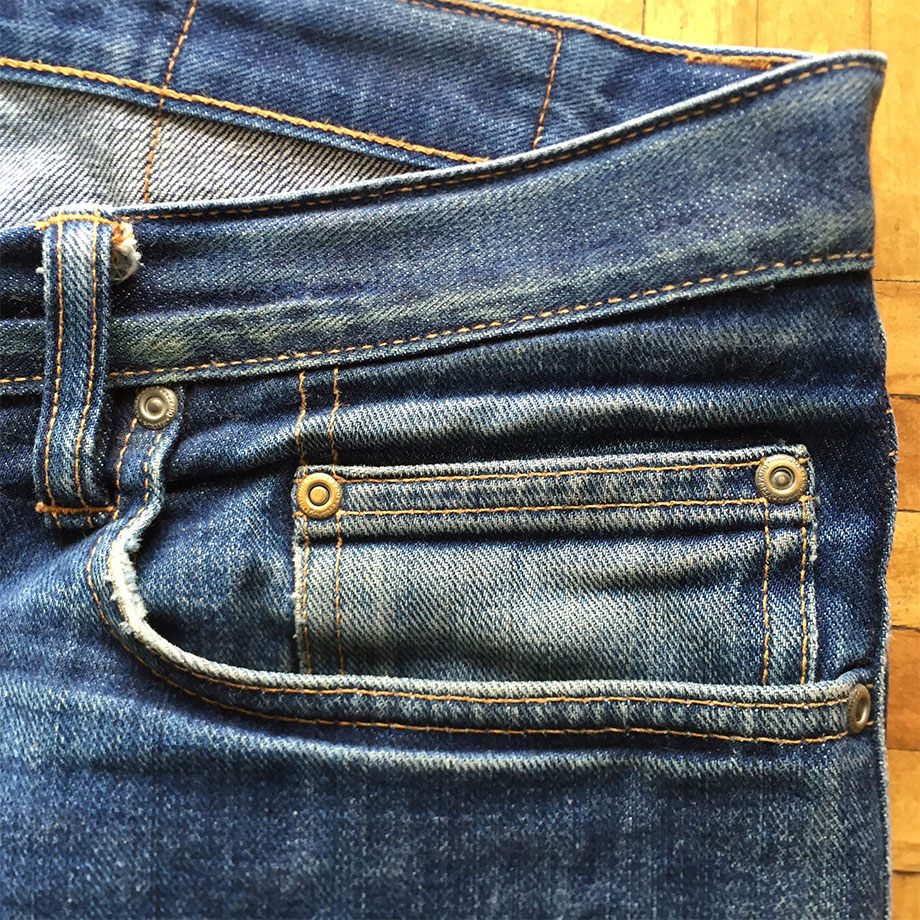
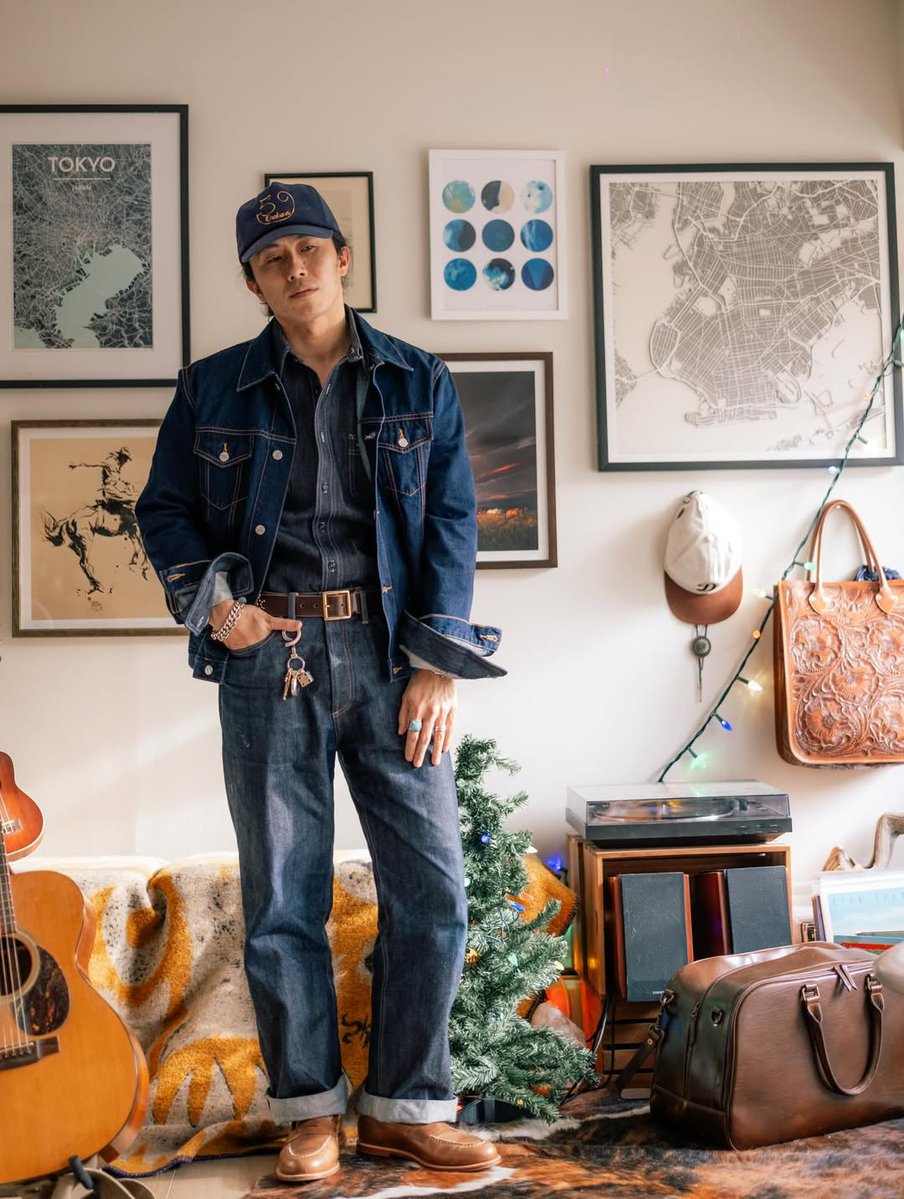
Fabric comes in different weights. In the menswear industry, this is measured in ounces or grams per square meter. American tailors tend to use ounces; Europeans and Asian tailors tend to use grams. Here we see swatches from Draper's Ascot book ranging from 8oz to 12oz. 

In men's tailoring, 12-14oz is considered midweight. Anything less than 12 oz is lightweight; anything above 14oz is heavyweight. Once you get above 18oz, this is considered "coating" weight, which is to say it's typically used for overcoats. 

If you live in a very hot, humid climate, then you might want to wear lighter weight fabrics, especially in open weaves, as they will wear cooler. Here's a suit made from a Harrisons of Edinburgh cloth (from their Indigo book). If I remember correctly, this is an 8oz fabric. 



Conversely, here's a pair of grey flannel trousers made from what I believe is a 16oz cloth and a wrap coat made from a whooping 27oz cloth. You would melt if you wore this outfit in the summer, so it's strictly for cold days. 



Lots of things go into how a fabric hangs or keeps its shape: the fiber composition, the weave, the finishing, etc. However, one important dimension is the weight. Here are two pure linen suits. Right is 11oz; left is 17oz. Look at the difference in the wrinkles around the lap. 



Men in the past wore much heavier fabrics. It wasn't unusual for a summer suit to start around 13oz; winter suits to start around 16oz. This is partly why everything hung so well and looked so great. Look at the sharpness of these trousers. 



Over time, fabric has gotten lighter weight for a variety of reasons. First, the spread of central heating meant that people no longer had to wear heavy clothes indoors. Second, a combination of technology and animal breeding made lightweight cloth more accessible. 



The fashion industry also sold men on the idea that lighter, shinier, and silkier fabrics were more luxurious. "Oh la la, monsieur! Just feel that fabric. So silky and smooth and lightweight. You will always be so comfortable!" 

There are two problems with lightweight fabrics. First, any mismatch between the tailoring and your body will show up in the form of ugly wrinkles and creases. Heavy fabrics hang better, so they're more forgiving. Check out how these heavy tweed trousers hang. 



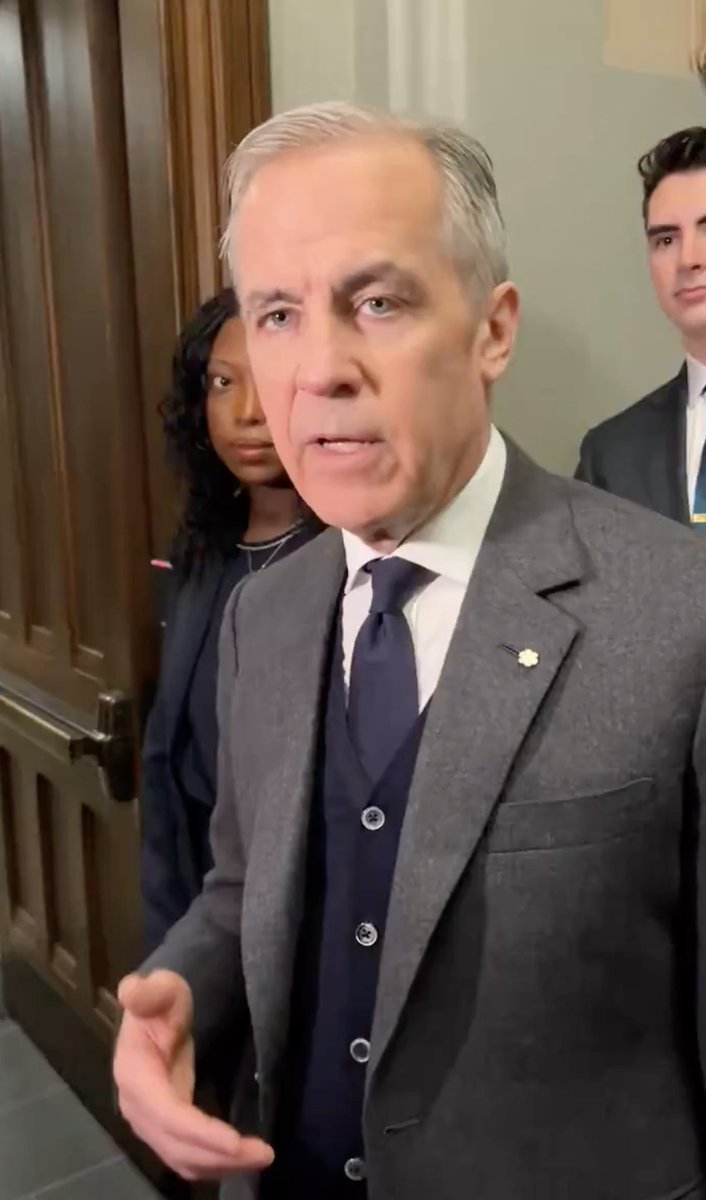
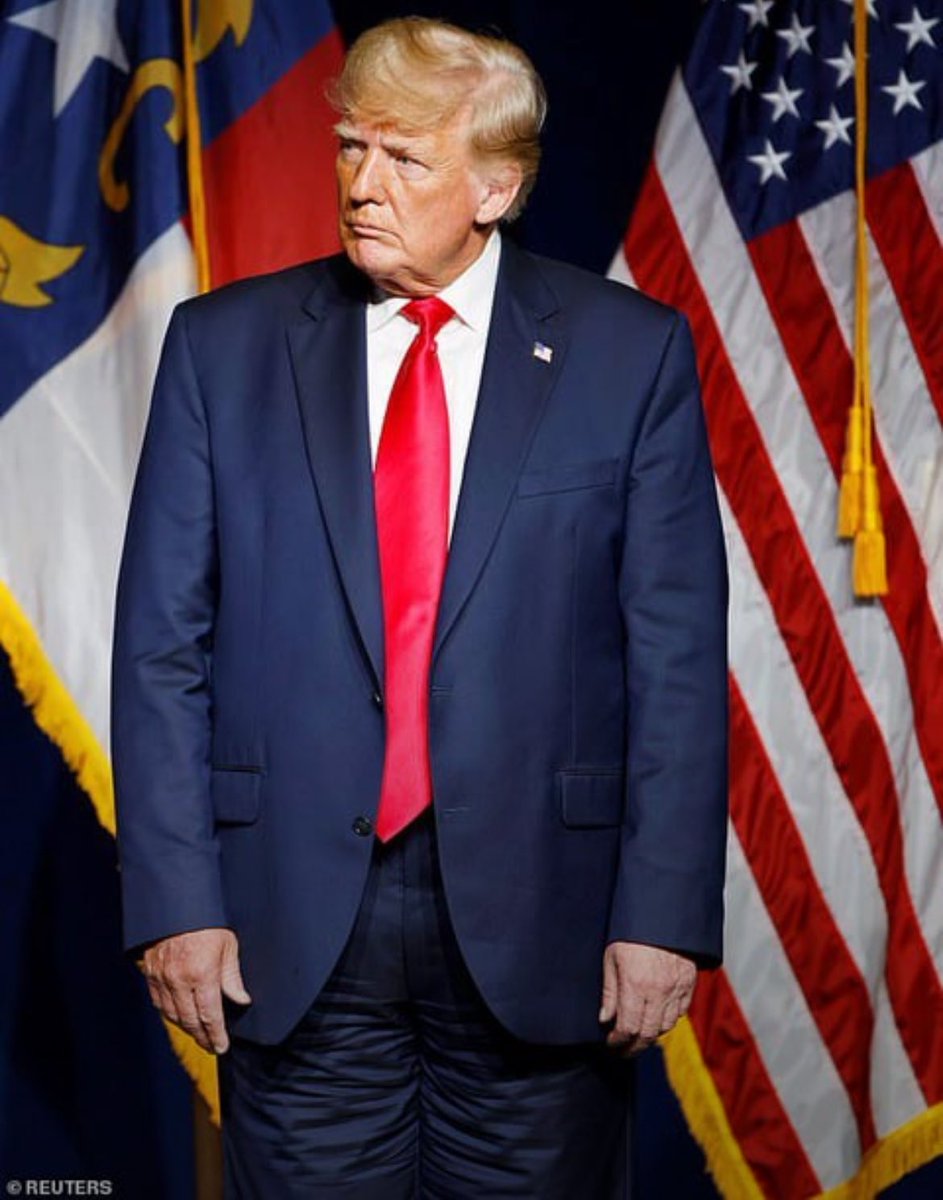
Second, as mentioned earlier, lightweight fabrics will hold their winkles more readily than their heavier counterparts (all things equal). Trump buys many of his suits from Brioni, and luxury Italian brands like these often sell customers on the idea of "luxurious" wools. 

If you get a lightweight fabric, you have to compensate in other ways. For instance, Ascot's 2-ply Ascot fabrics clock in at 8oz. But the yarn has been given an extra twist during the spinning process, which makes them naturally wrinkle resistant.
Everyone has to figure out which types of fabrics are right for them. Your internal furnace, sensitivity to heat, lifestyle, and climate all play a part. One person might sweat in 14oz fabrics; another person is totally fine in something as heavy as 18oz, even in the same area. 



But as a general rule of thumb, you should try to wear the heaviest fabrics you can bear. Trump favors lightweight, luxurious wools almost year round, and that's why his pants often look wrinkly. 



Sorry, this is switched. The suit on the left is made from an 11oz pure linen. The suit on the right is made from 17oz pure linen. You can see how the suit on the right is less wrinkly. This is due to the difference in fabric weight.
https://x.com/dieworkwear/status/1846687640948822424
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh