Huge new result:
Anti-racism trainings probably lead people to accuse others of racism even when they're not racist.
That's exactly the result of a new study on DEI trainings, with a special focus on the impacts of the works of Ibram X. Kendi and Robin DiAngelo.
Let's dig in🧵
Anti-racism trainings probably lead people to accuse others of racism even when they're not racist.
That's exactly the result of a new study on DEI trainings, with a special focus on the impacts of the works of Ibram X. Kendi and Robin DiAngelo.
Let's dig in🧵

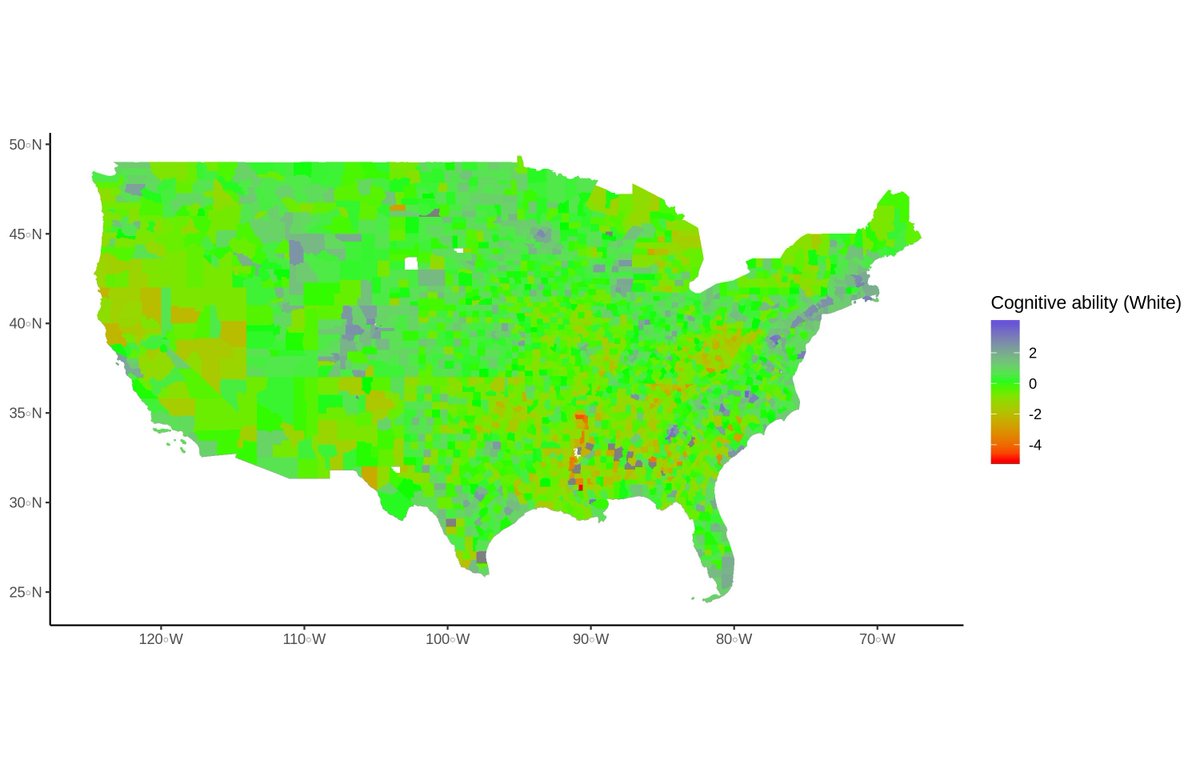
In the first experiment, the researchers took 324 participants and randomized them to either read an Ibram X. Kendi or Robin DiAngelo excerpt or to a racially-neutral condition where they read about corn.
Here are some excerpts from the reading materials, for your understanding:
Here are some excerpts from the reading materials, for your understanding:

After learning, for example, that western countries are compromised by virtue of their racist ideologies and pasts, participants were presented with a scenario that was totally racially neutral.
The scenario is described as follows, and everyone involved did nothing racist:
The scenario is described as follows, and everyone involved did nothing racist:

The participants who were exposed to the 'racism' scenario imagined more racism into existence.
They believed there was a lot more bias, tons of microaggressions and whatnot, even though there was nothing.
They believed there was a lot more bias, tons of microaggressions and whatnot, even though there was nothing.

What's worse, the participants who read the DEI passages also wanted to punish the "offenders" who—I'll remind—literally did nothing racially biased.
They were more likely to want to harm people who did nothing due to their own imaginations.
They were more likely to want to harm people who did nothing due to their own imaginations.

These findings were so shocking and forceful that the authors immediately sought to replicate them.
They gathered a nearly three-times larger sample and found... the same results!
They gathered a nearly three-times larger sample and found... the same results!

But this wasn't the last study. We know that people exposed to DEI racism trainings invent racism out of thin air, but what about other -isms?
Next up is Islamophobia.
The 2,017 participants in this study read either anti-Islamophobia materials or stuff about corn.
Next up is Islamophobia.
The 2,017 participants in this study read either anti-Islamophobia materials or stuff about corn.
After either reading about corn or materials from the Institute for Social Policy and Understanding (ISPU), participants were then asked to evaluate identical trials, for either the clearly-Muslim Ahmed Akhtar or the clearly-just-White George Green.

Participants though the trial of Ahmed was considerably more unfair after they "learned" about Islamophobia.
But once again, there was no bias. They just read the DEI materials and invented the bias in their minds.
But once again, there was no bias. They just read the DEI materials and invented the bias in their minds.

But why? Mechanistically, it does not seem that learning about (and seemingly believing in) Islamophobia increased tolerance for Muslims.
What it did was just to increase the perception of bias. Islamophobia materials did not boost positive sentiment towards Muslims:
What it did was just to increase the perception of bias. Islamophobia materials did not boost positive sentiment towards Muslims:

A final major point of DEI trainings nowadays is caste.
I am referring not to "involuntary caste" stuff a la scholars like Ogbu, but to the Indian caste system.
As the timeline shows, its supposed importance has rapidly gained acknowledgement across the U.S.
I am referring not to "involuntary caste" stuff a la scholars like Ogbu, but to the Indian caste system.
As the timeline shows, its supposed importance has rapidly gained acknowledgement across the U.S.

Despite institutional acceptance that caste matters, and in particular because of bias against members of low castes, most Americans probably still don't understand caste.
So in this experiment, participants were exposed to caste oppression information, or to neutral caste info:
So in this experiment, participants were exposed to caste oppression information, or to neutral caste info:

Participants were then exposed to a totally caste-neutral scenario in which an Indian admissions officer at an elite East Coast university interviews Raj Kumar and, ultimately, Raj gets rejected. 

As you might predict from the other results, the nearly 850 respondents who read about casteism invented a lot more caste bias into the scenario than people who read about caste in general. 

Not only that, but the people exposed to casteism reading material were more likely to see Hindus as racists and to want to punish the admissions officer.

What was really alarming was that, after the casteism readings, people were considerably more likely to agree with explicitly anti-Brahmin statements that were really rough, like "Brahmins are parasites", "Brahmins are a virus".
These seem like damaging ideas to promote!
These seem like damaging ideas to promote!

Turning back to the original sample, we see something interesting: the people who scored higher on Left-Wing Authoritarianism were more likely to want to punish the people they believed were being racist.
Keep that in mind. Now let's review.
Keep that in mind. Now let's review.

All these large-scale studies, with their simple designs, and direct and conceptual replications, with all of their results, support several conclusions.
First, DEI training introduces narratives that lead people to assume certain groups are oppressors and others are victims.
First, DEI training introduces narratives that lead people to assume certain groups are oppressors and others are victims.
Second, DEI trainings lead to hostile attribution biases, leading participants to see discrimination when there is none.
DEI trainings ironically promote racial prejudice, hostility, suspicion, and division.
DEI trainings ironically promote racial prejudice, hostility, suspicion, and division.
Third, DEI trainings lead to demands for punishment again perceived oppressors, as well as the ideologically impure.
This happens despite the perception of being an oppressor always being wrong in these studies.
This happens despite the perception of being an oppressor always being wrong in these studies.
Fourth, heightened suspicion of "oppressors" and the "impure" triggers people with authoritarian tendencies to endorse surveillance, purity testing, strict social control, and ever-increasing responses that range from corrective to coercive.
Authoritarians want to punish.
Authoritarians want to punish.
And fifth, the heightened punitive atmosphere generated by DEI trainings feeds into demands for more anti-oppression trainings, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of totally needless suspicion and intolerance.
DEI trainings have been noted to be ineffective at promoting tolerance and productivity, and plenty of people have noticed backfiring.
This adds a new dimension that teaches us about feelings and perceptions of oppression more generally.
This adds a new dimension that teaches us about feelings and perceptions of oppression more generally.
With these results in mind, we now know that people are more than willing to totally invent racism and other forms of bias in their heads and to want to harm people because of fully-imagined bias on those people's parts.
The era when everyone was colorblind was better.
The era when everyone was colorblind was better.
Future studies replications with fake groups would be neat, but these probably got close enough using unfamiliar groups and with these large trials due to the nature of them being randomized
These are strong results worth keeping in mind
Here's the link: networkcontagion.us/wp-content/upl…
These are strong results worth keeping in mind
Here's the link: networkcontagion.us/wp-content/upl…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh