Sending North Korean troops to Ukraine could be a serious mistake for Putin for a number of reasons, one of which is the active position of South Korea. Seoul has declared its readiness to begin providing direct military assistance to Ukraine, including the supply of
1/12
1/12

artillery, tanks and other modern weapons. South Korea is one of the world's largest defense powers with a powerful military-industrial base, whose products are in demand all over the world. South Korea's decision to join the conflict could significantly change the balance
2/12
2/12

of power. South Korea has not only high-tech weapons, but also trained military specialists who can provide advisory support to Ukraine in the fight against North Korean troops. The South Koreans are well aware of the specifics of the actions of North Korean forces: their
3/12
3/12

strategies, methods of warfare and the psychological state of soldiers under constant threat of reprisals. Moreover, South Korea can provide linguistic and intelligence assistance, facilitating interaction with the North Korean military on the battlefield. For Putin,
4/12
4/12

North Korean troops may seem like a beneficial addition to Russian forces. North Korean soldiers are accustomed to strict discipline and unquestioning obedience to orders, even the most brutal and dangerous ones. Putin needs "cannon fodder", and North Korea can become a
5/12
5/12

source of these resources. Russian tactics remain unchanged: the destruction of the settlements by aircraft and artillery, followed by ground assaults. North Korea has probably sent one of the world's most brutal special forces, which once guarded the father of dictator
6/12
6/12

Kim Jong-un, to fight against Ukraine, Bild reports. The publication calls them "combat slaves", because they grew up in an information vacuum: without the Internet, communications, phones and Western TV. However, South Korea's intervention could lead to serious consequences
7/12
7/12
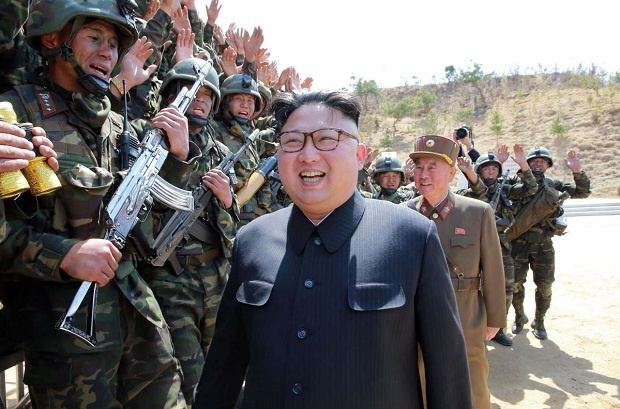

for Russia. Sending its troops to Ukraine, as well as supplying weapons, could push other countries to follow its example. South Korean weapons and technology will give Ukraine a new advantage, and their specialists will help cope with the threat from North Korean soldiers.
8/12
8/12

De-escalation does not work. Current methods of containing Russian aggression, such as a ban on the use of Western weapons to strike Russia itself, have proven ineffective. However, Putin's actions could become a catalyst for new decisive steps by the West. The United
9/12
9/12

States has allocated a new $400 million defense aid package to Ukraine. This was announced by US Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin during a meeting with President Volodymyr Zelenskyy in Kyiv. If restrictions on the use of Western weapons are lifted and Ukraine receives all the
10/12
10/12

support it needs to fully confront Russian troops, South Korea could play a key role here, and its participation in the conflict would further strengthen support for Ukraine. Putin, trying to strengthen his position, risks receiving an even more decisive rebuff from
11/12
11/12

the international community. However, the longer the community delays responding, the more Putin will escalate. Sending NATO troops to Ukraine for non-combat missions, such as guarding the Belarusian border, would help free up the country's resources to fight against Russia
12/12
12/12

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh