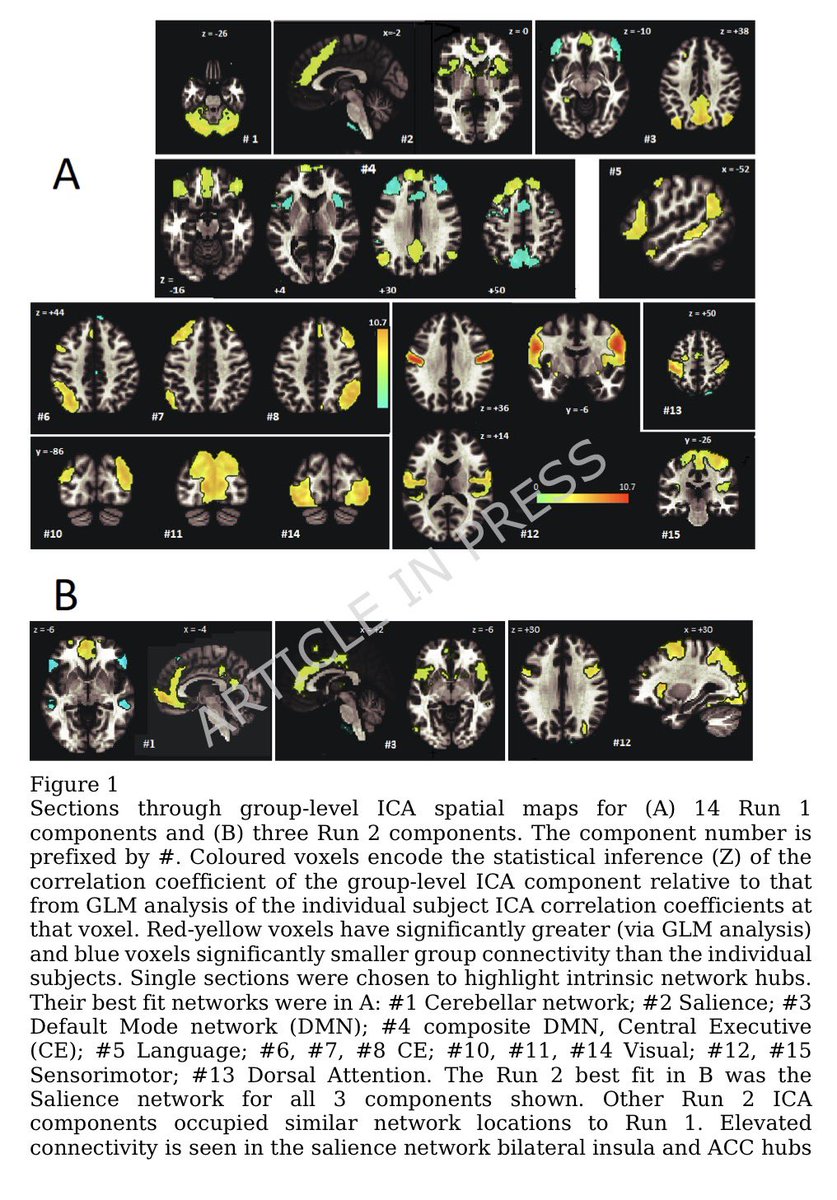
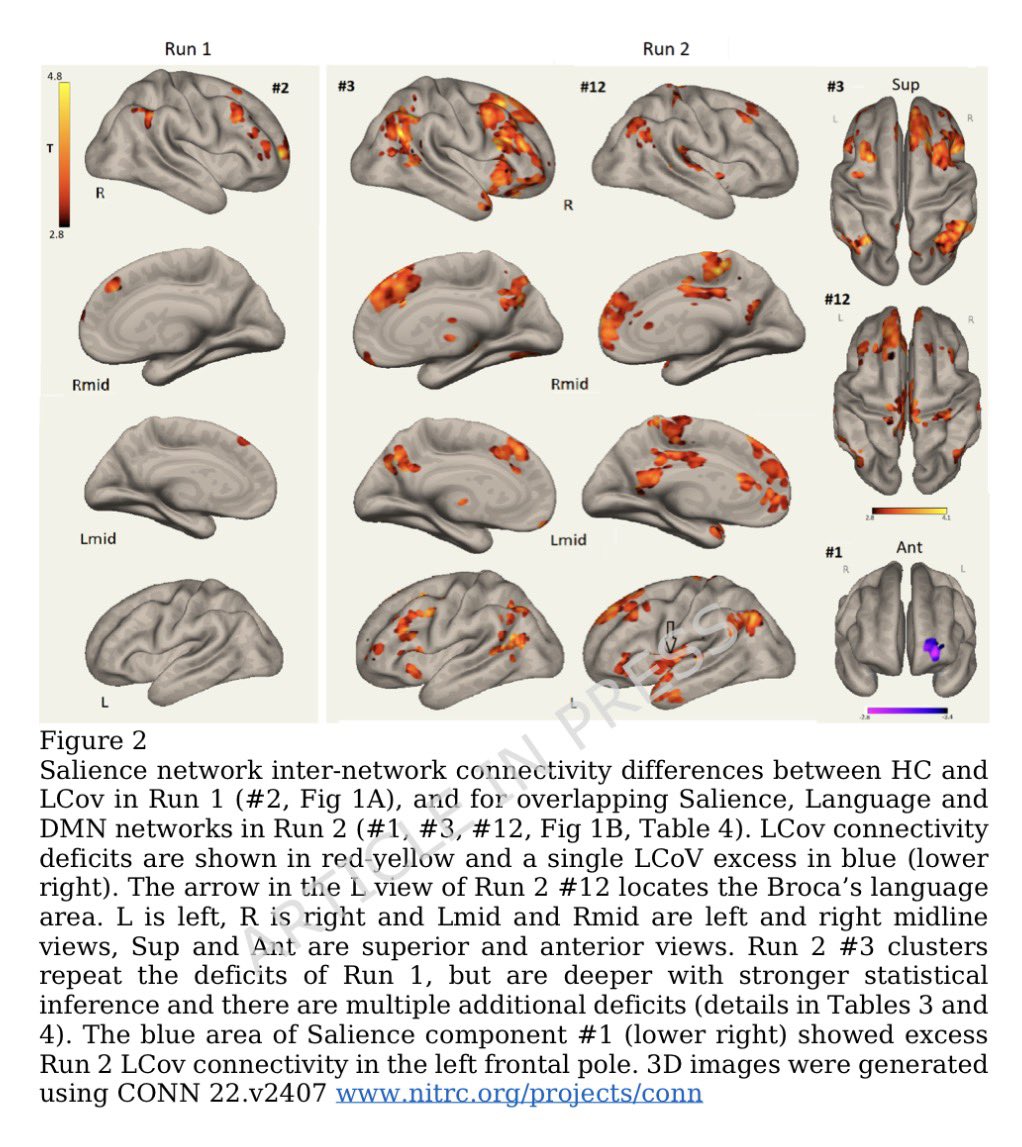
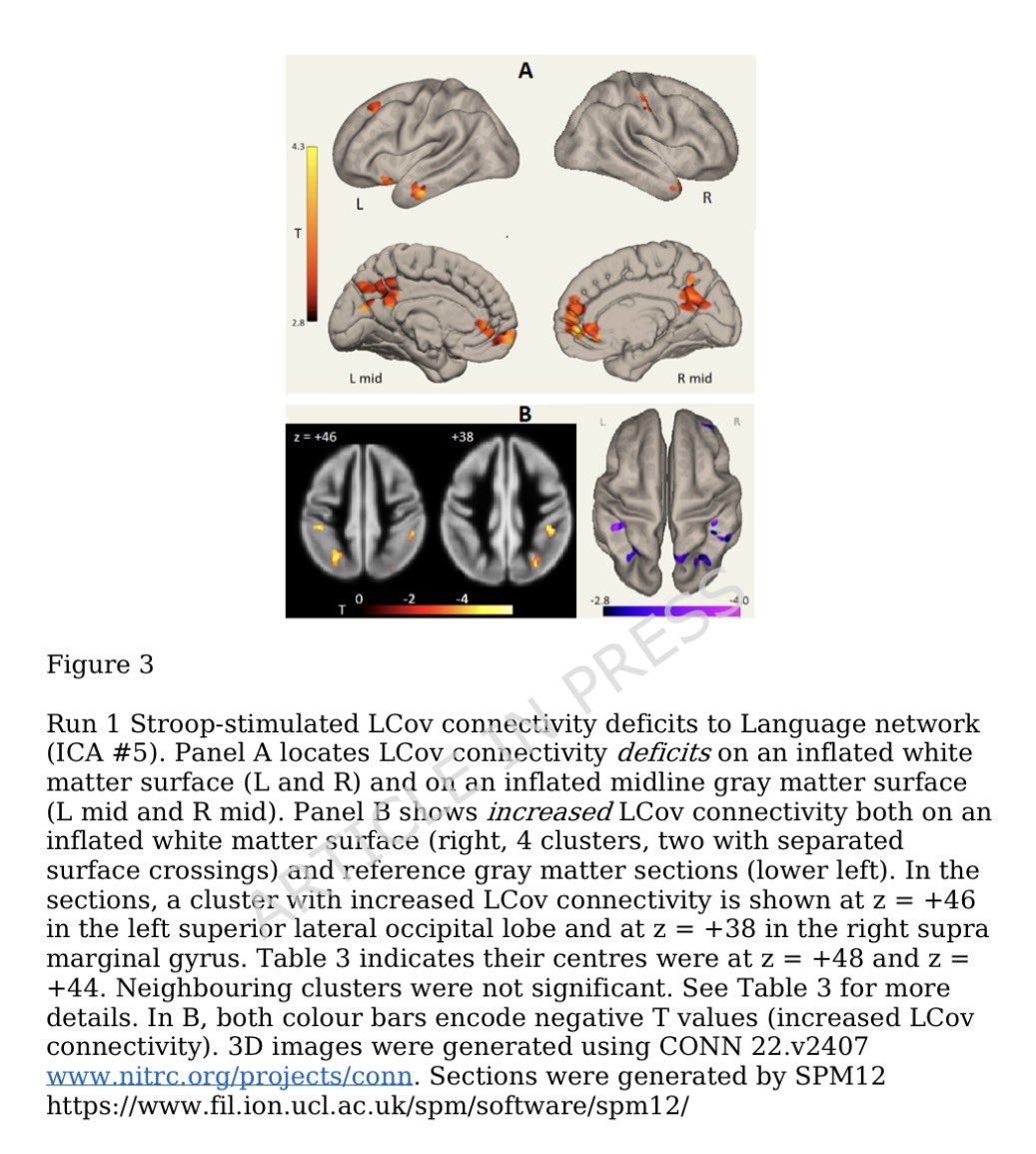
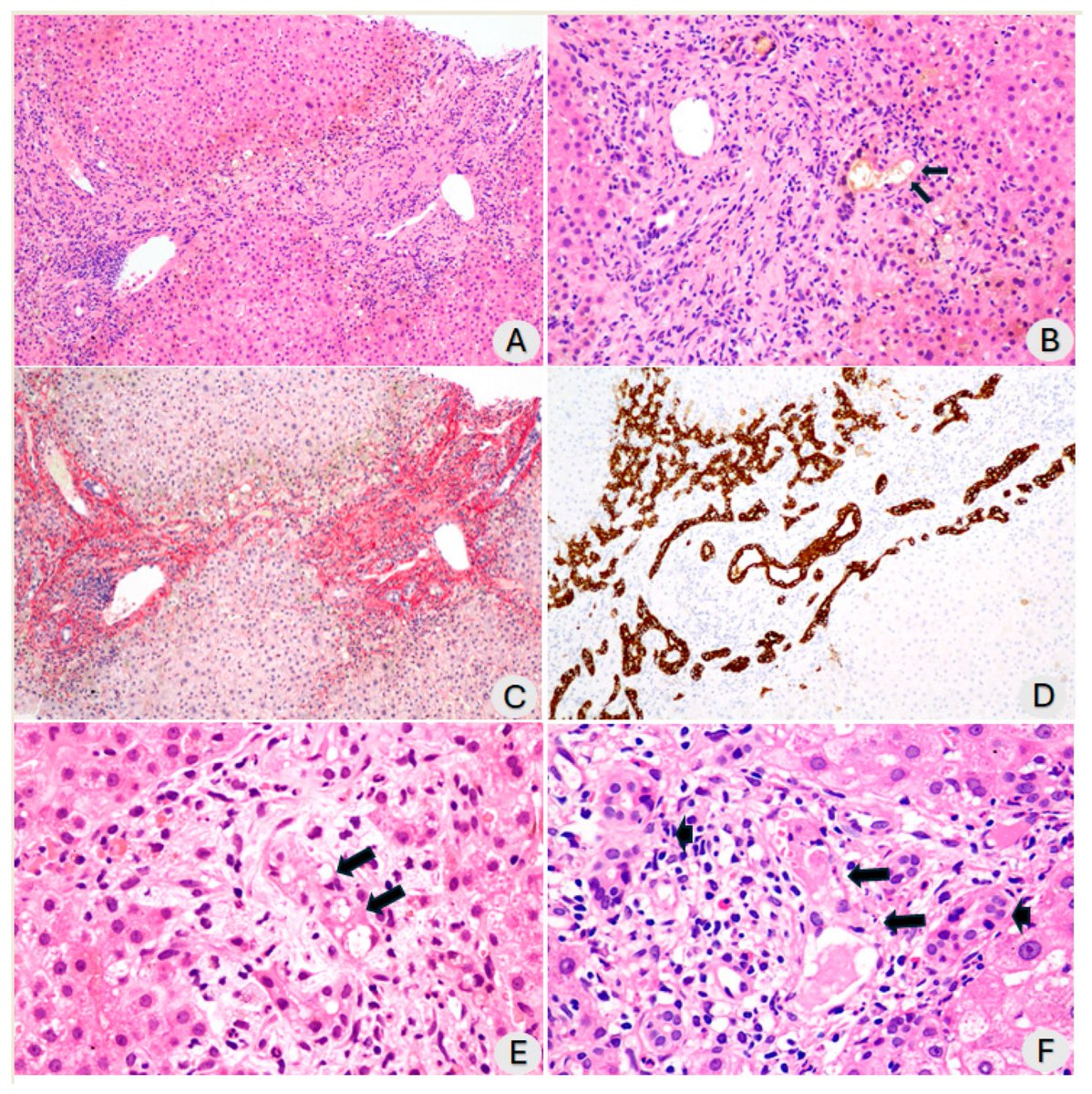
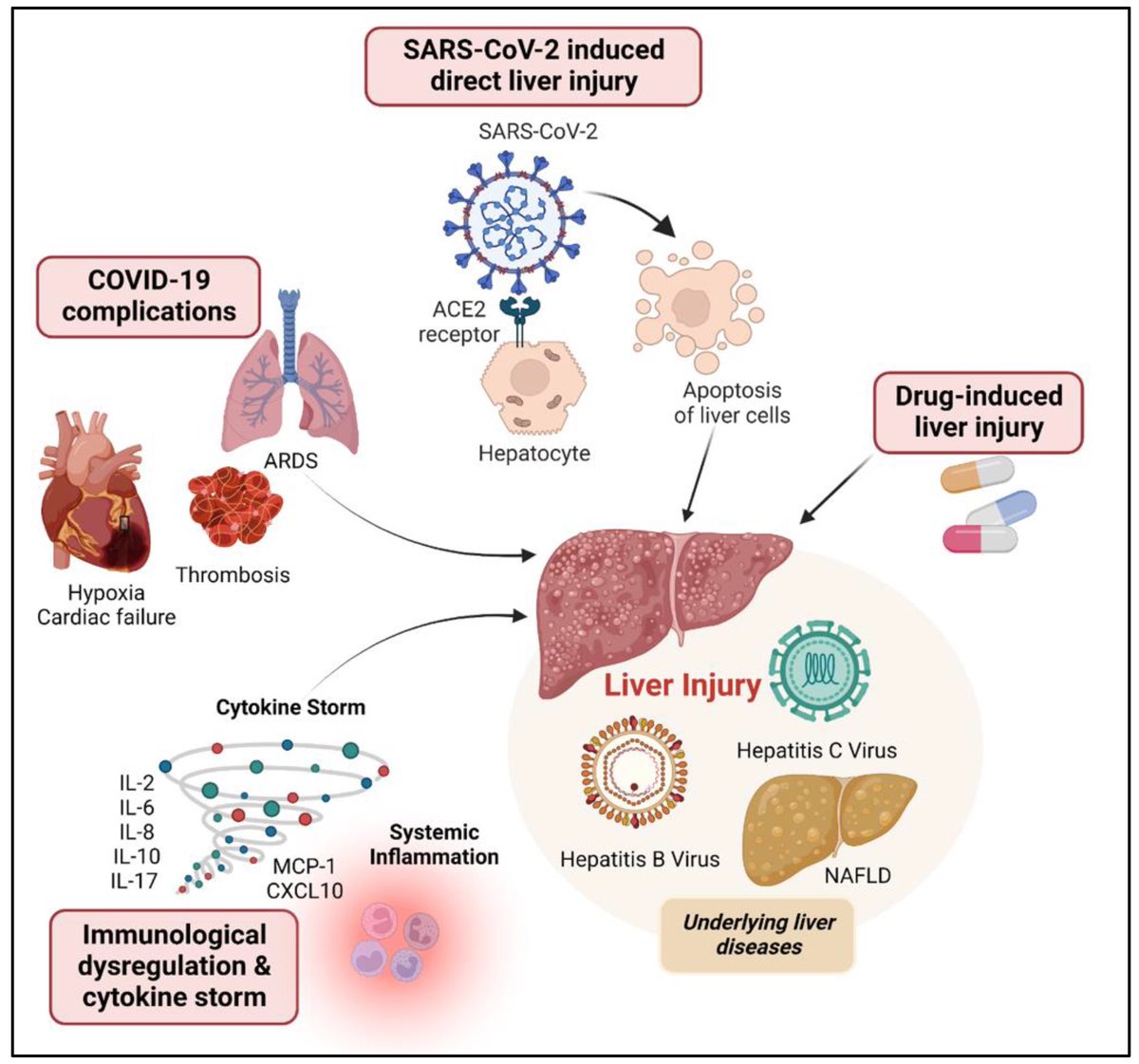
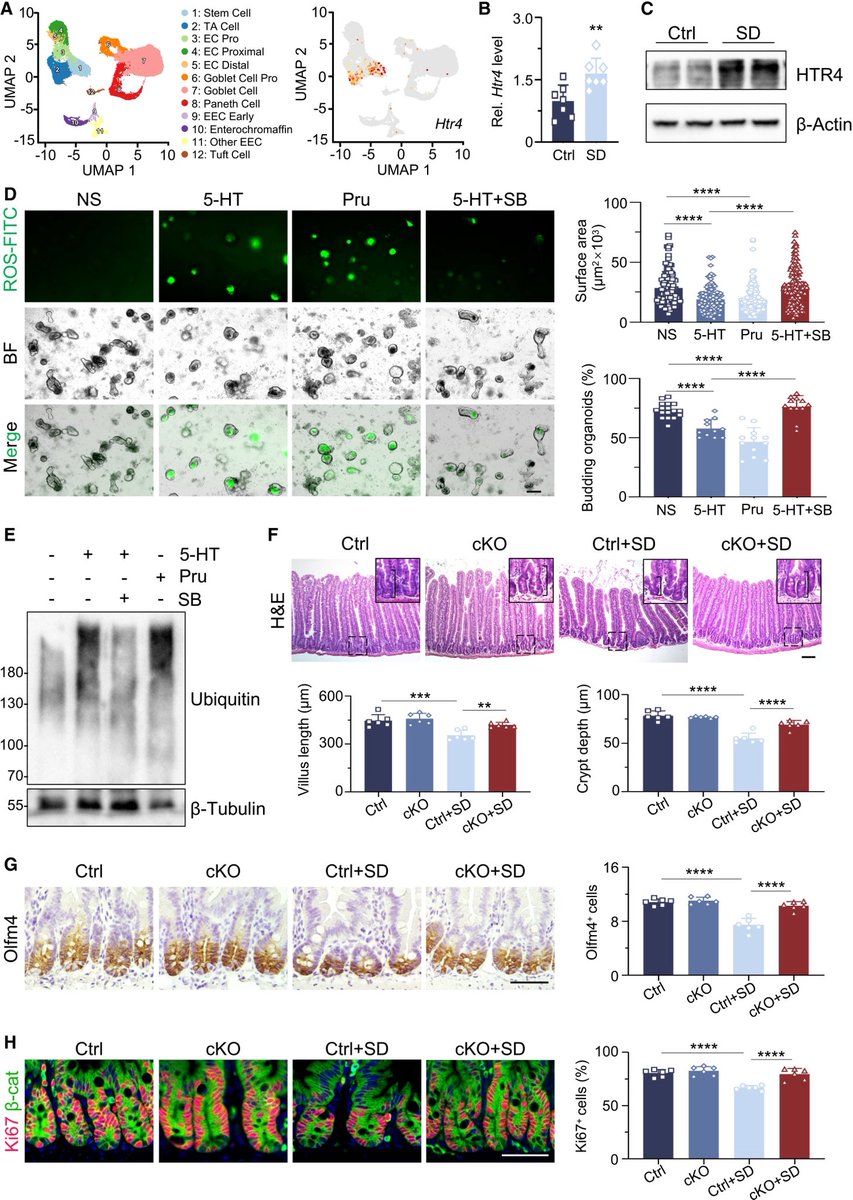
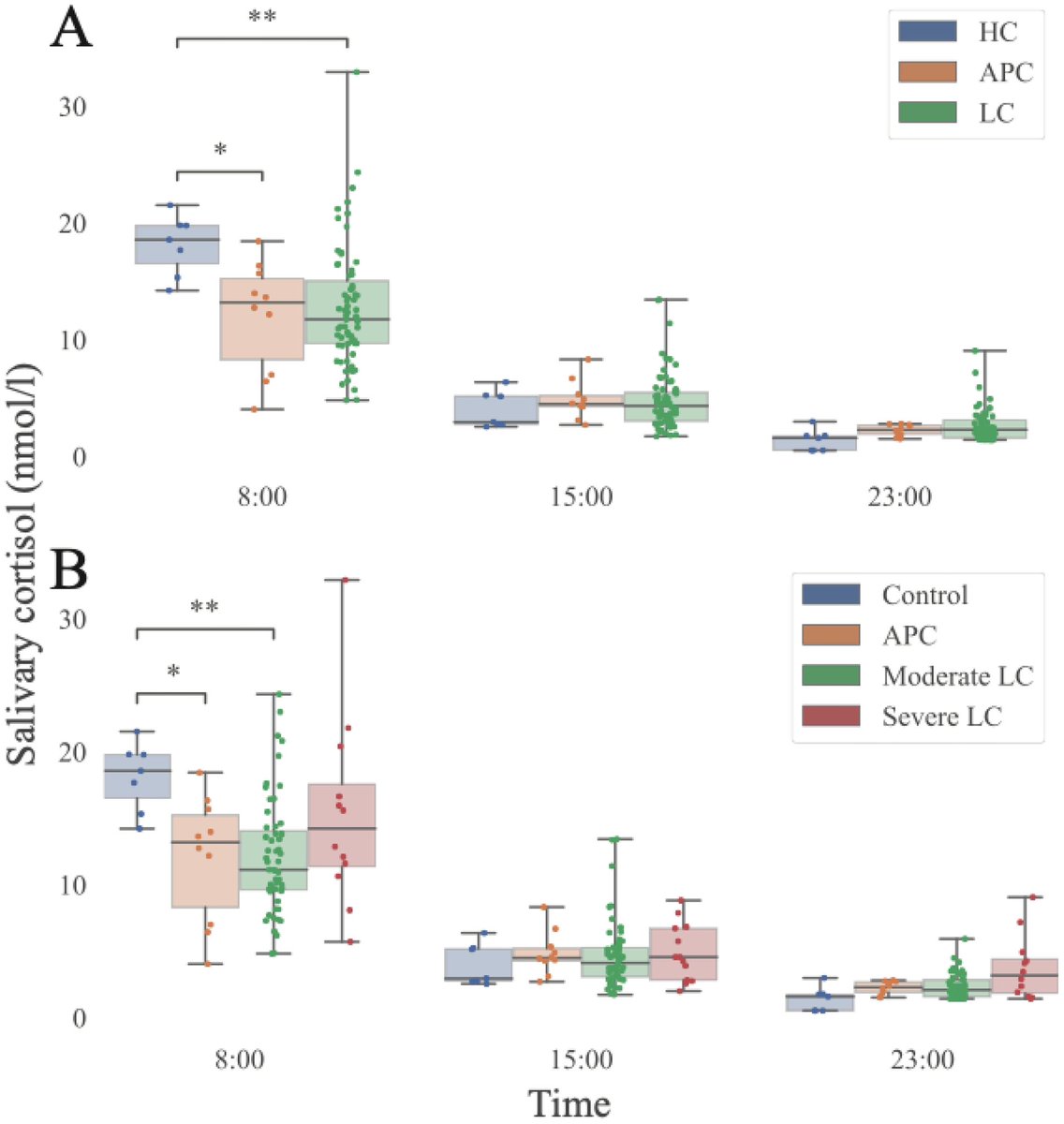
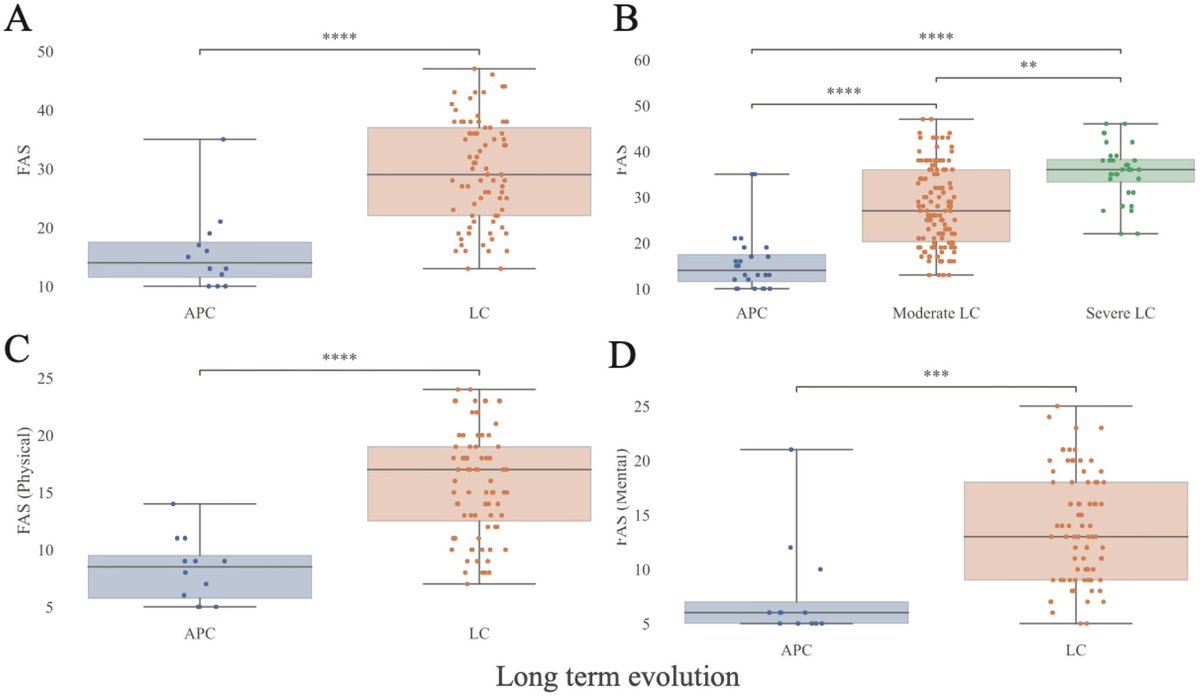
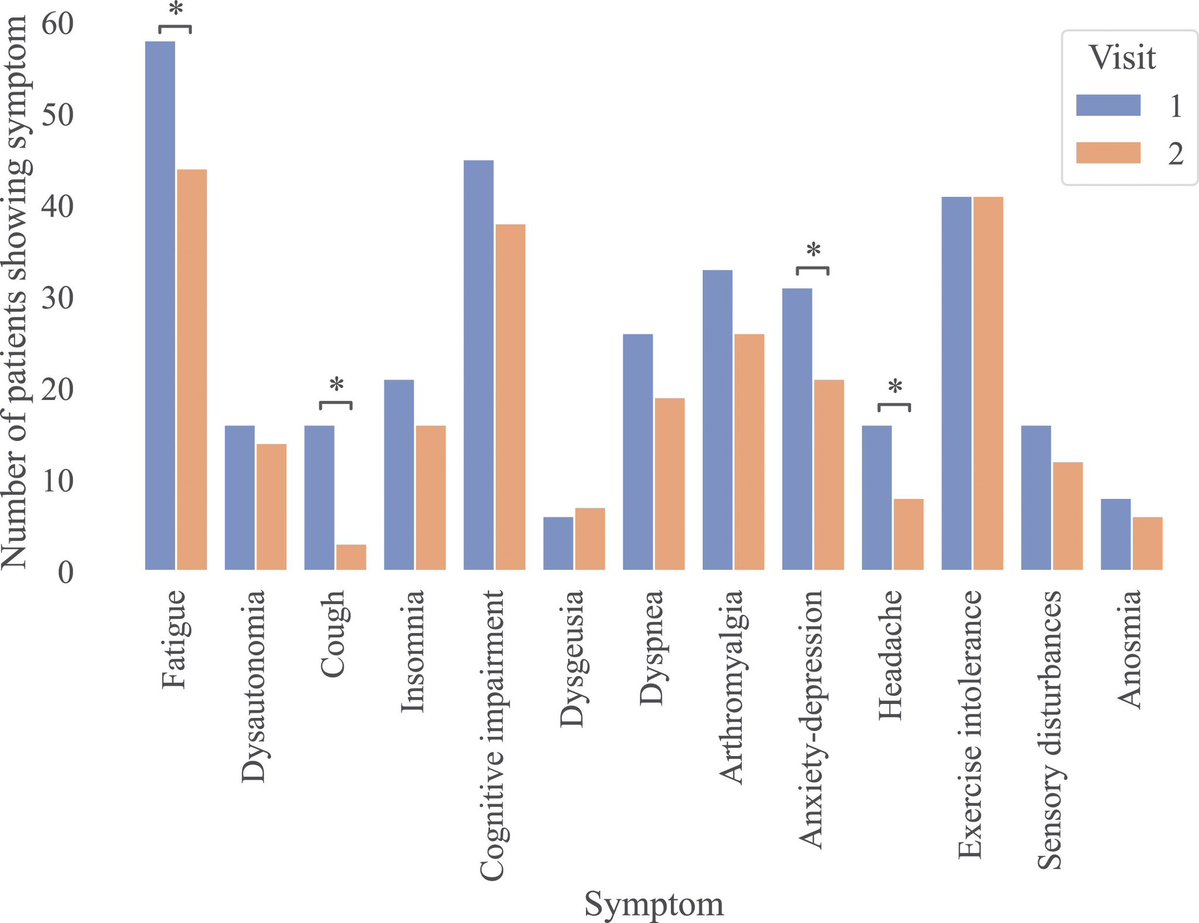
