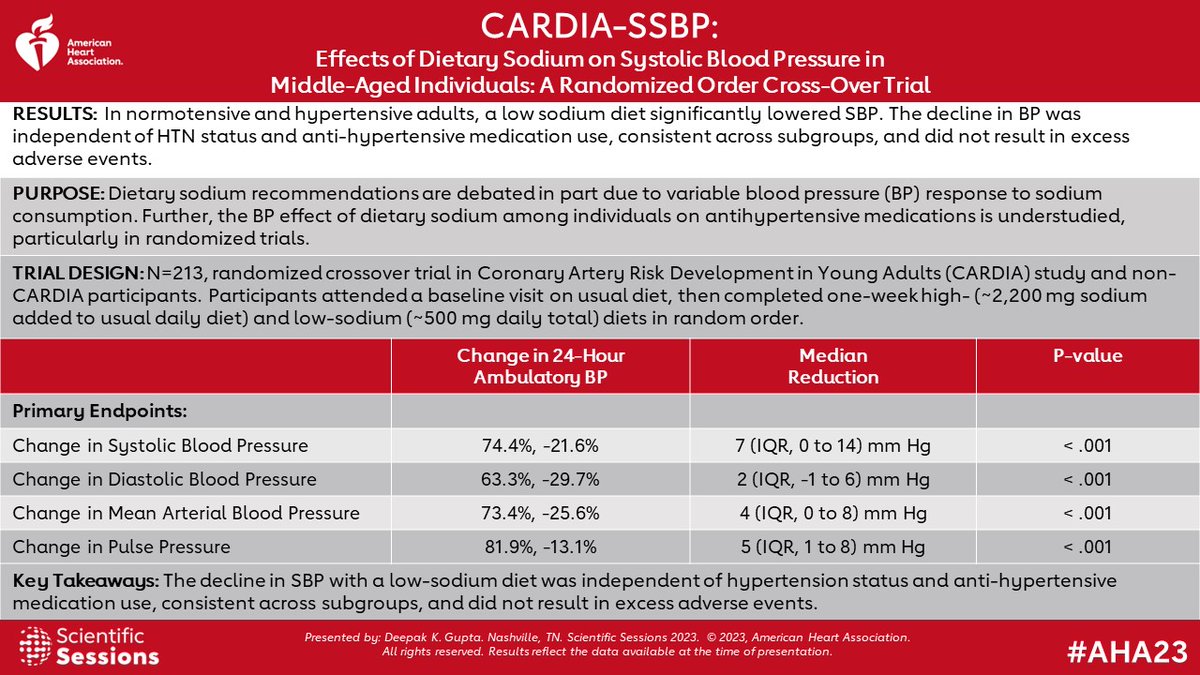
SCAI Expert Consensus Statement on the Management of Patients With STEMI Referred for Primary PCI: @MyJSCAI
🥸 Nice documents on STEMI and primary PCI: congratulations to authors and @SCAI
😱 Here are few recommendations from the document
👇👇👇
🥸 Nice documents on STEMI and primary PCI: congratulations to authors and @SCAI
😱 Here are few recommendations from the document
👇👇👇

🥸1️⃣ Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory (CCL) Equipment: Ensure availability of plaque modification devices, guide extension devices, and intracoronary imaging tools for effective STEMI management in the catheterization lab.
🥸2️⃣ Use microcatheters to enhance precision by facilitating medication delivery and wire exchange in tortuous coronary arteries during STEMI interventions.
🥸3️⃣ In cases with a large thrombus burden, aspiration catheters—manual or mechanical—should be available to help reduce thrombus and improve reperfusion.
🥸4️⃣ Prioritize team readiness with protocols for rapid CCL activation and streamlined prehospital ECG transmission to cut down on time-to-treatment.
🥸5️⃣ ED Bypass: For stable STEMI patients, bypassing the emergency department can expedite transfer to the CCL and minimize delays in reperfusion.
🥸6️⃣ Opt for transradial access over femoral when possible, as it carries a lower risk of bleeding and vascular complications in STEMI interventions.
#radialfirst
#radialfirst
🥸7️⃣ For femoral access cases, use ultrasound and fluoroscopy to ensure accurate access and reduce potential complications at the femoral artery.
🥸8️⃣ Always perform a complete coronary angiogram to assess the full scope of coronary disease, aiding in revascularization strategy for both infarct and non-infarct arteries.
🥸9️⃣ Thrombus Management: Use bail-out aspiration thrombectomy in selected cases with a high thrombus burden to mitigate the risk of no-reflow and distal embolization.
🥸🔟 For the no-reflow phenomenon, intracoronary vasodilators such as adenosine, nitroprusside, and calcium channel blockers are essential to restore microvascular flow.
🥸1️⃣1️⃣ Employ intracoronary imaging (IVUS or OCT) to guide PCI, optimize stent placement, assess stent expansion, and detect complications like malapposition.
🥸1️⃣2️⃣ Newer therapies, like supersaturated oxygen (SSO2) therapy and left ventricular unloading, show potential in reducing myocardial damage by minimizing infarct size during PCI.
🥸1️⃣3️⃣ In cardiogenic shock, implement MCS promptly and perform careful hemodynamic monitoring during and after PCI to improve patient outcomes.
🥸1️⃣4️⃣ Post-fibrinolytic therapy in STEMI, prioritize radial access for rescue PCI to lower bleeding risk and enhance safety.
🥸1️⃣5️⃣ In stent thrombosis cases, utilize intracoronary imaging to assess underlying causes like underexpansion or stent fracture, tailoring interventions based on findings.
🥸1️⃣6️⃣ For STEMI patients with multivessel disease, consider complete revascularization for better outcomes, particularly in stable patients without cardiogenic shock.
🥸1️⃣7️⃣ When treating calcified lesions, use plaque modification tools like atherectomy or intravascular lithotripsy to facilitate stent delivery and expansion.
🥸1️⃣8️⃣ In cases of coronary artery aneurysms, focus on restoring flow using mechanical thrombus management strategies; consider surgical options for large aneurysms.
🥸1️⃣9️⃣ Manage nonatherosclerotic causes of STEMI like SCAD, coronary embolism, and epicardial spasm with tailored approaches; for SCAD, conservative management is preferred for stable patients.
🥸2️⃣0️⃣ For coronary embolism with large thrombus burden, consider PCI with thrombectomy to restore flow, while smaller, distal emboli may be managed conservatively.
🥸2️⃣1️⃣ MINOCA (Myocardial Infarction with Non-Obstructive Coronary Arteries): In suspected cases, additional imaging such as IVUS or OCT, and cardiac MRI can clarify the underlying cause and guide management.
🥸2️⃣2️⃣ Track quality metrics like door-to-device times and activation delays across the STEMI system to identify areas for improvement and ensure consistent care.
🥸2️⃣3️⃣ False STEMI activations should be minimized through education on ECG interpretation and protocols, as they can lead to unnecessary procedures and resource strain.
🥸2️⃣4️⃣ Intracoronary nitroglycerin is advised during angiography to help identify and treat vasospasm and accurately assess vessel diameter during PCI.
🥸2️⃣5️⃣ In SCAD with TIMI 3 flow, conservative management is advised, reserving PCI for cases with large areas of myocardium at risk or hemodynamic instability.
🥸2️⃣6️⃣ For suspected coronary embolism, evaluate for potential sources such as atrial fibrillation or cardiac thrombus; use thrombectomy devices when necessary for large proximal thrombi.
🥸2️⃣7️⃣ When performing PCI on bifurcation lesions during STEMI, a provisional one-stent strategy is preferred to minimize procedural complexity and potential complications.
🥸2️⃣8️⃣ Ensure CCL team readiness includes protocols for fast prehospital notification, streamlined communication, and an efficient reperfusion timeline to optimize outcomes.
🥸2️⃣9️⃣ Use plaque modification in cases of significant calcification to enhance stent expansion and minimize the risk of post-PCI complications.
🥸3️⃣0️⃣ Continually assess and improve STEMI care protocols by tracking procedural times, outcomes, and complications, aiming for a comprehensive quality improvement approach across the system.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh