A concise DAY-BY-DAY SUMMARY of the KEY EVENTS during SARS-CoV-2 INFECTION 💯👍
We've chosen to share this remarkable study again, offering a different perspective that enhances our understanding of the infection process.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
We've chosen to share this remarkable study again, offering a different perspective that enhances our understanding of the infection process.
nature.com/articles/s4158…
2) ▶️ Day -1: Participants with higher pre-existing HLA-DQA2 expression were less likely to develop sustained infection.
▶️ Days 1-3: Even in transient/abortive infections, rapid antiviral responses occurred, including MAIT cell activation and decreased inflammatory monocytes.
▶️ Days 1-3: Even in transient/abortive infections, rapid antiviral responses occurred, including MAIT cell activation and decreased inflammatory monocytes.
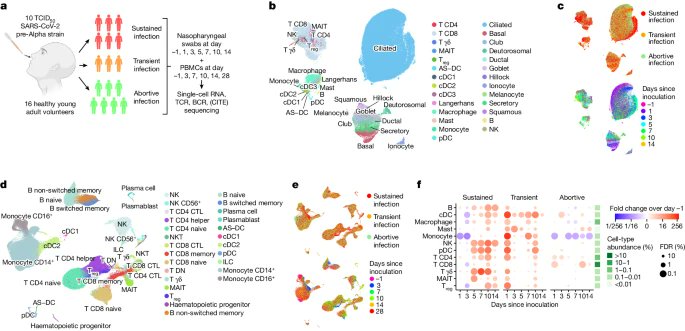
3) ▶️ Days 3-5: In sustained infections, interferon signaling rapidly activated in blood, preceding the mucosal response.
▶️ Days 5-7: Immune infiltration and viral load peaked in the nasopharynx, with a subset of hyperinfected ciliated cells driving viral production.
▶️ Days 5-7: Immune infiltration and viral load peaked in the nasopharynx, with a subset of hyperinfected ciliated cells driving viral production.
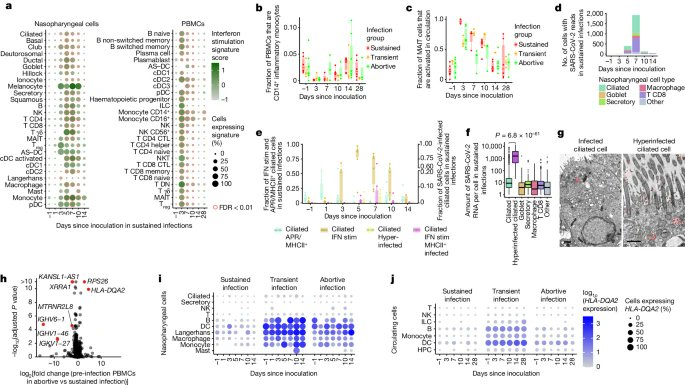
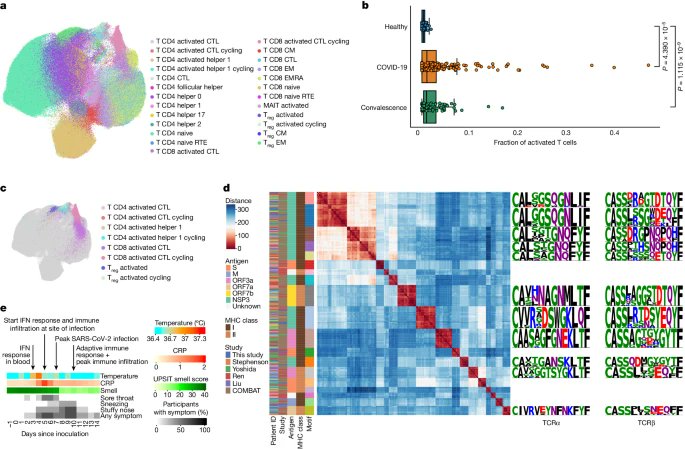
4) ▶️ Day 10: SARS-CoV-2 specific activated T cells expanded, with an unexpected prominent role for cytotoxic CD4+ T cells in the mucosal response.
▶️ Day 14: Regulatory T cells peaked, potentially helping resolve inflammation after viral clearance.
▶️ Day 14: Regulatory T cells peaked, potentially helping resolve inflammation after viral clearance.
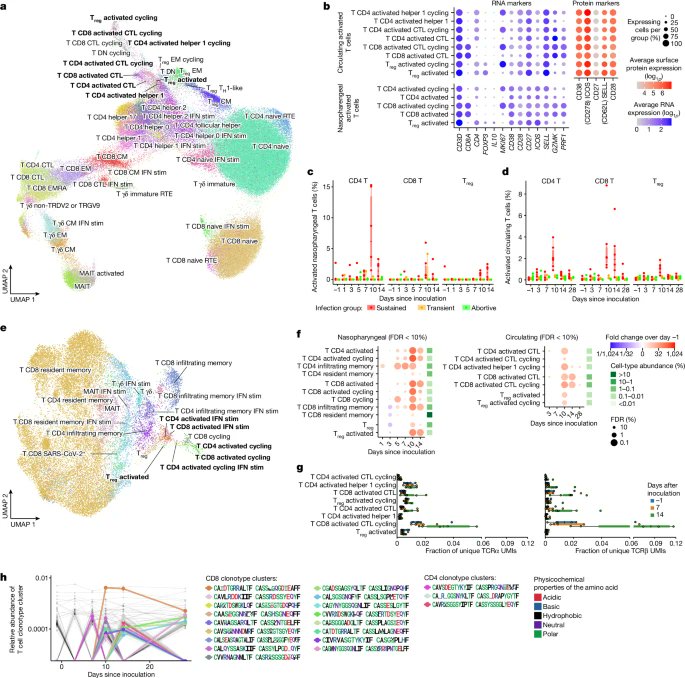
5) Overall, this dataset provides unprecedented insights into the dynamic interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and the host immune response over time.
Thanks for reading 🙏
Thanks for reading 🙏
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




