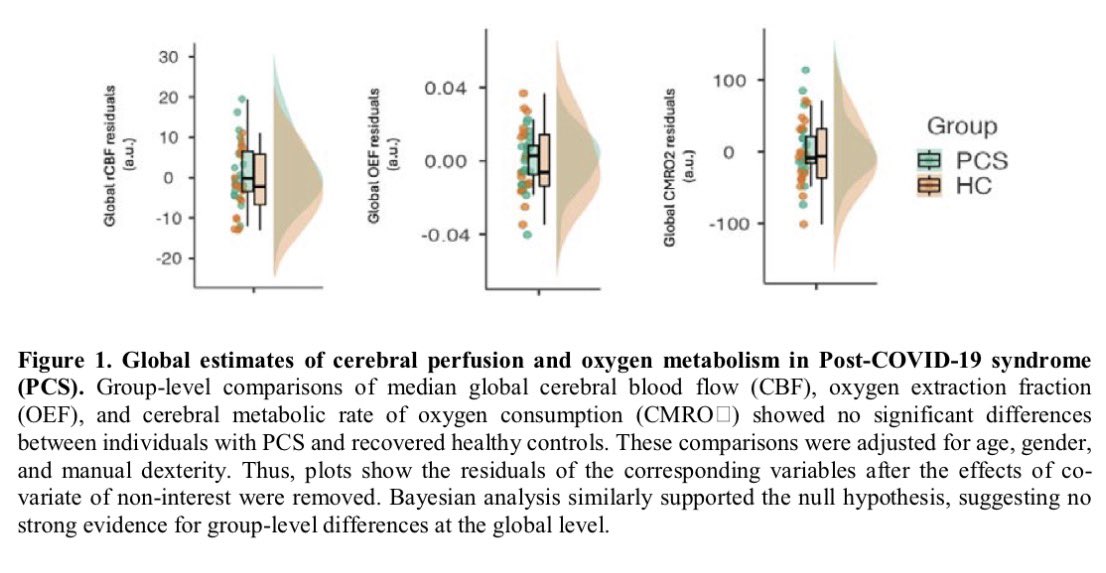
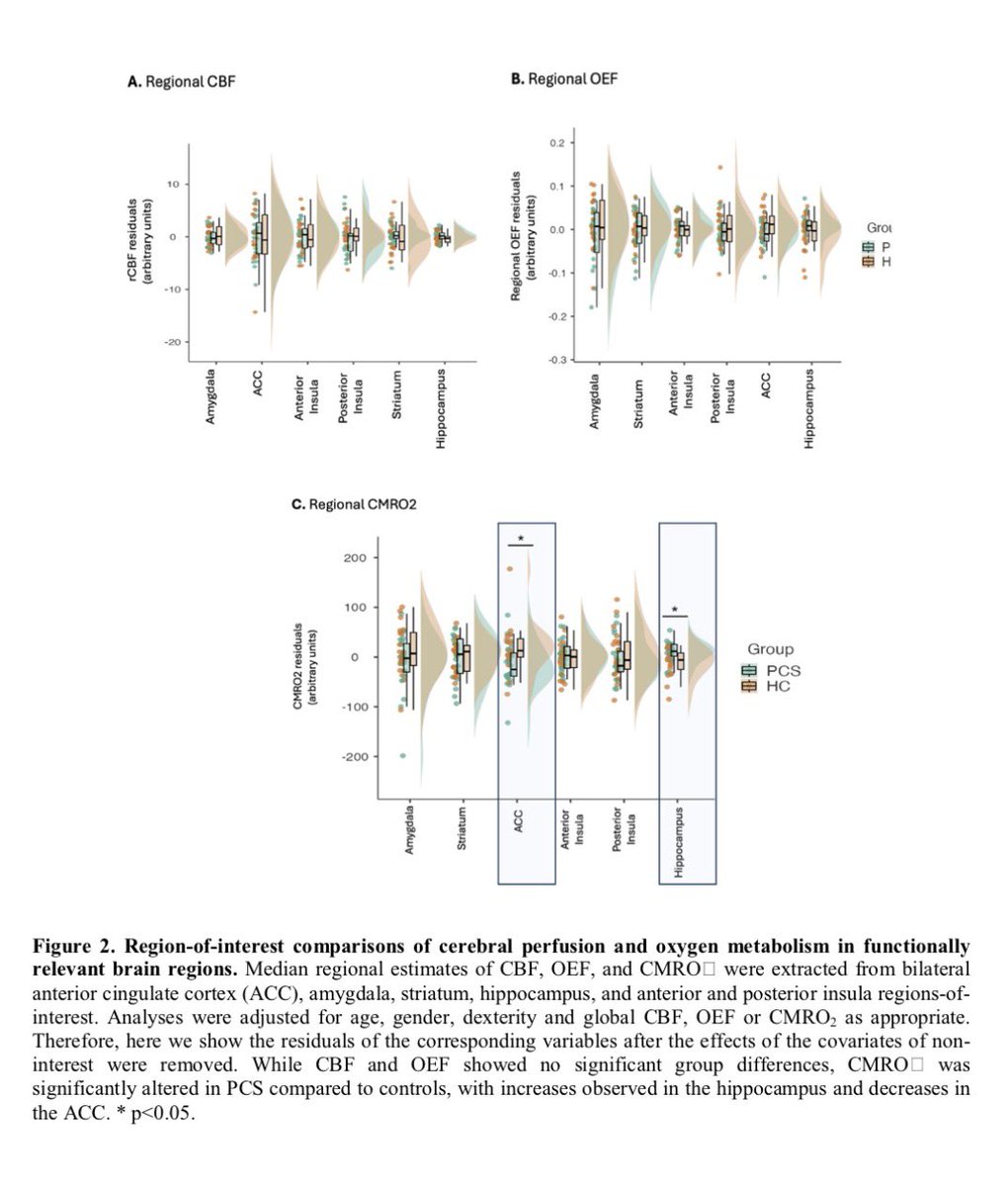
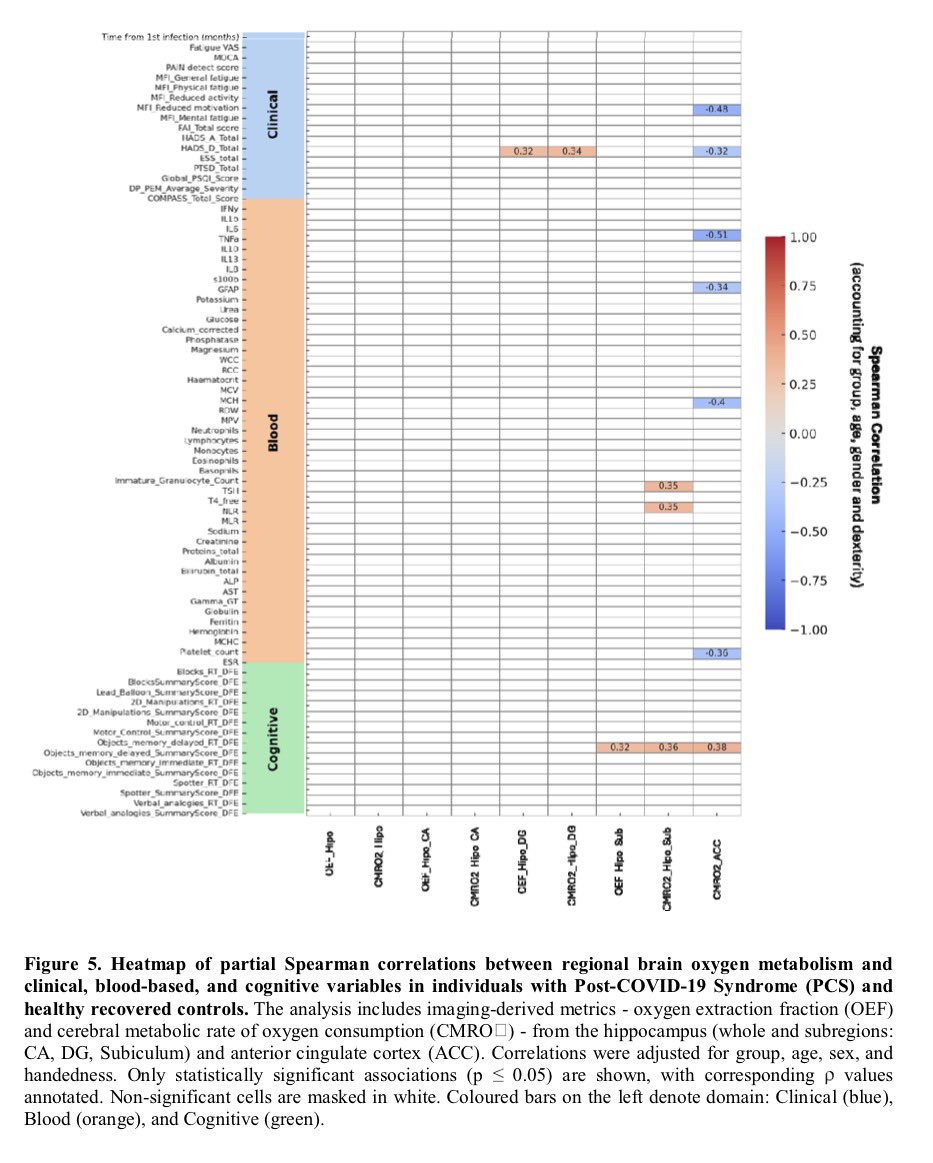
In a study that reshapes what we know about COVID19, scientists have discovered that coagulation protein fibrin causes unusual clotting & inflammation that have become hallmarks of the disease, while also suppressing the body's ability to clear virus.
nature.com/articles/s4158…

nature.com/articles/s4158…

Importantly, the team also identified a new antibody therapy to combat all of these deleterious effects. The study by overturns the prevailing theory that blood clotting is merely a consequence of inflammation in COVID-19. 
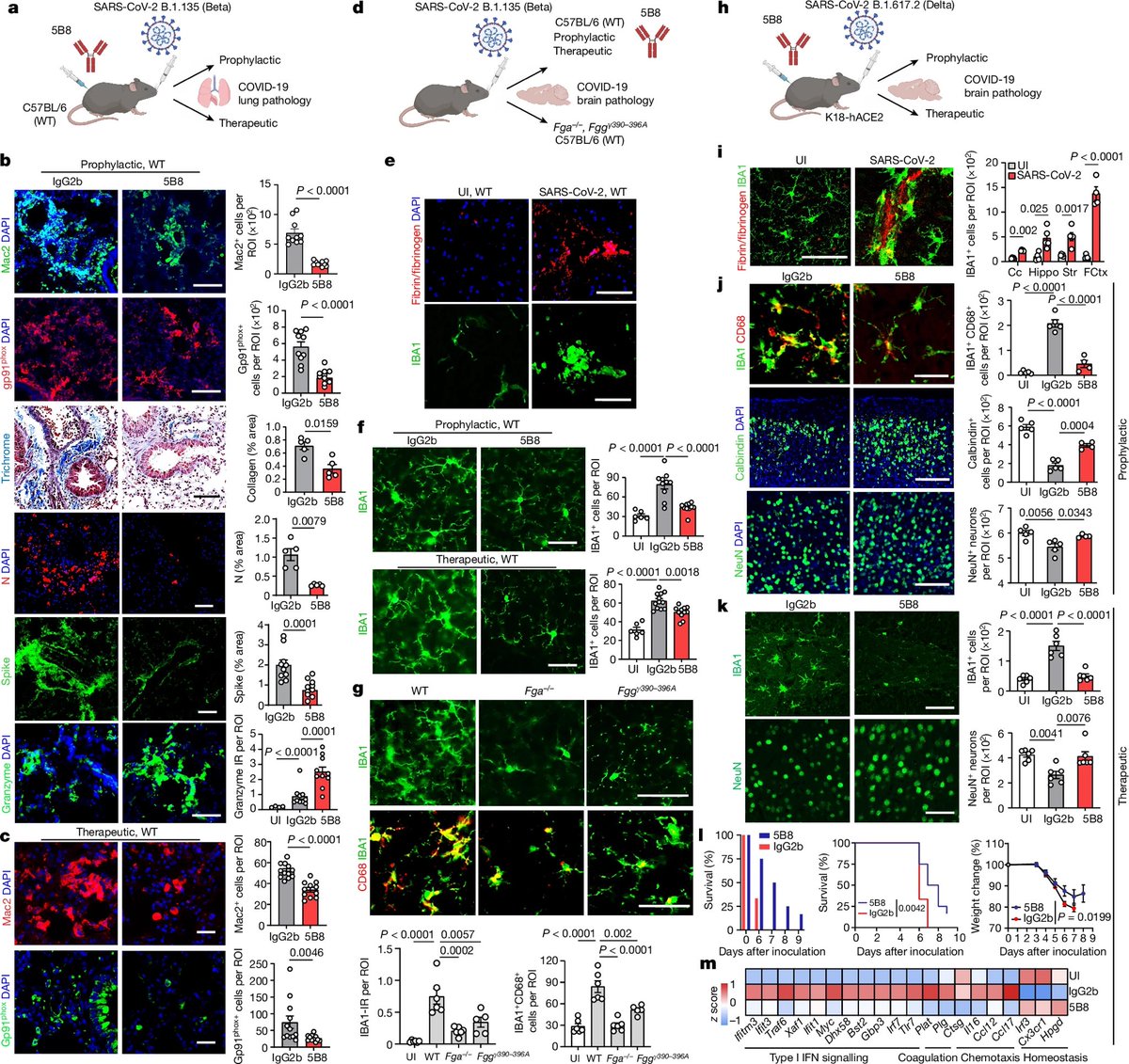
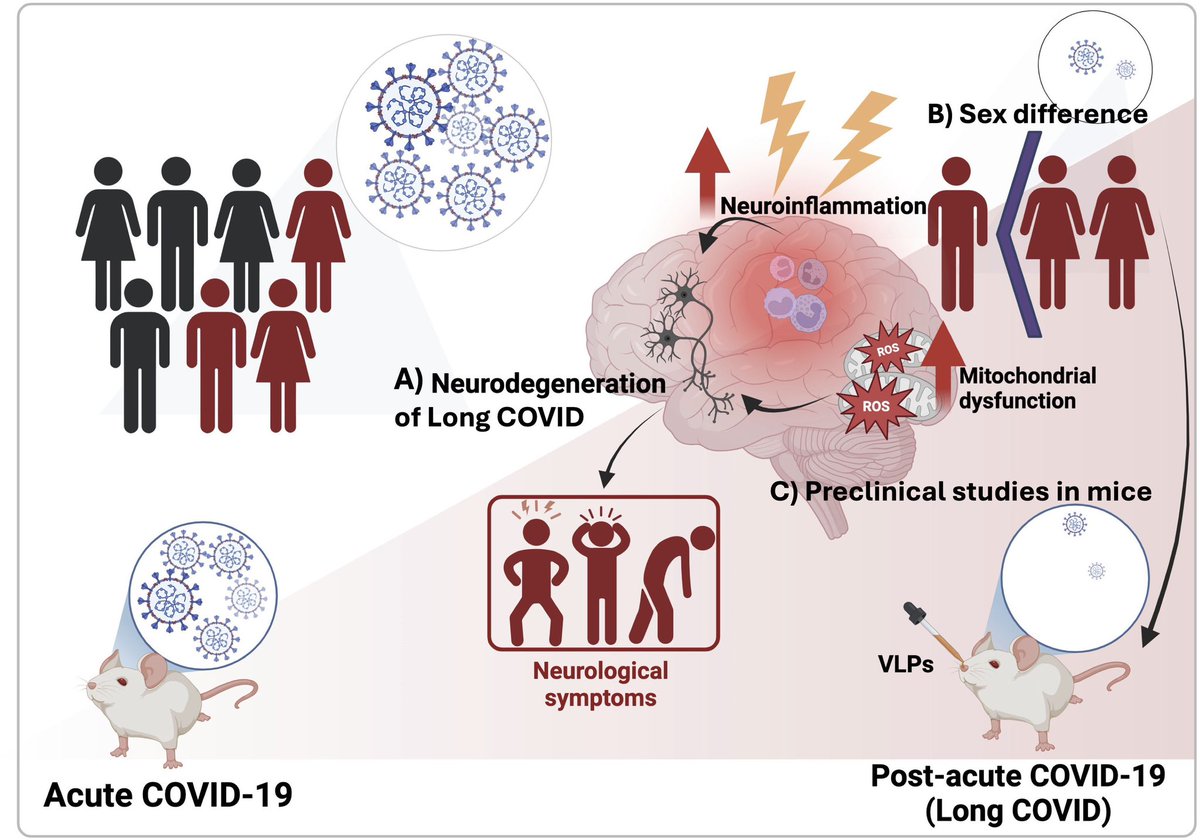
Through experiments in the lab and with mice, the researchers show that blood clotting is instead a primary effect, driving other problems—including toxic inflammation, impaired viral clearance, and neurological symptoms prevalent in those with COVID-19 and long COVID.
In this study, scientists found that fibrin becomes even more toxic in COVID-19 as it binds to both the virus and immune cells, creating unusual clots that lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and loss of neurons.
Knowing that fibrin is instigator of inflammation & neurological symptoms, we can build a new path forward for treating the disease at the root. In their experiments, neutralizing blood toxicity with fibrin antibody therapy can protect the brain and body after COVID infection.
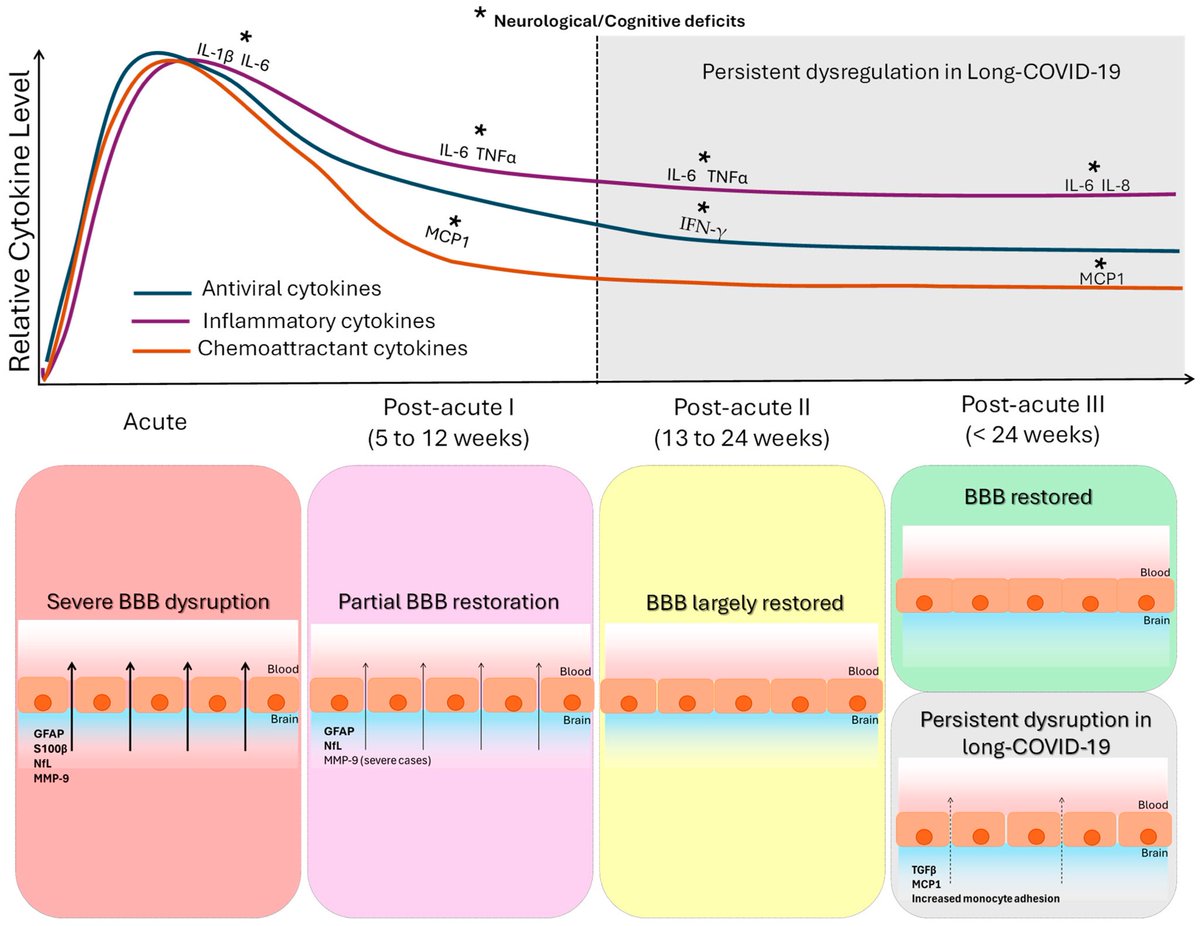
As fibrinogen plasma levels in acute COVID-19 are a predictive biomarker for cognitive impairment in longCOVID, it could be used to stratify patients as candidates for entry into phase 2 trials. 

Fibrin immunotherapy can be tested for its potential to reduce adverse health outcomes due to long COVID as part of a multipronged approach with prevention and vaccination measures.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
nature.com/articles/s4158…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh