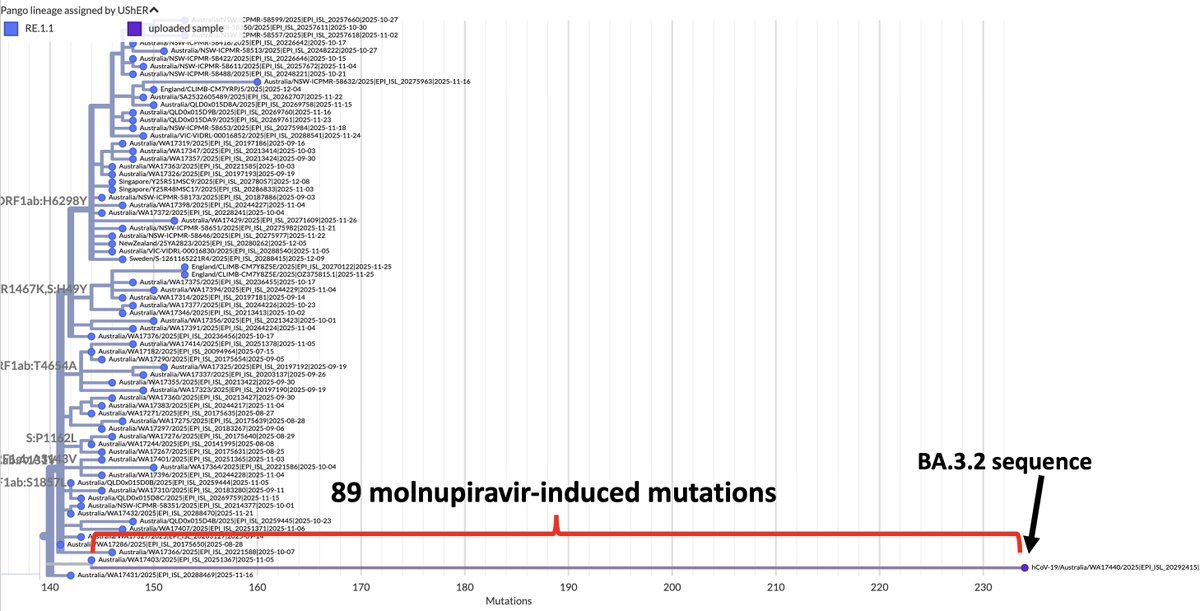
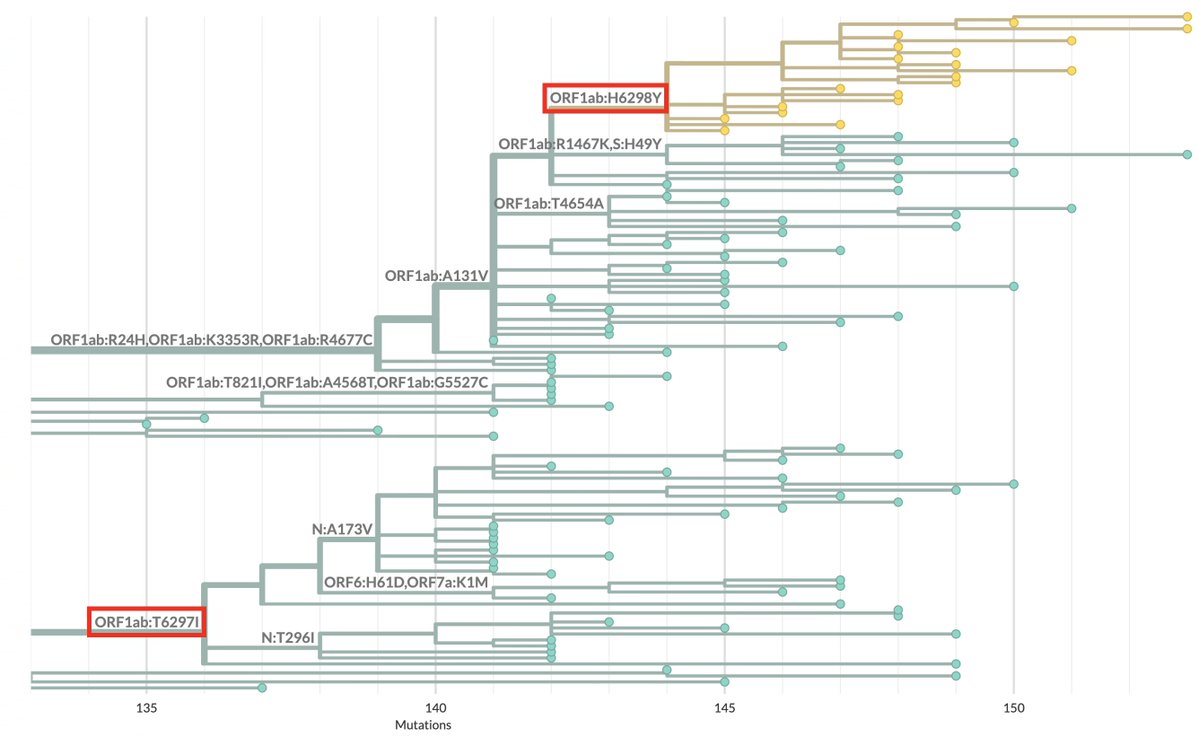
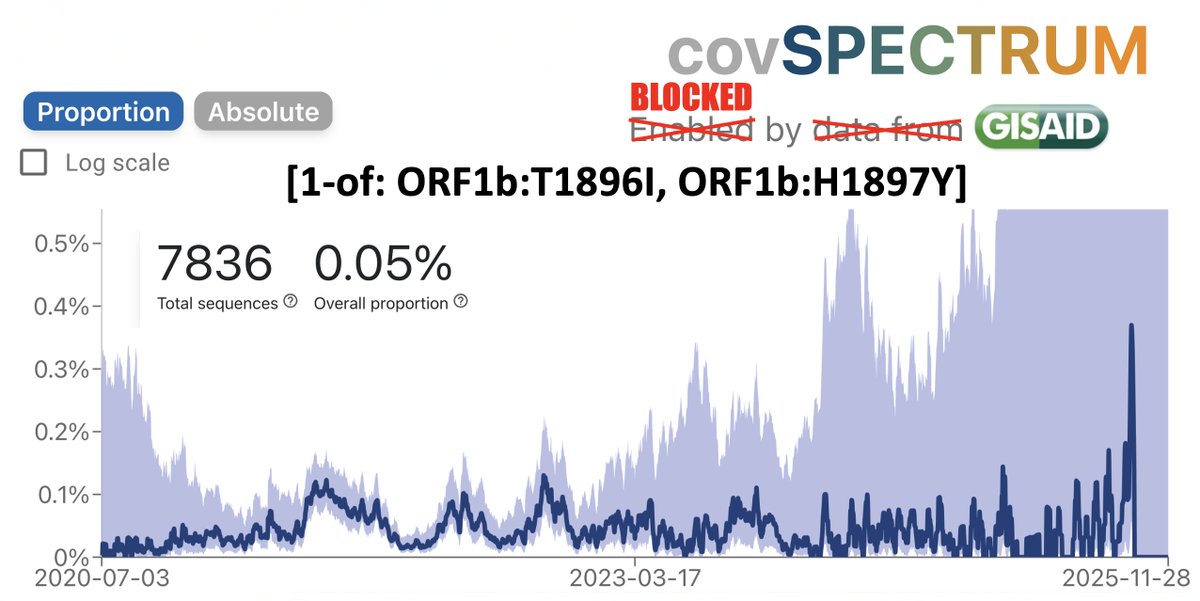
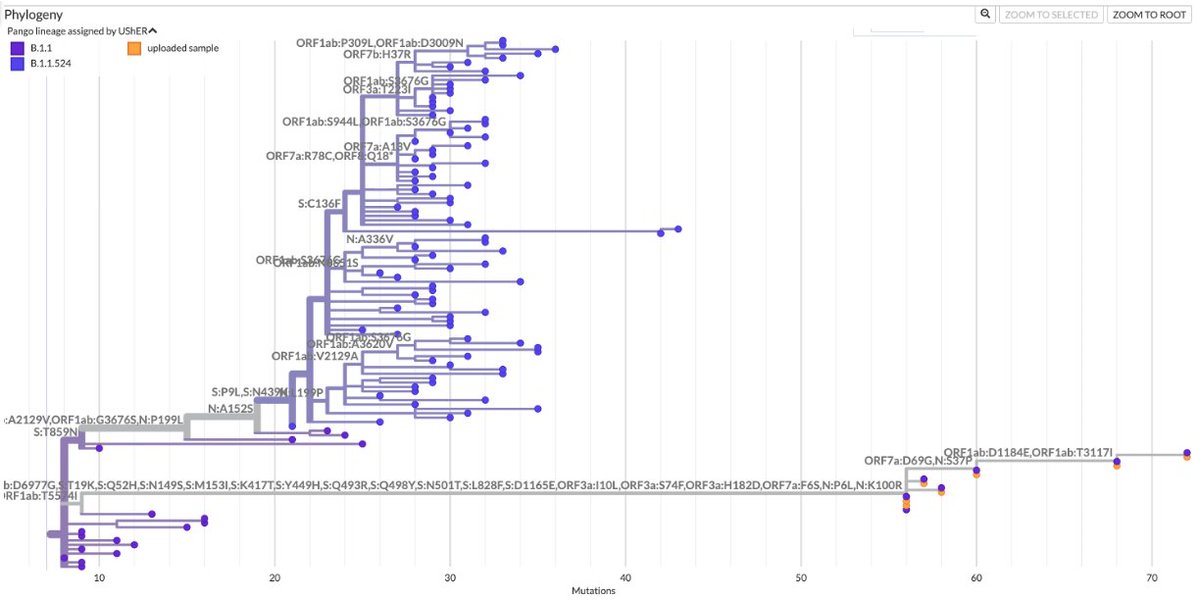
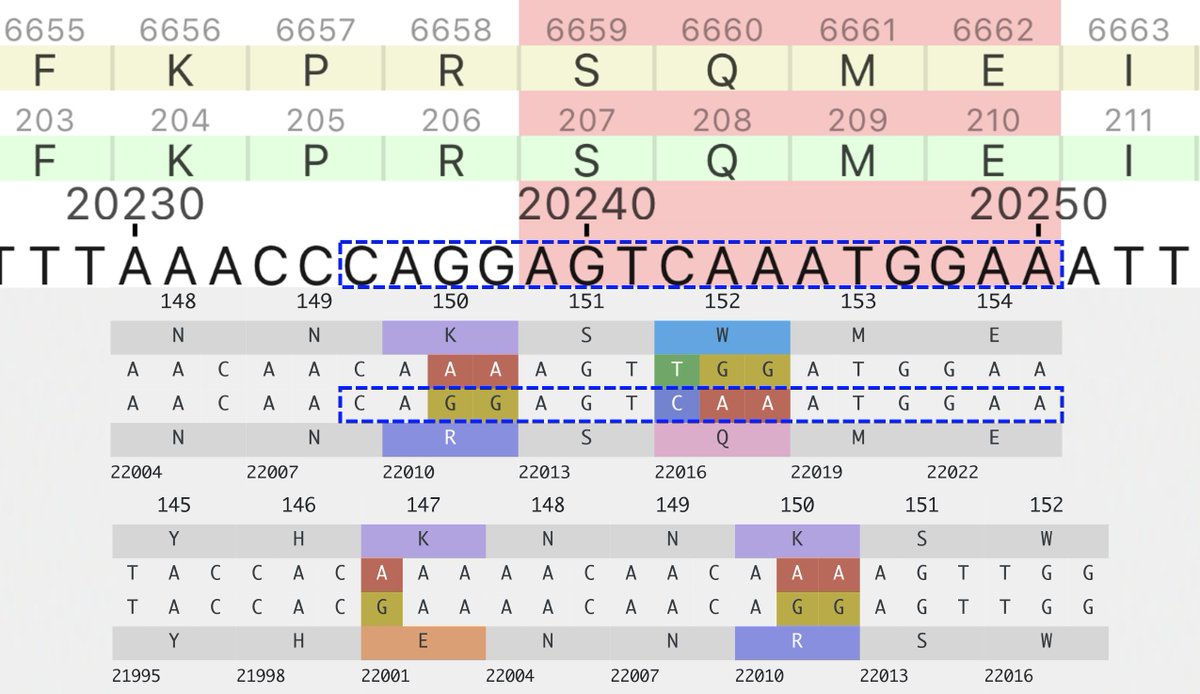
So the following four multi-A->G mutation patterns have shown up in sequences collected July 30 or later. These are all in the spike NTD. In each case, all the mutations were acquired in one step. The bottom one has appeared in numerous US states. What's going on here? 1/3 

To be clear, I have no idea. I can't recall ever seeing clusters of A->G mutations like this before. There's a human enzyme called ADAR that can causes A->G mutations. Is there something in the JN.1 secondary RNA structure in this region that attracts ADAR? 2/3
These are not the only multi-A->G mutation clusters in this area. A 2-nuc version of K150R has appeared many times, sometimes w/K147E, & two sequences seem to have acquired K150R via recombination with NSP15.
Just throwing this out there to see if anyone has ideas.
3/3
Just throwing this out there to see if anyone has ideas.
3/3
Nothing in particular stands out about their location in the WT secondary RNA structure. But it looks like an area of low-confidence structure prediction, & there have been a lot of mutations/deletions in this region of the genome. So the real structure may be entirely different. 
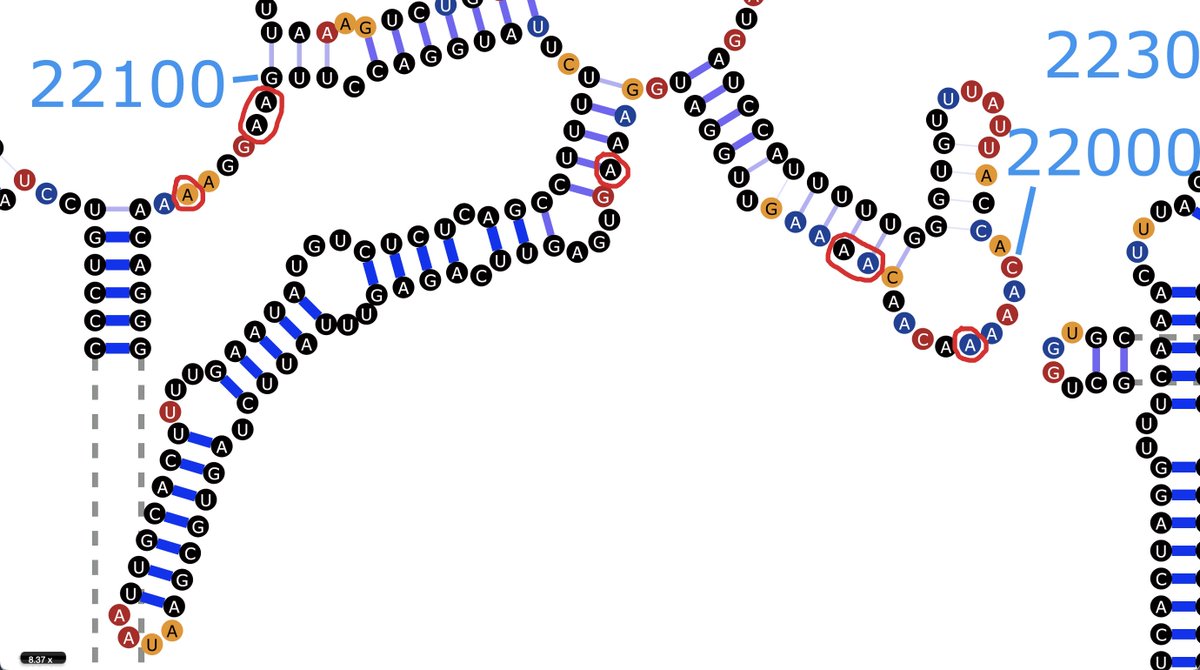
...to the extent that there is a "true" structure anyway. I know it tends to fluctuate and switch between different structures, probably influenced by a bunch of hard-to-account-for factors in the cellular environment.
@threadreaderapp unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh