LARGEST MULTI-ANCESTRY GENOME-WIDE ASSOCIATION STUDY (GWAS) of Long COVID
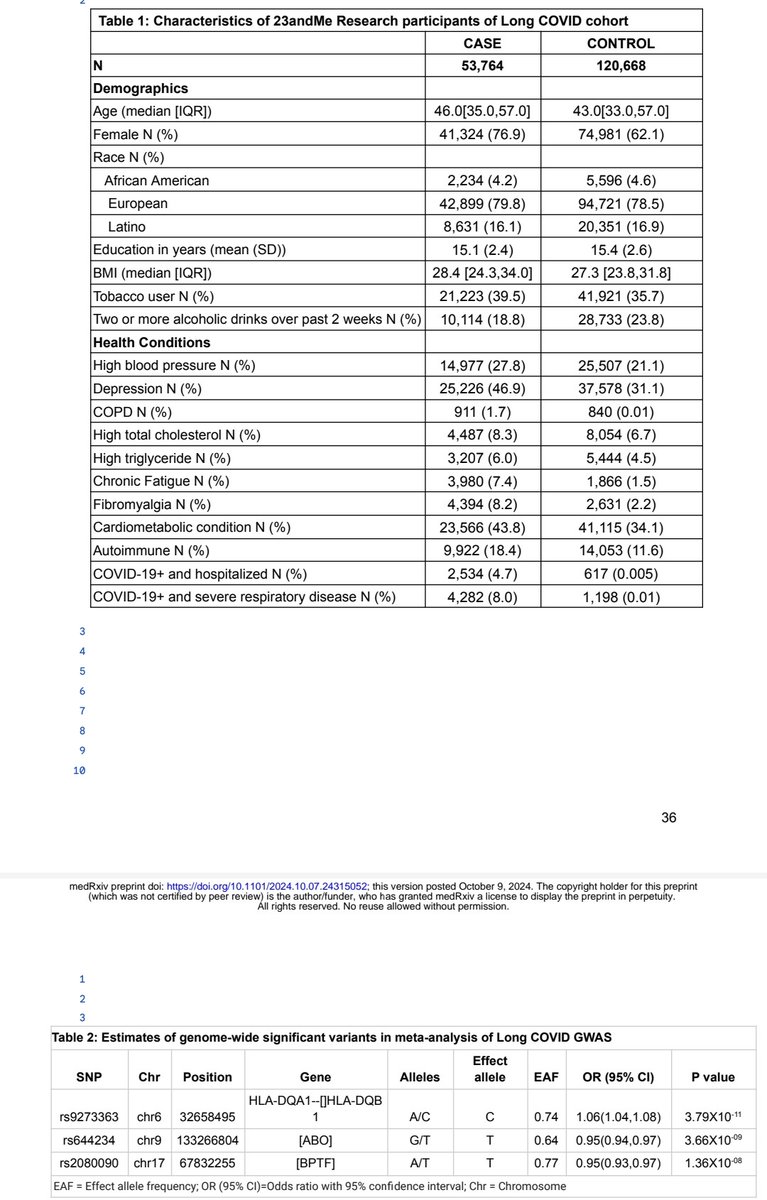
...using data from over 53,000 cases and 120,000 controls from the 23andMe research cohort
H/t @VirusesImmunity
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
...using data from over 53,000 cases and 120,000 controls from the 23andMe research cohort
H/t @VirusesImmunity
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…

2) This study looked at the genetics behind "Long COVID" - the persistent symptoms some people experience after recovering from COVID-19. Using data from over 53,000 Long COVID patients and 120,000 healthy controls, the researchers conducted the largest genetic analysis ... 
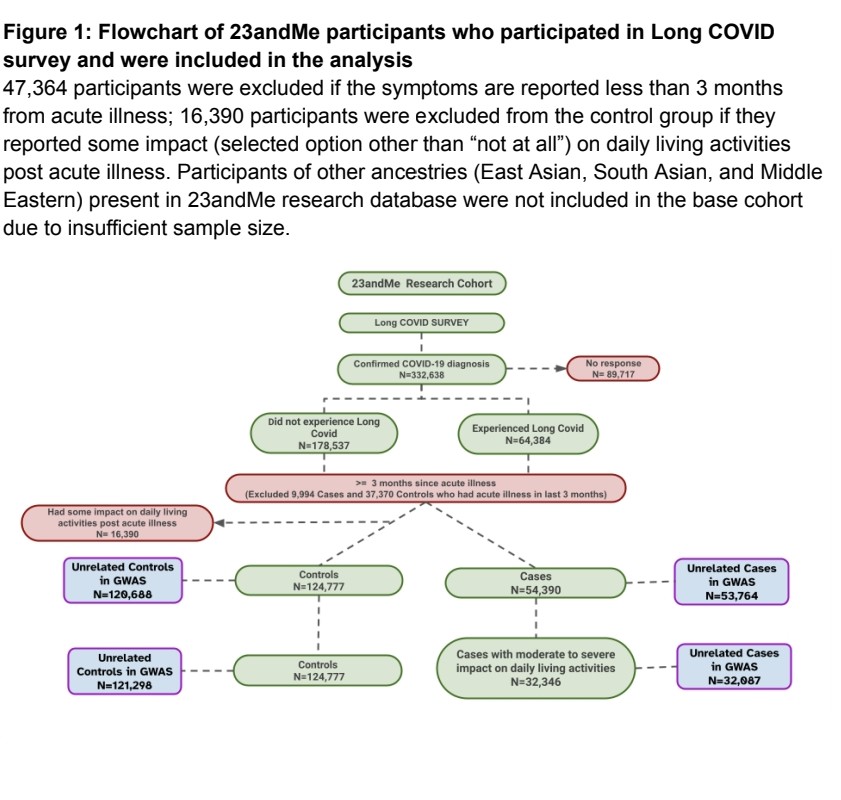
3) ...of Long COVID to date.
They identified three key genetic regions linked to Long COVID risk:
▶️ Genes involved in the immune system's response to infection. This suggests immune dysfunction plays a role in Long COVID.
They identified three key genetic regions linked to Long COVID risk:
▶️ Genes involved in the immune system's response to infection. This suggests immune dysfunction plays a role in Long COVID.
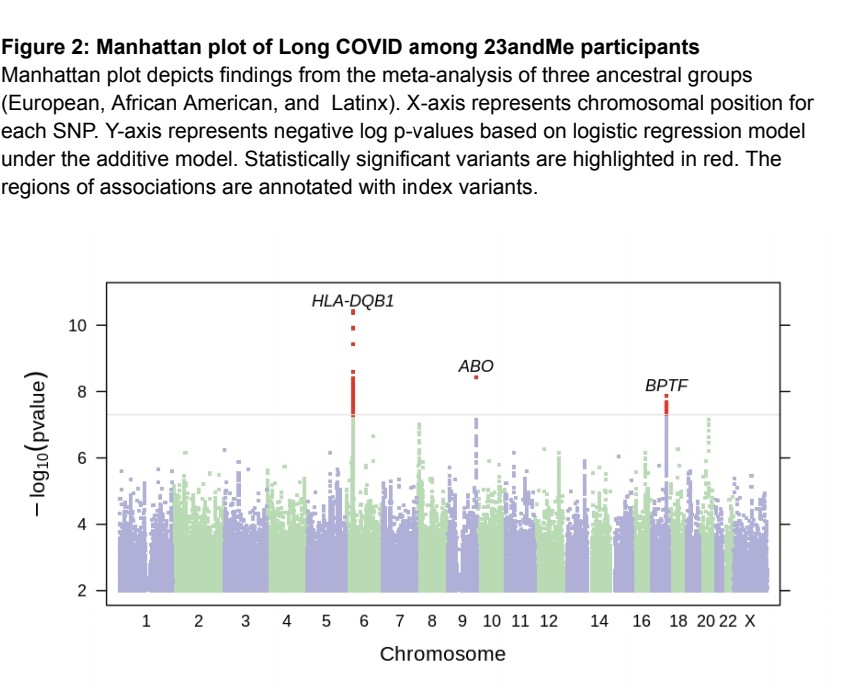
4)▶️ The ABO gene, which has previously been associated with COVID-19 severity. This indicates that factors affecting the initial COVID-19 infection may influence the development of Long COVID.
▶️ Genes related to viral suppression and inflammation pointing ...
▶️ Genes related to viral suppression and inflammation pointing ...
5) ... to underlying biological pathways that could contribute to Long COVID.
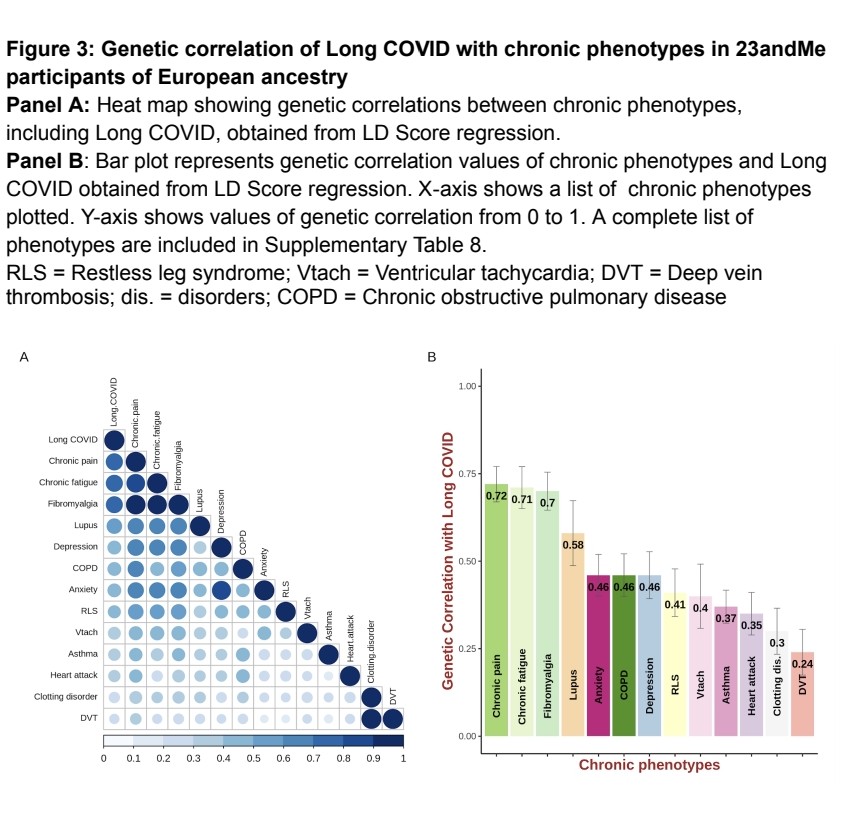
Interestingly, the study also found strong genetic connections between Long COVID and other chronic conditions with similar symptoms, like chronic fatigue and depression.
Interestingly, the study also found strong genetic connections between Long COVID and other chronic conditions with similar symptoms, like chronic fatigue and depression.
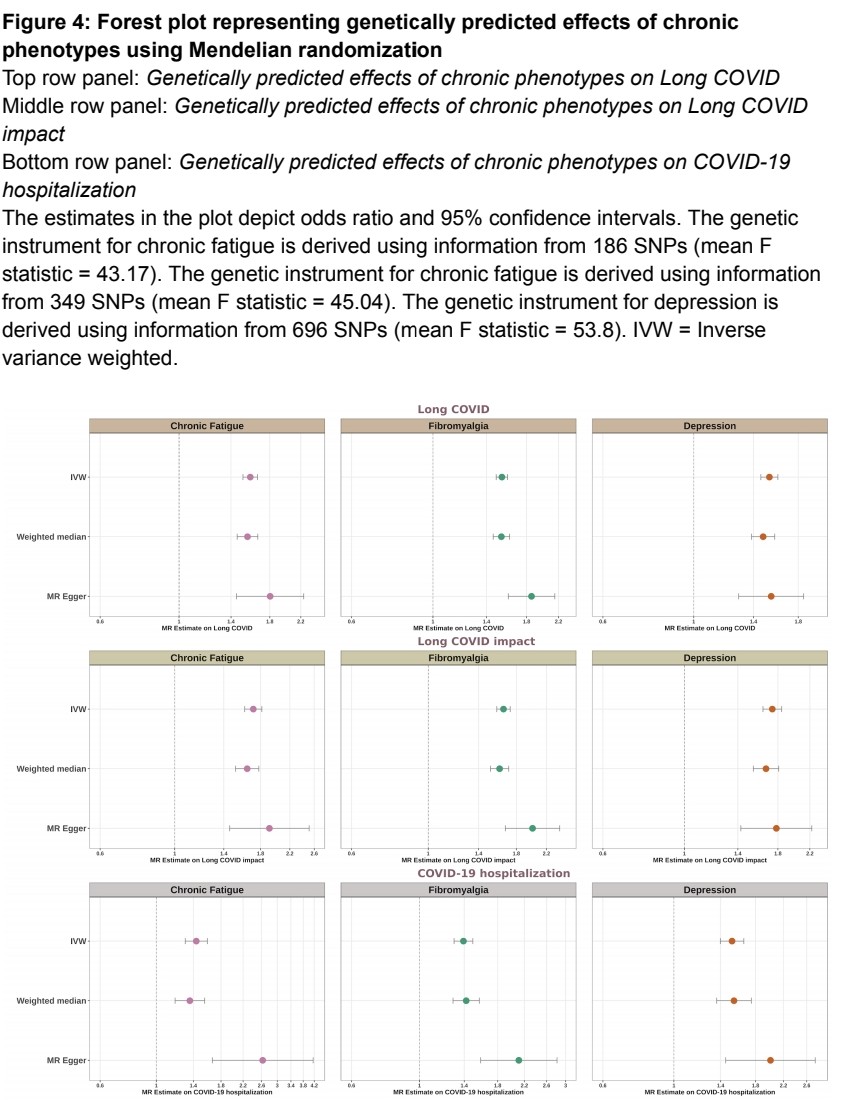
6) This implies that some people may be genetically predisposed to developing post-viral syndromes after COVID-19.
Overall, these findings provide important insights into the genetic basis of Long COVID.
Overall, these findings provide important insights into the genetic basis of Long COVID.
7) This could help identify individuals at high risk and guide the development of targeted treatments for this debilitating condition.
Thanks for reading 🙏 and thanks to @23andMeResearch and @ninaadsc for this study
Thanks for reading 🙏 and thanks to @23andMeResearch and @ninaadsc for this study
8) And safeguard yourself from COVID-19, avoid reinfection, as even mild cases can pose significant risks.
https://x.com/ejustin46/status/1842094032790475040?t=8ziq89zySKJzK8mWawghCA&s=19
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh


















