The most overused, oddly glorified, yet under-respected topic on the internet:
Childhood Trauma.
It’s why your dad won’t cry, your relationships don’t stick, and why you feel exhausted every morning.
Here’s what trauma is—and how to reverse its effects (backed by science): 🧵

Childhood Trauma.
It’s why your dad won’t cry, your relationships don’t stick, and why you feel exhausted every morning.
Here’s what trauma is—and how to reverse its effects (backed by science): 🧵

Trauma is an invisible epidemic, affecting 75% of people today.
Society tells you to “suck it up” and pretend it never happened—but science says otherwise.
Let’s dive in↓
Society tells you to “suck it up” and pretend it never happened—but science says otherwise.
Let’s dive in↓
What is trauma?
Trauma isn’t the event that happened to you. It’s the psychological wound that happens after.
The good news? Trauma can be healed when properly addressed.
We can’t change the past, but we can heal its effects on our minds today.
Trauma isn’t the event that happened to you. It’s the psychological wound that happens after.
The good news? Trauma can be healed when properly addressed.
We can’t change the past, but we can heal its effects on our minds today.
Impacts of Trauma
This study shows childhood trauma raises inflammation levels as an adult.
“Physical, sexual, emotional abuse, neglect, and caregiver separation all increase the risk of mental & physical illness later in life.”
This study shows childhood trauma raises inflammation levels as an adult.
“Physical, sexual, emotional abuse, neglect, and caregiver separation all increase the risk of mental & physical illness later in life.”

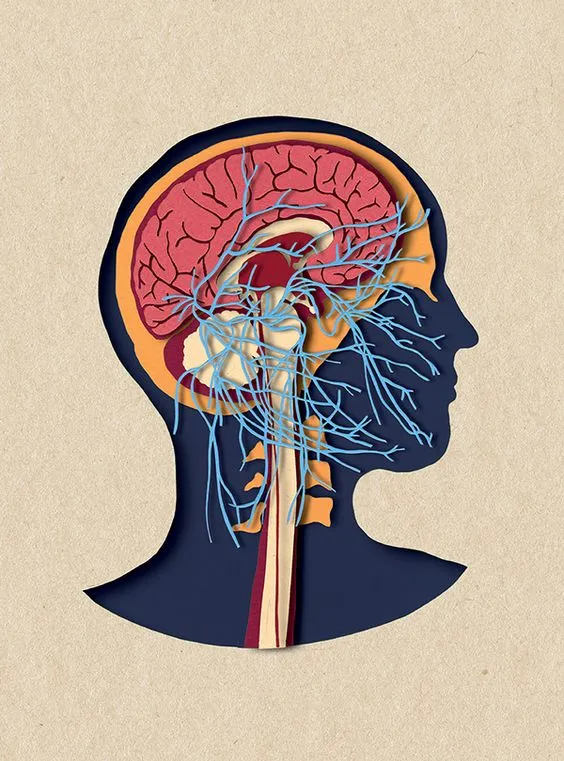
Brain Changes
Trauma has profound effects on the brain and its everyday function:
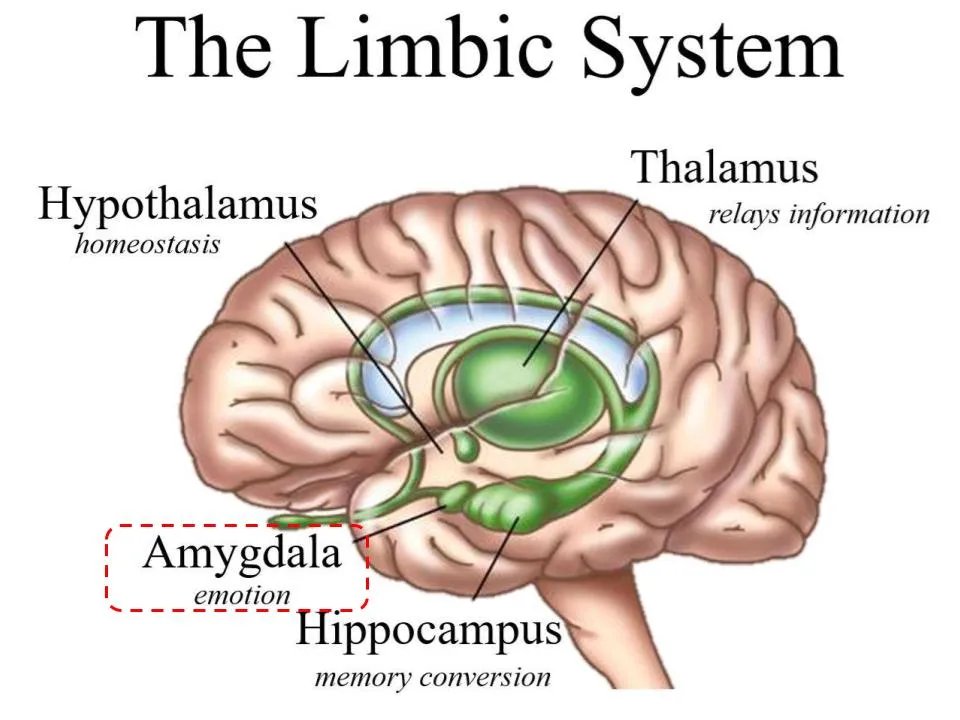
1. Hypersensitive Amygdala – Making people see danger where other people see manageable stuff.
2. Weakened Hippocampus – Making it harder to remember or think clearly.
3. Weakened Prefrontal Cortex – Making it harder to think ahead or make good choices.
Trauma has profound effects on the brain and its everyday function:
1. Hypersensitive Amygdala – Making people see danger where other people see manageable stuff.
2. Weakened Hippocampus – Making it harder to remember or think clearly.
3. Weakened Prefrontal Cortex – Making it harder to think ahead or make good choices.
Chronic Fight-or-Flight response
Trauma turns the amygdala into a “fear-driven” brain.
This causes:
• Decreased focus & creativity
• Heightened stress sensitivity
• Increased anxiety & depression
• Higher chronic disease risk from constant cortisol release
But does trauma mean no cure?
Trauma turns the amygdala into a “fear-driven” brain.
This causes:
• Decreased focus & creativity
• Heightened stress sensitivity
• Increased anxiety & depression
• Higher chronic disease risk from constant cortisol release
But does trauma mean no cure?

Trauma Can Be Healed Naturally
Talk therapy alone doesn’t fully heal trauma because it bypasses the limbic brain.
Today, neuroscience-based therapies are changing that.
Here are 5 therapies proven to help heal trauma’s impact on the brain ↓
Talk therapy alone doesn’t fully heal trauma because it bypasses the limbic brain.
Today, neuroscience-based therapies are changing that.
Here are 5 therapies proven to help heal trauma’s impact on the brain ↓
1. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR helps process traumatic memories by:
• Reducing amygdala hyperactivity for better emotional response
• Strengthening the hippocampus & prefrontal cortex, improving memory and emotional control
EMDR helps process traumatic memories by:
• Reducing amygdala hyperactivity for better emotional response
• Strengthening the hippocampus & prefrontal cortex, improving memory and emotional control
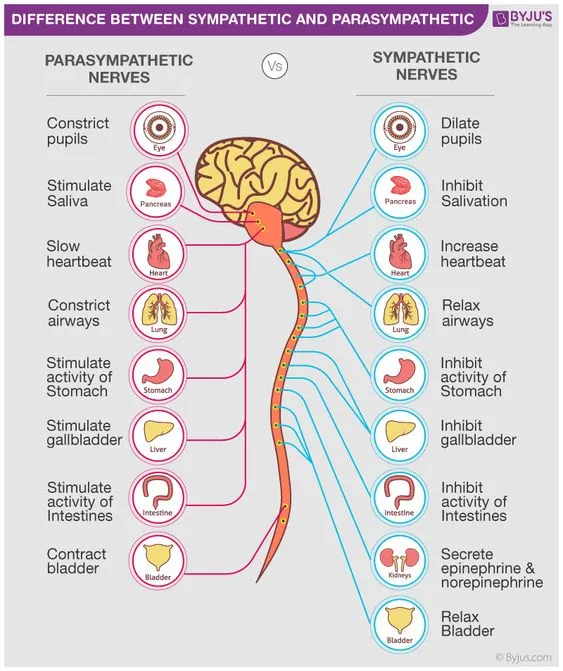
2. Narrative Exposure Therapy (NET)
NET, a form of CBT, effectively reduces anxiety in trauma patients by:
It works by:
• Creating a coherent life narrative to make sense of trauma
• Easing fear and anxiety linked to the sympathetic nervous system response
NET, a form of CBT, effectively reduces anxiety in trauma patients by:
It works by:
• Creating a coherent life narrative to make sense of trauma
• Easing fear and anxiety linked to the sympathetic nervous system response
3. Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback trains the brain to function better using real-time brain activity feedback.
Benefits include:
• Calming an overactive amygdala
• Strengthening the prefrontal cortex’s regulatory control

Neurofeedback trains the brain to function better using real-time brain activity feedback.
Benefits include:
• Calming an overactive amygdala
• Strengthening the prefrontal cortex’s regulatory control
4. Somatic Experiencing (SE)
A natural healing method, SE blends biology, neuroscience, and psychology to reset the brain's hypersensitivity to stress.
It’s especially useful for:
• PTSD
• Sleep issues
• Anxiety & depression
• Relationship struggles
• Stress-related symptoms (e.g., chronic pain)
A natural healing method, SE blends biology, neuroscience, and psychology to reset the brain's hypersensitivity to stress.
It’s especially useful for:
• PTSD
• Sleep issues
• Anxiety & depression
• Relationship struggles
• Stress-related symptoms (e.g., chronic pain)
5. Art, Movement, & Performance Therapy
A study with over 14,000 participants found that dance was a more effective treatment for depression, than medications.
It allows you to relax and feel your emotions, even the ones you've been avoiding for years.
A study with over 14,000 participants found that dance was a more effective treatment for depression, than medications.
It allows you to relax and feel your emotions, even the ones you've been avoiding for years.
Your past wounds can either break you or empower you—depending on how you address them.
Instead of burying them in distractions or numbing them…(societal norm)
Learn to work with them directly through neuroscience.
Your pain can become your greatest power...
Instead of burying them in distractions or numbing them…(societal norm)
Learn to work with them directly through neuroscience.
Your pain can become your greatest power...
I'm genuinely curious, which of these sounds the most interesting to you?
Have you tried any of them?
Let me know below.
Have you tried any of them?
Let me know below.
If you want to prioritize what matters most—your mind & body—you might like my newsletters:
I share proven insights on somatic psychology and neuroscience-based therapies to help you optimize your well-being.
Join 6,000+ people inside: brianmaierhofer.com/newsletter/
I share proven insights on somatic psychology and neuroscience-based therapies to help you optimize your well-being.
Join 6,000+ people inside: brianmaierhofer.com/newsletter/
Thanks for reading!
For more content like this:
Drop a like and follow me @IamProHuman
For more content like this:
Drop a like and follow me @IamProHuman
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh