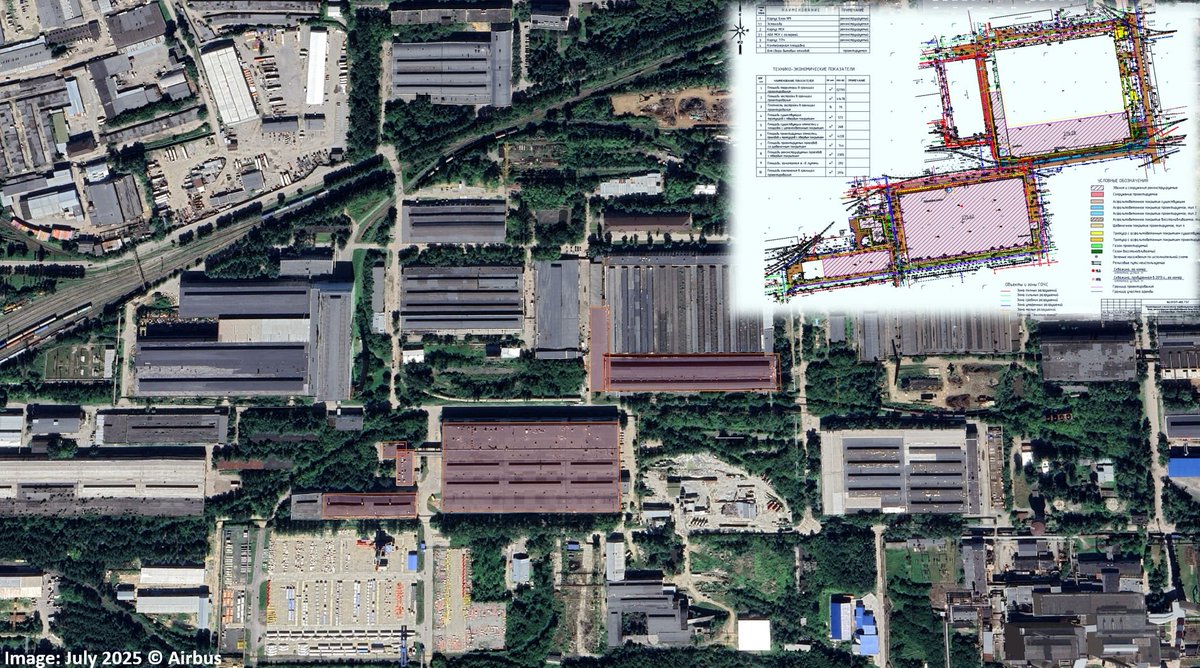
Overnight, Ukraine carried out a series of missile strikes on Khalino Airbase in Kursk Oblast, reportedly using ATACMS missiles. Here’s what we can anticipate based on previous data gathered by Frontelligence Insight:
🧵Thread
🧵Thread

2/ In recent months, the airfield had been spotted to home SU-25 close air support jets, helicopters, and UAVs. 

3/ For some time, the airfield hasn’t been heavily utilized by Russia in the same way as other air bases. Instead, it has primarily hosted helicopters and Su-25 for close-air support, rather than for KAB deployments like those conducted from bases in Voronezh or Lipetsk.
4/ Activity at the base had noticeably decreased in recent days, leaving it unclear whether significant numbers of aircraft were hit. It’s likely the strikes targeted supply depots, air defense and radar systems, potentially temporarily putting the airfield out of action.
5/ Since early October, Russians have been fortifying the Khalino airbase by constructing new revetments and reinforcing existing ones with what appear to be concrete blocks. By the time of the strike, the construction seemed to be in its later stages but was not done yet 

6/ The Frontelligence Insight team has very modest expectations regarding the number of air assets destroyed on the airfield. If Ukraine successfully targeted air-defense assets in the area, it could create opportunities for future strikes with more cheap and numerous drones
7/ We should keep in mind that ATACMS strikes continue to target military objects within Russia, despite threats and nuclear saber-rattling PsyOp from Moscow. These threats, just like all previous are aimed to sow fear of nuclear escalation and weaken support for Ukraine
8/ Ukraine is likely to continue carrying out ATACMS and Storm Shadow/SCALP strikes within Russia. However, the impact of such a campaign might be seriously constrained by factors like limited missile stockpiles.
If you enjoyed these free materials, consider supporting our work:
https://x.com/Tatarigami_UA/status/1861192545453416480
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh