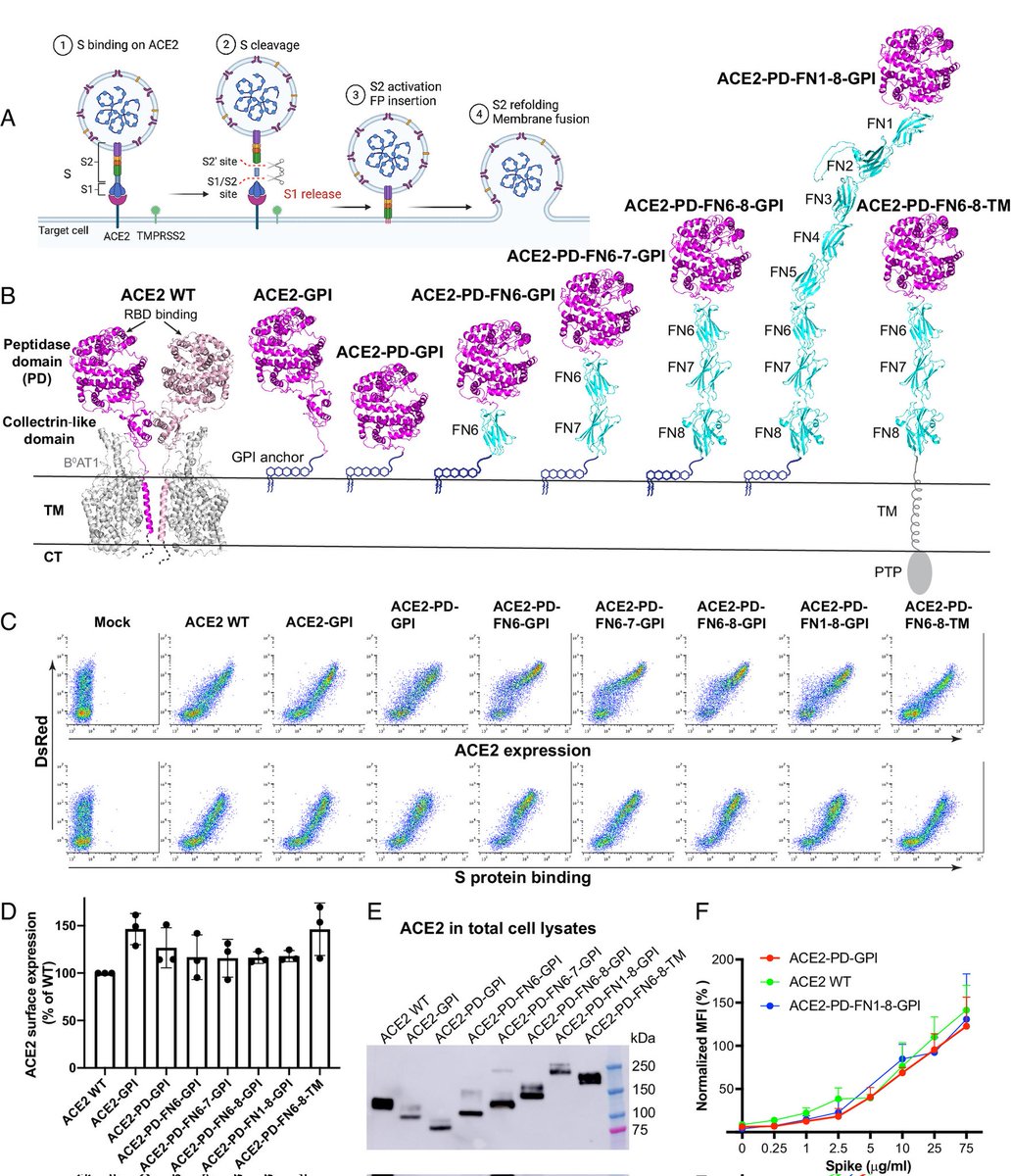
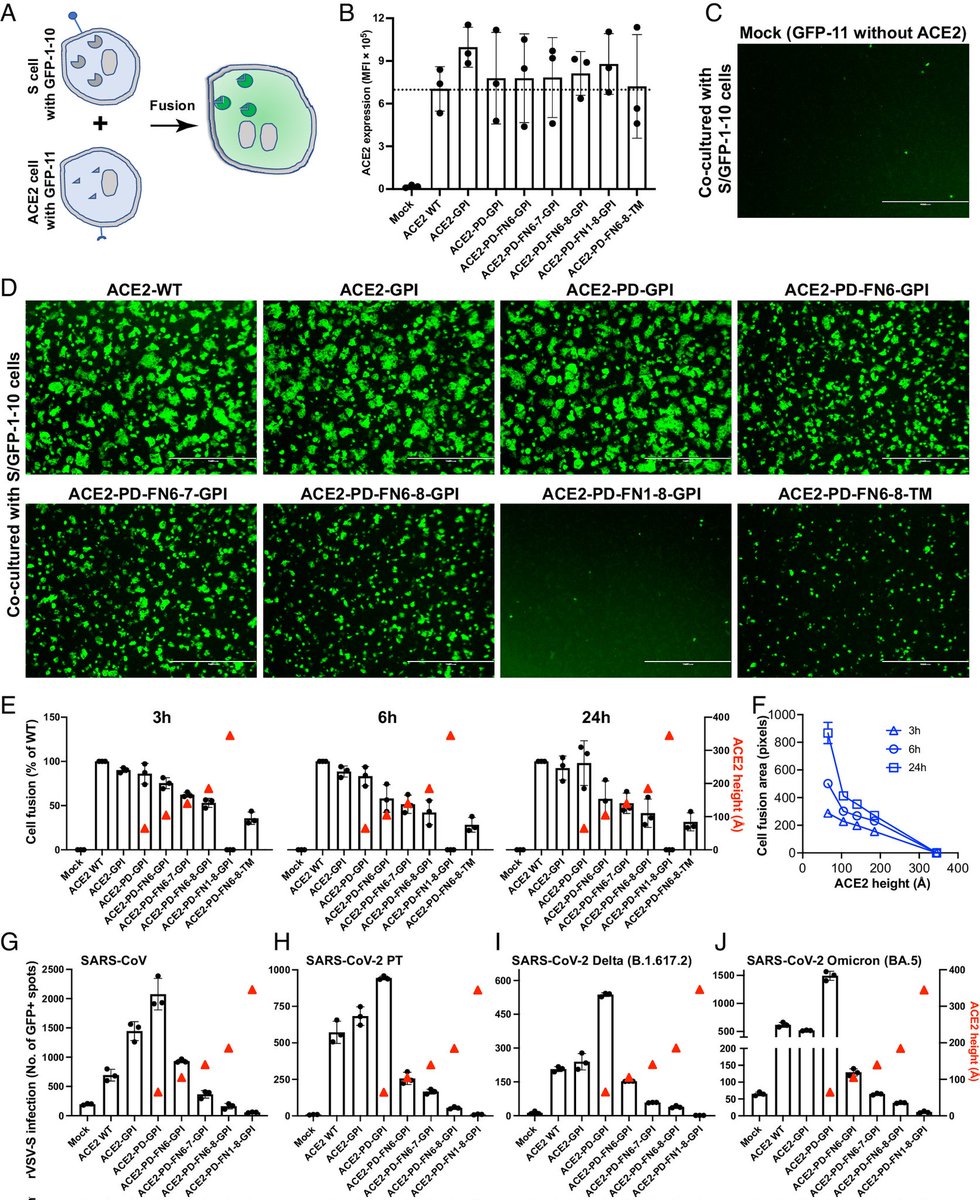
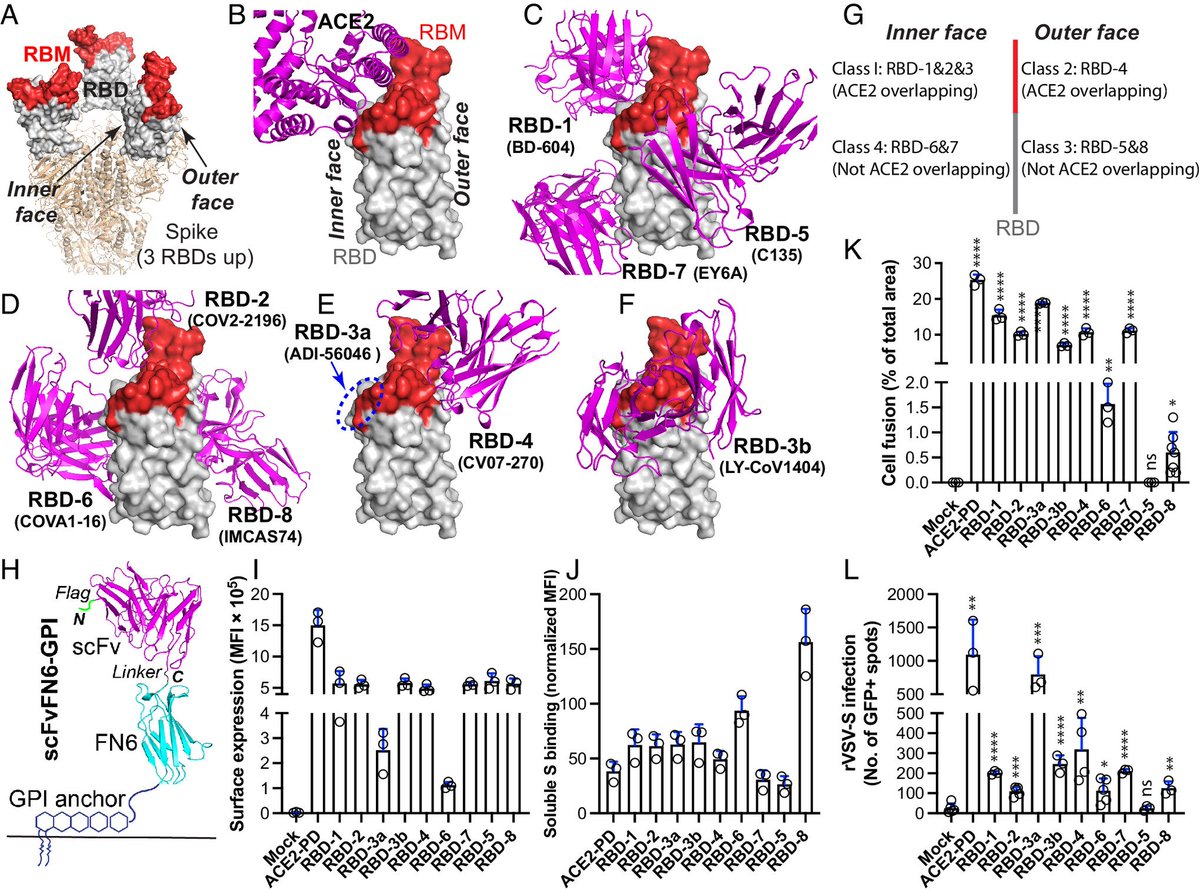
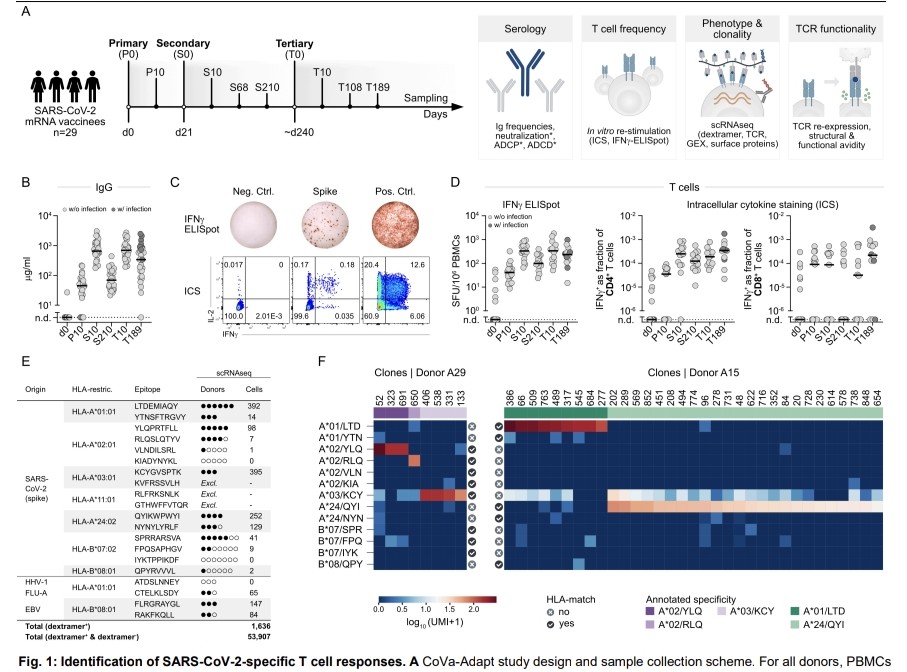
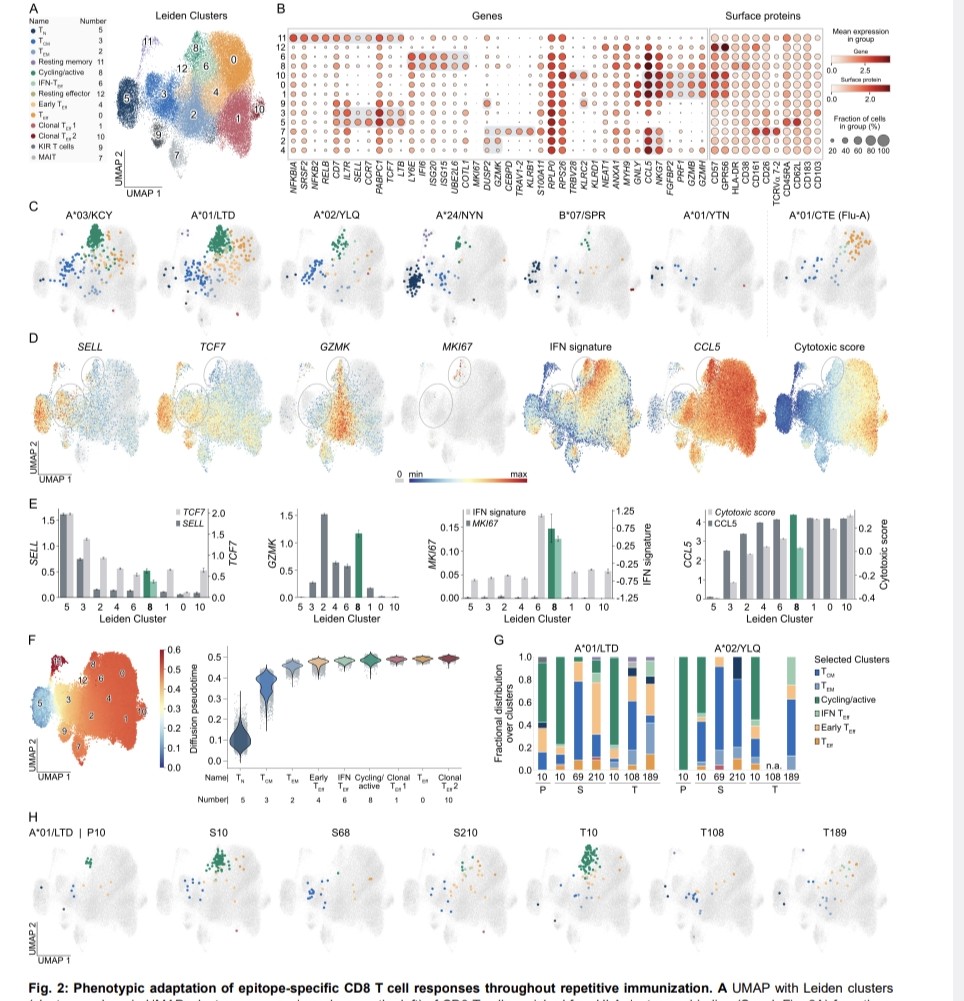
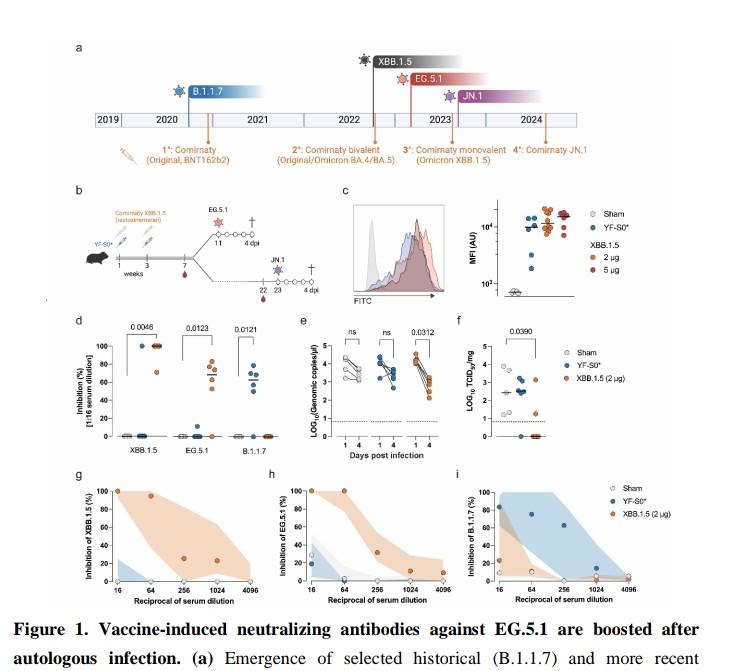
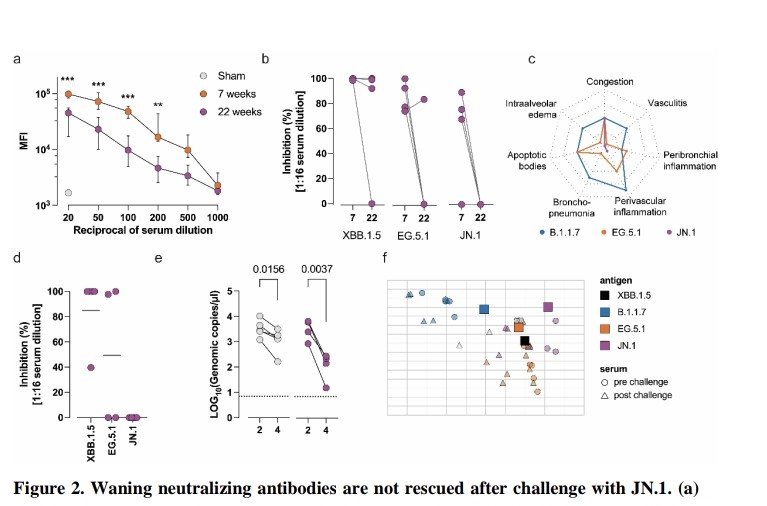
"Impact of UNIVERSAL MASKING in REDUCING the RISK of NOSOCOMIAL RESPIRATORY VIRUSES among PEOPLE with CANCER"
cambridge.org/core/journals/…
cambridge.org/core/journals/…
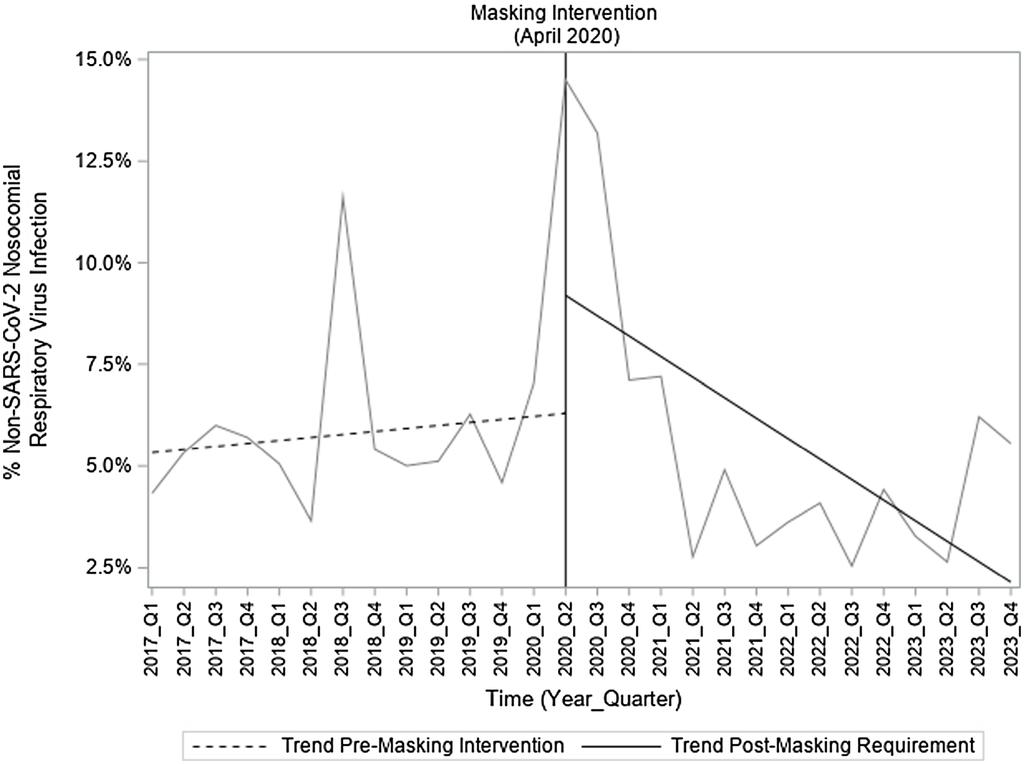
2) Brief summary : Universal masking reduced nosocomial spread of common respiratory viruses among cancer patients, protecting vulnerable immunocompromised patients. Findings support continued mask use in healthcare to control respiratory virus transmission beyond COVID-19.
3) NB. New studies are being published with increasing irregularity and tend to come in waves.
Given the substantial volume of studies we received today (over 100!), we will need to provide shorter summaries than usual.
Thank you for your understanding 🙏
Given the substantial volume of studies we received today (over 100!), we will need to provide shorter summaries than usual.
Thank you for your understanding 🙏
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh