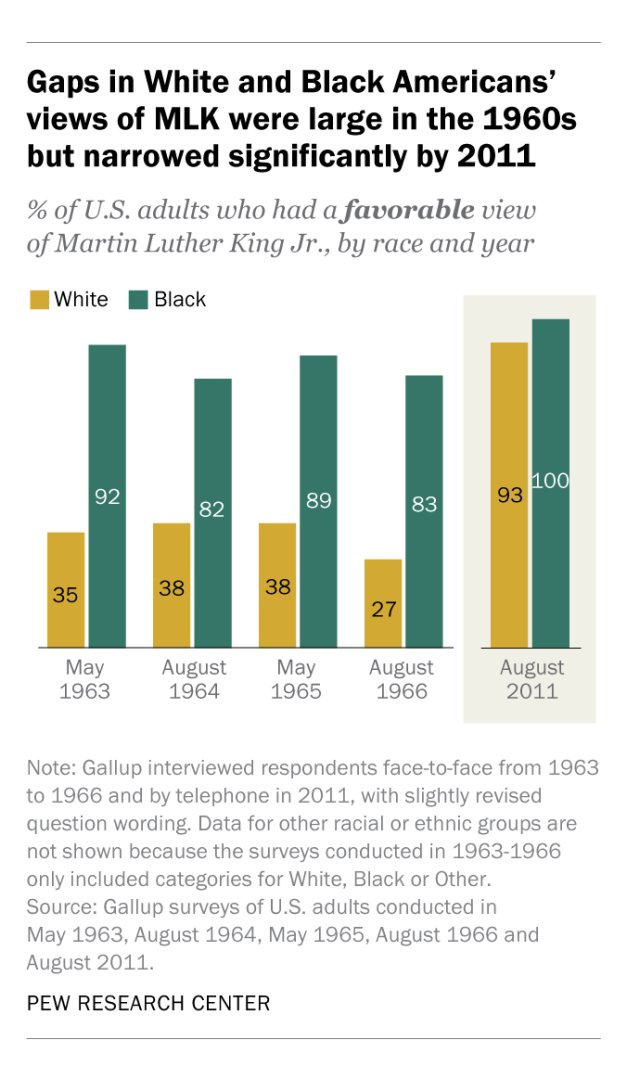
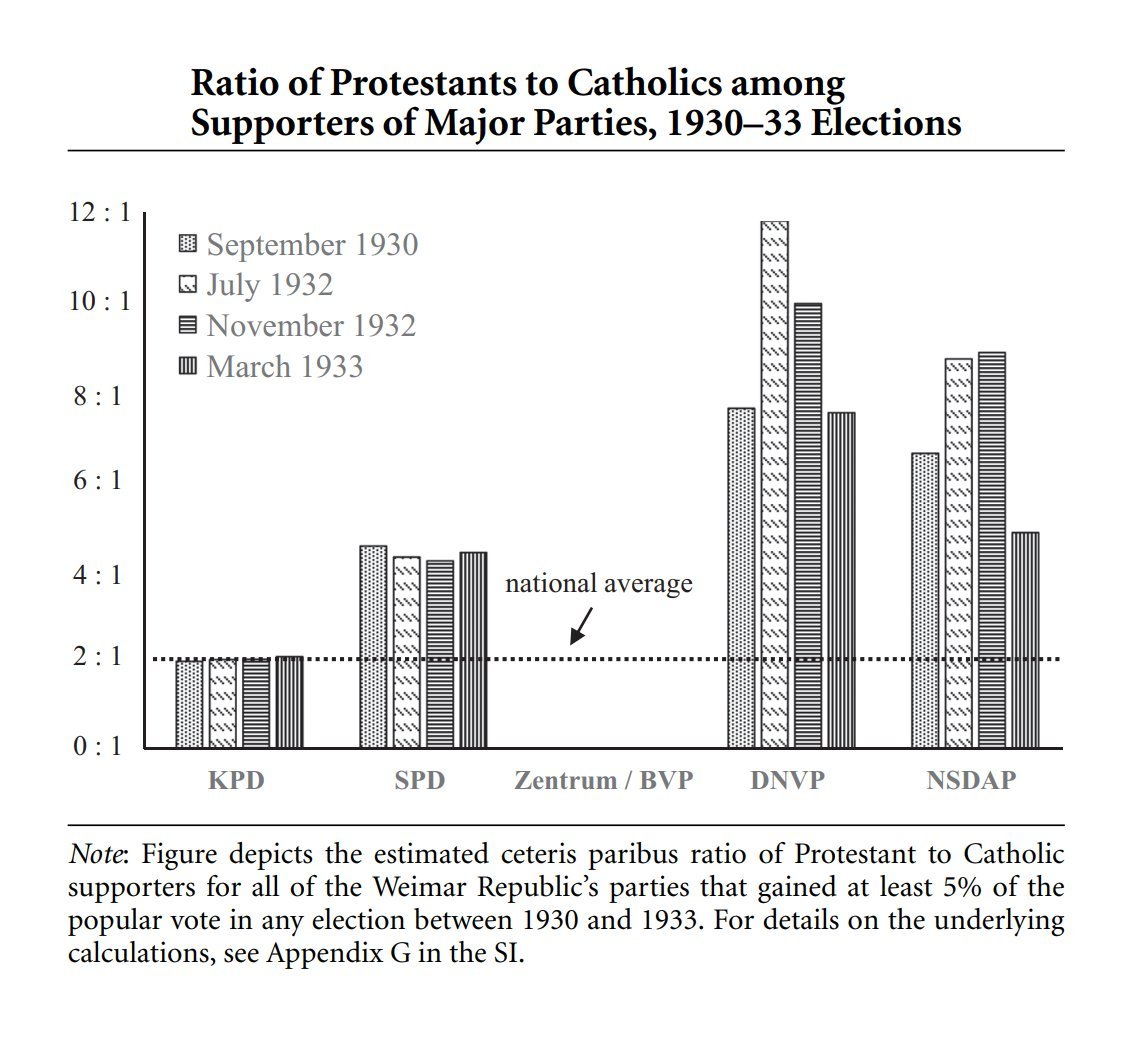
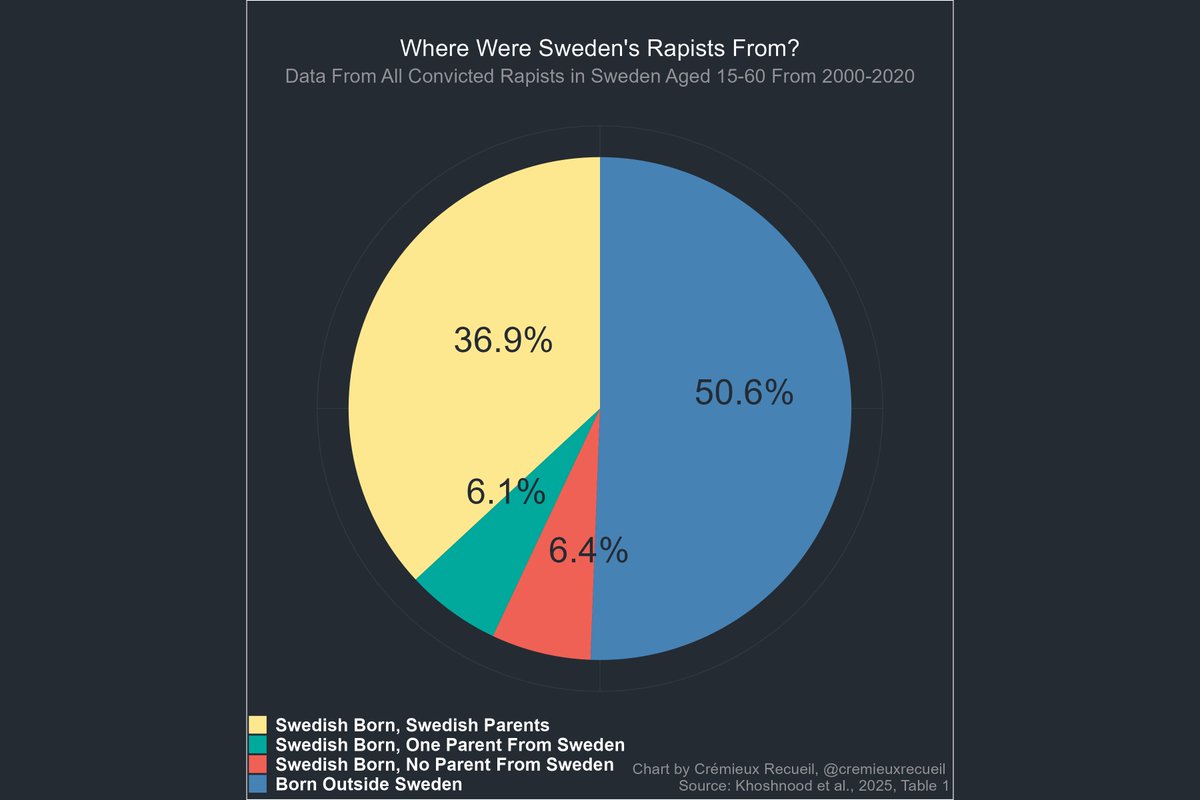
I know just one person over 100 with an actual birth certificate.
Across U.S. states, the total and per capita numbers of supercentenarians dramatically decline right after the introduction of birth certificates (blue line).
The reason? Most such cases are fake.

Across U.S. states, the total and per capita numbers of supercentenarians dramatically decline right after the introduction of birth certificates (blue line).
The reason? Most such cases are fake.
https://twitter.com/zwotheramabale/status/1827639087429189781

Also, have you ever noticed that supercentenarians are more common in areas with more crime, more poverty, and lower average life expectancies?
Here's data for England:
Here's data for England:

The same pattern of supercentenarian numbers being correlated with poverty holds in (A, D) England, (B, E) France, and (C, F) Japan.

Across countries, you just see the same things over and over, from age heaping to weird correlations, so the conclusion is clear:
Supercentenarian numbers are driven less by regionally exceptional longevity and more by people defrauding pension systems and making up their ages.
Supercentenarian numbers are driven less by regionally exceptional longevity and more by people defrauding pension systems and making up their ages.

Oh, and if you wanted to learn how to live a long life from the "blue zones" in Sardinia, Okinawa, and Icaria, good luck. Those places have low life expectancies and literacy levels, high crime, and lots of poverty.
Their long-lived people are not able to validate their ages.
Their long-lived people are not able to validate their ages.

This also applies to Loma Linda (not all that exceptional of a place).
In fact, across the whole U.S., at least 17% of centenarians were found to be non-centenarians in 2019 when someone just read through two plain-text files and found dates didn't match.
In fact, across the whole U.S., at least 17% of centenarians were found to be non-centenarians in 2019 when someone just read through two plain-text files and found dates didn't match.

If someone says they know someone super old, ask them: Where were they born? If it's in some place that was poor in the not-too-distant past, then they probably have the wrong age.
Source: biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
Source: biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh