An important study by F. Eun-Hyung Lee's team shows that long lived plasma cells (the source of long-term circulating antibodies) fail to establish after mRNA vaccination (even combined with SARS-CoV-2 infection). 🧵 (1/)
nature.com/articles/s4159…
nature.com/articles/s4159…
The longevity of antibody-mediated protection against infectious diseases rely on whether or not the vaccines can establish long lived plasma cells (LLPC) in the bone marrow. They are the source of circulating antibodies for years to decades. (2/)
nature.com/articles/s4159…

nature.com/articles/s4159…

The study by Nguyen et al examined the long lived and short lived plasma cells in the bone marrow in people who received COVID mRNA vaccines, tetanus and flu vaccines at various time points . They found no LLPC (PopD) specific to COVID but found PopD against tetanus and flu. (3/) 
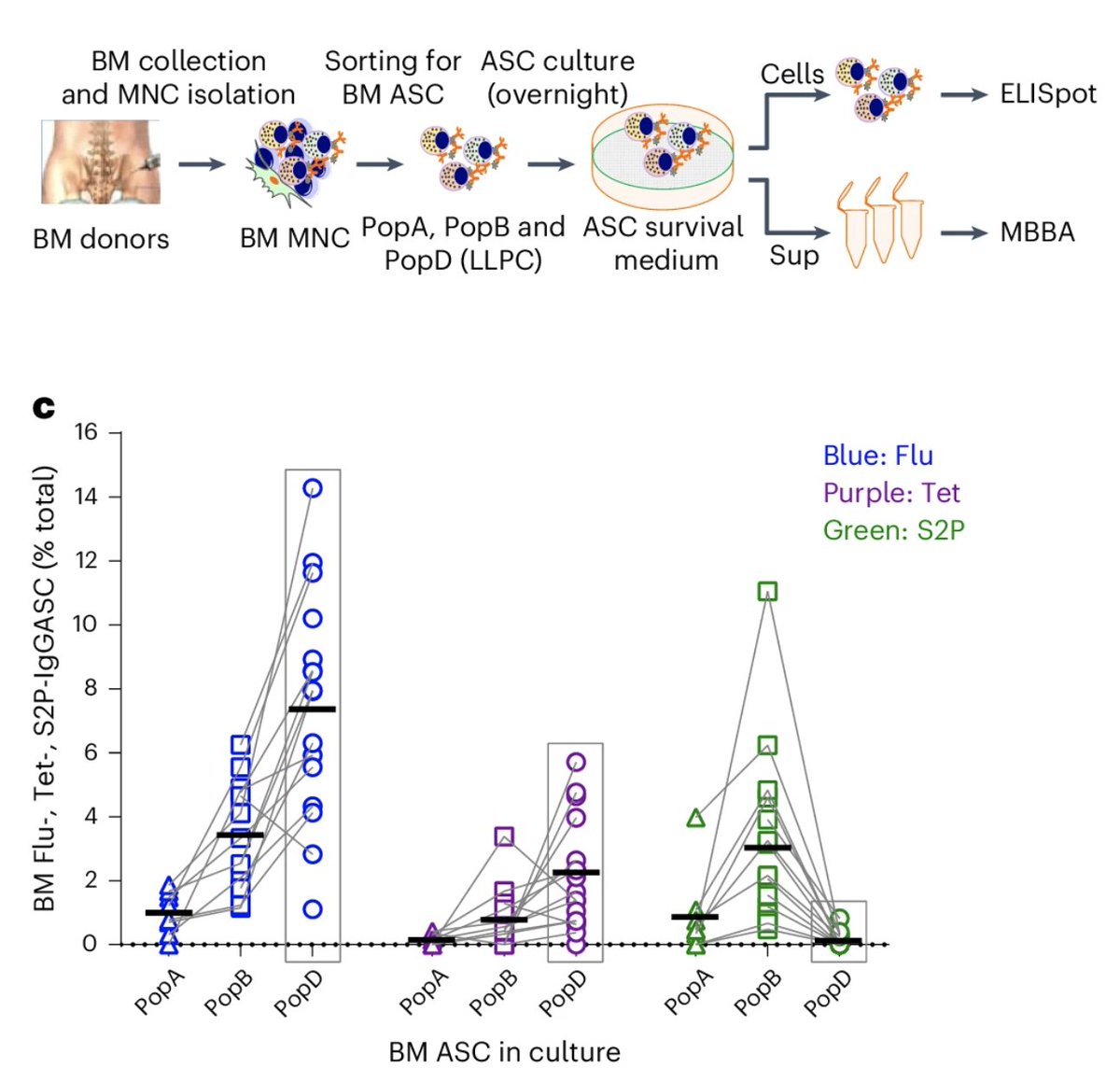
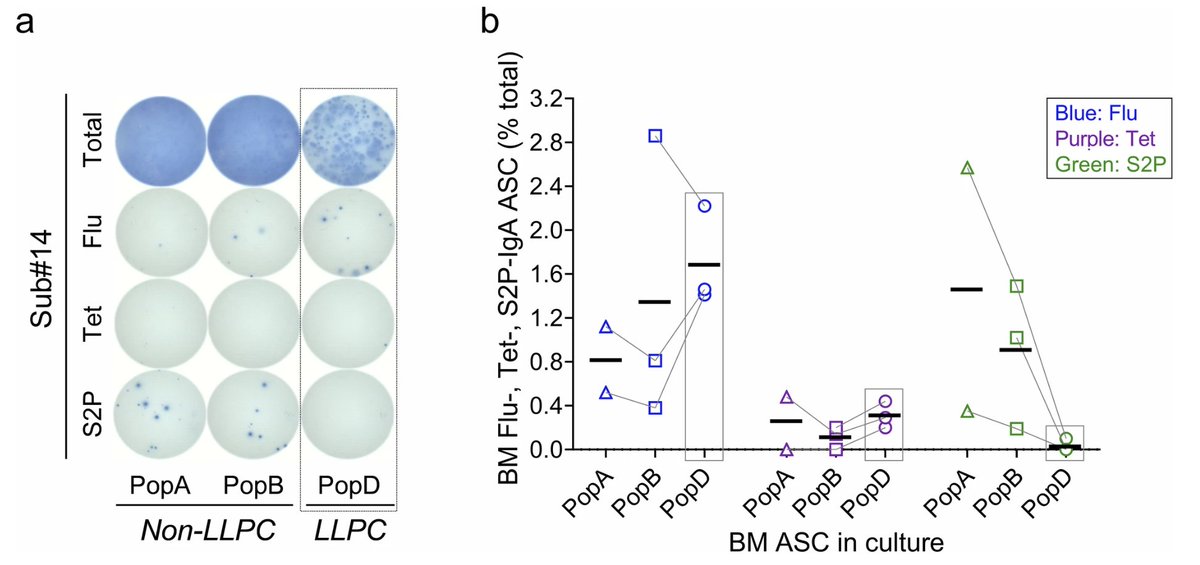
This lack of LLPC against the spike protein is also true for IgA-secreting plasma cells. IgA is an isotype of antibody that can be transported across the mucosal epithelial cells. Plasma cells secreting IgA may be present in the respiratory tract esp after infection (not tested here). (4/)
Can infection boost spike-specific LLPC in the bone marrow? The answer appears to be no. Vaccinated people who also had infection still made very little LLPC against spike. (5/) 
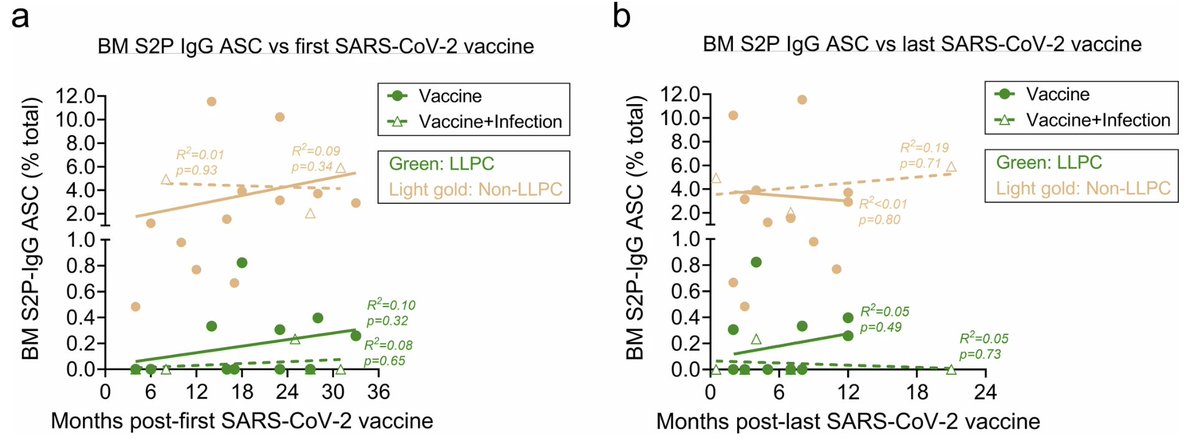
In summary, this study shows that for some reason, vaccination against Spike with mRNA vaccine (even combined with infection) fails to establish long lived plasma cells that provide IgG against the virus long term. (6/)
Why is this? Is it the vaccine or antigen? We can test whether other vax platforms (subunit, viral vectored), routes (mucosal, epidermal) or adjuvants can overcome the limitations of establishing LLPC against spike. We may also need to modify the spike antigen to elicit LLPCs. (7/)
Note that current vaccines are still important, as they boost short-term antibody responses, restimulate memory cells, generate variant-matched immune responses...etc. But we can do better. (8/)
For example, nasal boosters given every few months may be able to maintain protective IgA in the nose and throat. Self-administration can make this easier. We need out of the box thinking to combat respiratory viruses like COVID and to prevent infection, transmission & #longCOVID (end)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh