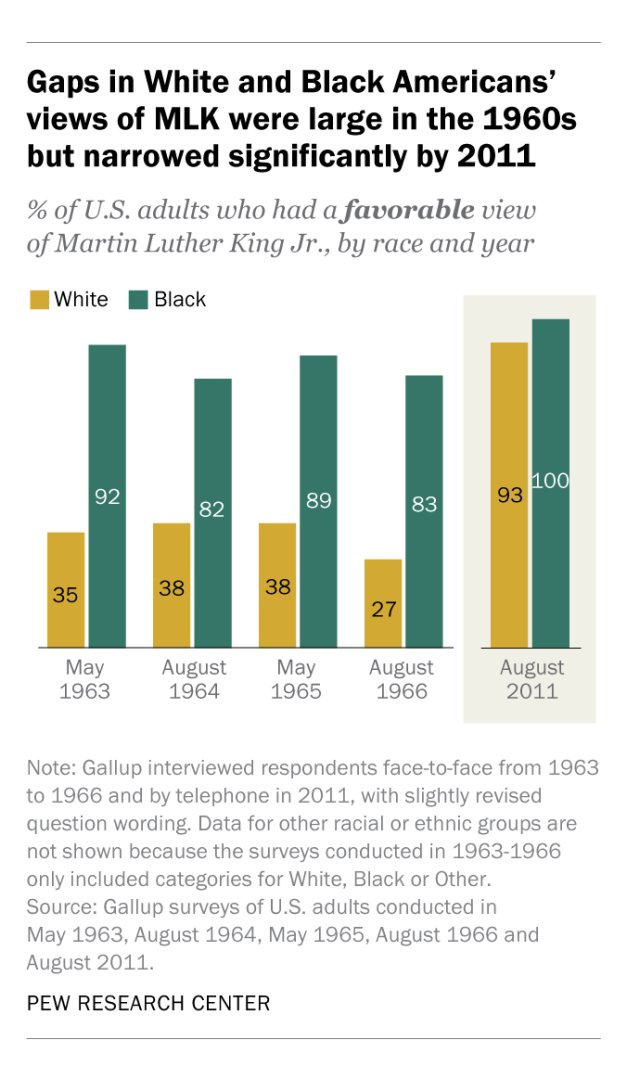
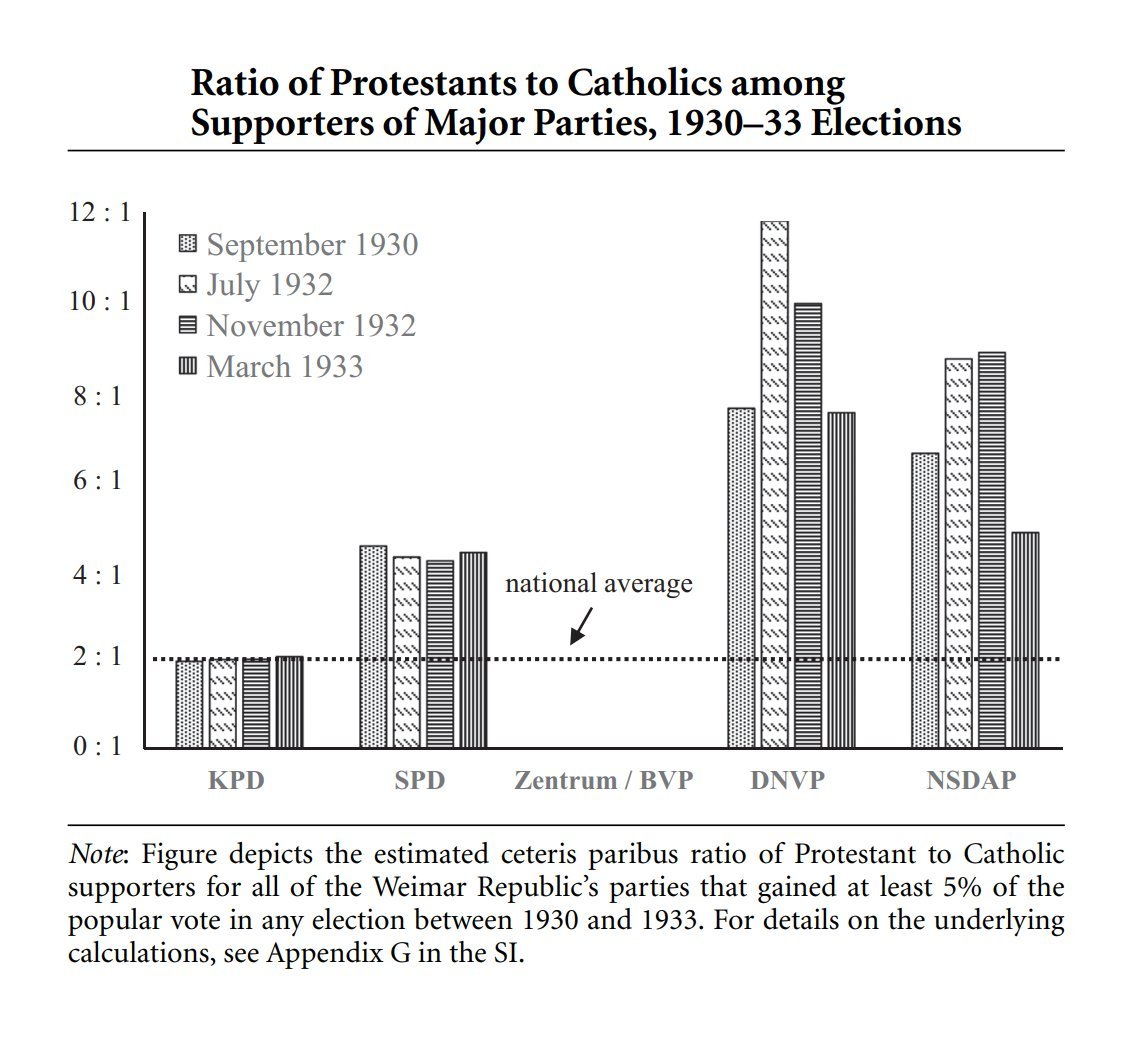
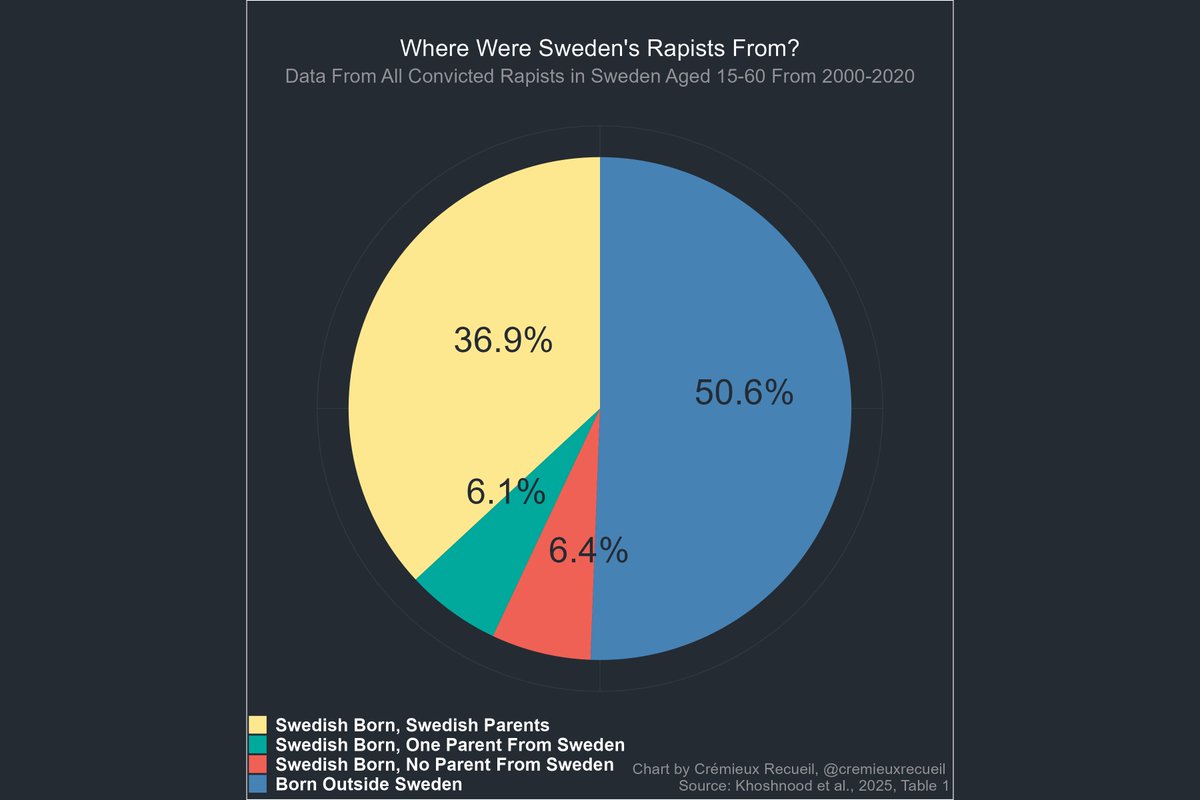
The FBI has finally released crime statistics for 2023!
Let's have a short thread.
First thing up is recent violent crime trends:
Let's have a short thread.
First thing up is recent violent crime trends:

Now let's focus in on homicides.
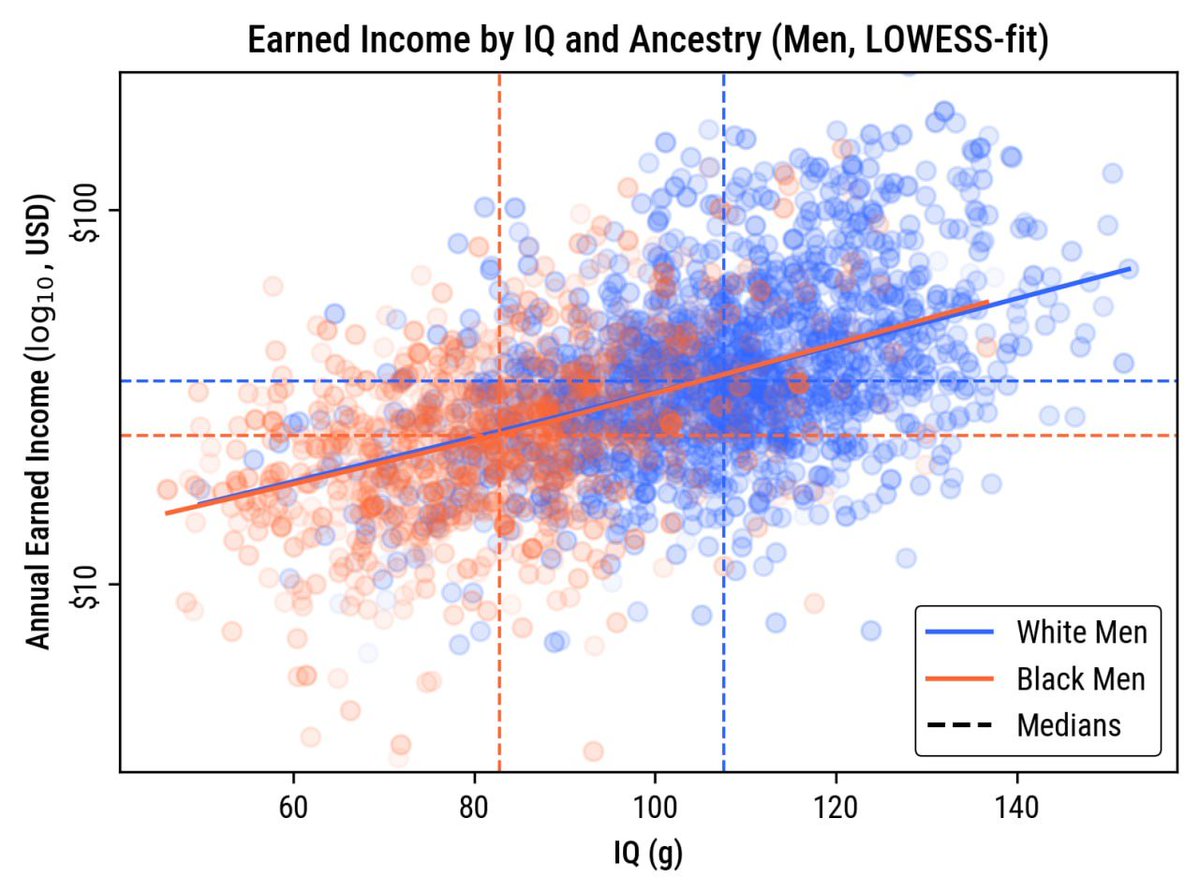
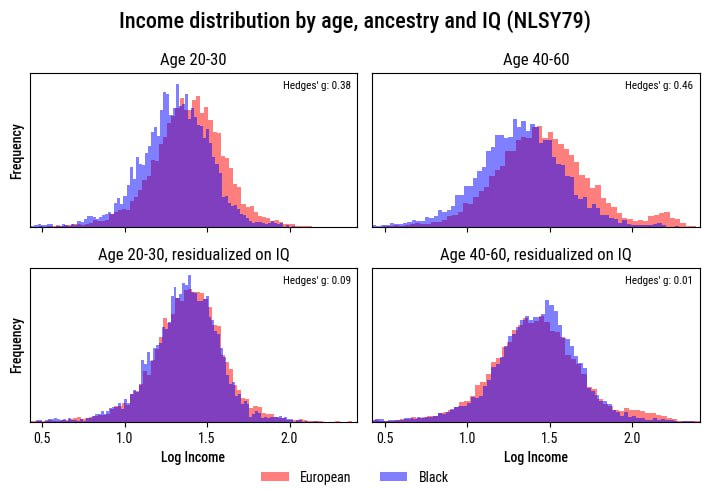
The homicide statistics split by race show the same distribution they have for years.
The homicide statistics split by race show the same distribution they have for years.

The age-crime curve last year looked pretty typical. How about this year?
Same as always. Victims and offenders still have highly similar, relatively young ages.
Same as always. Victims and offenders still have highly similar, relatively young ages.

Everything else, from locations to motives to weapons is pretty similar to previous years. What's different is that the OP might show incorrect numbers.
For the past two years, the FBI has silently updated their numbers after about two weeks.
You can use the web archive to see that the data from the OP is the data shown at release last year, and the data from 2023 is the 2022 data with the FBI's suggested reductions (i.e., -11.6% homicides, -2.8% aggravated assaults, -0.3% robberies, etc.).
But you can see on their site now that they've adjusted the numbers up, so the reduction they suggested has brought us down to a figure that's less impressive than my chart shows. The difference isn't huge so I showed the OP without updating to their new data.
For reference, 2022 as reported then had a homicide rate of 6.3/100k, and they silently updated that to 7.48/100k. The 2023 data they provided today actually has a murder rate of 6.61/100k, higher than last year's initially-reported number, but lower than the updated number. To make matters worse, if you use their Expanded Homicides Report, you get a rate of 5.94 for 2022 and 5.24 for 2023.
Methodology matters and we get to see inconsistency in this year's data, not even data that's been updated or anything. It's a mess, so take everything with a grain of salt and, in the interest of caution, only interpret trends. Trends are mostly common between all data sources even if the absolute magnitudes are off, constantly updated, etc.
For the past two years, the FBI has silently updated their numbers after about two weeks.
You can use the web archive to see that the data from the OP is the data shown at release last year, and the data from 2023 is the 2022 data with the FBI's suggested reductions (i.e., -11.6% homicides, -2.8% aggravated assaults, -0.3% robberies, etc.).
But you can see on their site now that they've adjusted the numbers up, so the reduction they suggested has brought us down to a figure that's less impressive than my chart shows. The difference isn't huge so I showed the OP without updating to their new data.
For reference, 2022 as reported then had a homicide rate of 6.3/100k, and they silently updated that to 7.48/100k. The 2023 data they provided today actually has a murder rate of 6.61/100k, higher than last year's initially-reported number, but lower than the updated number. To make matters worse, if you use their Expanded Homicides Report, you get a rate of 5.94 for 2022 and 5.24 for 2023.
Methodology matters and we get to see inconsistency in this year's data, not even data that's been updated or anything. It's a mess, so take everything with a grain of salt and, in the interest of caution, only interpret trends. Trends are mostly common between all data sources even if the absolute magnitudes are off, constantly updated, etc.
Sources:
cde.ucr.cjis.gov/LATEST/webapp/…
cde.ucr.cjis.gov/LATEST/webapp/…
cde.ucr.cjis.gov/LATEST/webapp/…
cde.ucr.cjis.gov/LATEST/webapp/…
cde.ucr.cjis.gov/LATEST/webapp/…
cde.ucr.cjis.gov/LATEST/webapp/…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh